2 About OCECAS Services
This chapter explains the functionality of VoLTE services that you create and manage on an Oracle Communications Evolved Communications Application Server (OCECAS) implementation.
About Using the Session Design Center GUI to Create Multimedia Services
You use the Session Design Center graphical user interface (GUI) to create the control flows that define the multimedia services that you sell to subscribes, and the change sets that you use to manage changes to your OCECAS implementation.
See "About the Session Design Center" for a thorough overview of the Session Design Center.
About Using SRVCC Functionality to Handover Multimedia Calls
Enhanced service centralization and continuity application server (SCC-AS) is an LTE functionality that allows you to transition a voice call from a packet-switched domain to a legacy circuit-switched domain. This functionality allows you to offer VoLTE capabilities while using networks that also includes circuit-switched coverage. OCECAS supports the SRVCC procedure for handover from packet-switched to circuit-switched networks. The handover requires access and transfer control function (ATCF) and access and transfer gateway (ATGW) functionality. This is specified in the 3GPP Release 10 specification for SRVCC, and most parts of the 3GPP Release 12 specification.
OCECAS provides this functionality in conjunction with Oracle Communications Session Border Controller (Session Border Controller). Session Border Controller acts as the ATCF and ATGW required for SRVCC. Session Border Controller is a different Oracle product that you purchase separately.
OCECAS itself acts as the service centralization and continuity application server (SCC-AS). It also provides home network anchoring, and terminating access domain selection (T-ADS).
About Service Centralization
OCECAS acts as a Service Continuity and Centralization Application Server (SCC-AS) to deliver services, such as supplementary services, from the IMS network across different network technologies and user entities. By acting as a single service point, it is able to provide service centralization. In so doing, it assumes that the MSC is enhanced to support the use of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) towards the IMS because this supports service centralization before, during, and after SRVCC hand-over. However, your MSC might not be enhanced for IMS centralized services (ICS) and roaming networks also are not necessarily enhanced for ICS. OCECAS, therefore, also uses a network-based solution that uses ISUP and CAMEL capabilities to support integration with an MSC that is not enhanced for ICS. OCECAS uses Oracle Communications Converged Application Server Server Controller (OCCAS-SC) to integrate with an MSC that is not enhanced for ICS and provide the following capabilities:
-
Support for SIP messages that are mapped from CAMEL
-
Access from within the control flow editor to all SIP messages and header information mapped from CAMEL
-
Inherent IP Multimedia Routing Number (IMRN) facility
-
Required service logic for inherent integration with OCCAS service controller for service centralization
Figure 2-1 illustrates how OCECAS woks together with OCCAS to support an MSC that is not enhanced for ICS.
Figure 2-1 Service Centralization Support for MSC Not Enhanced for ICS
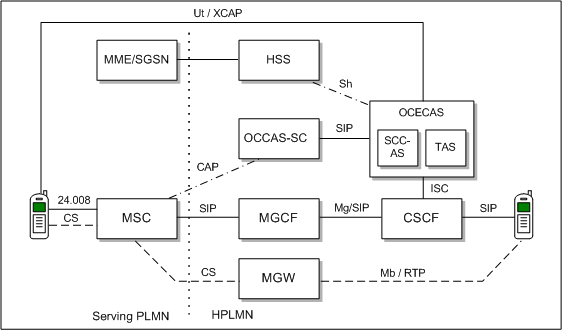
Description of ''Figure 2-1 Service Centralization Support for MSC Not Enhanced for ICS''
For information about configuring OCECAS for an MSC not enhanced for ICS, as well related configuration options, see "Configuring Transfer" in Oracle Communications Evolved Communications Application Server System Administrator's Guide.
About HSS-HLR Synchronization
OCECAS supports synchronisation of supplementary service (SS) data changes to both the Home Subscriber Server (HSS) and the Home Location Register (HLR). On receipt of a supplementary service change from an IMS user equipment (UE), OCECAS updates the subscriber profile in the HSS and updates the HLR. Similarly, on receipt of a supplementary service change notification from the HLR, OCECAS updates the subscriber profile in the HSS.
OCECAS integrates with OCCAS-SC to communicate with the HLR. Specifically, OCCAS-SC forwards MAP NoteSubscriberDataModified messages from HLR to OCECAS, and OCECAS sends MAP AnyTimeModification messages to HLR by way of OCCAS-SC. MAP messages are encoded through XML Encoding Rules (XER-encoded) and passed in the body of SIP SUBSCRIBE or NOTIFY messages between OCECAS and OCCAS-SC.
For information on configuring HSS-HLR synchronization, see configuration settings under "Configuring Transfer" in Oracle Communications Evolved Communications Application Server System Administrator's Guide.
About the Business Logic that Your Calls Can Use
OCECAS provides these tools in a drag-and-drop environment that you use to create VoLTE services:
-
Make control flow decisions based on:
-
Date and time
-
Geographic location
-
Data in data stores
-
SIP message headers
-
Session context or call state
-
-
Interact with other systems, including:
-
Media servers (JSR 309)
-
Charging systems (using Diameter Ro and Gy)
-
Messaging gateways (using SOAP or JSON)
-
Enterprise and Middleware (using SOAP, JSON, JMX, and SNMP traps)
-
-
Perform Actions, including:
-
Manipulating the session state (end session or participant, hold participant, forward session, or add participant)
-
Early media and pre-call, in-call, or post-call announcements
-
Call hunting, call forwarding, and call barring
-
Using location services
-
Using cross-session context look-up
-
Using a charging trigger function
-
Using custom operations, such as raising alarms and branching on statistics
-
Execute other session logic
-
-
Add responses to actions:
-
Manage call failure
-
Wait for and act on an event
-
Store information for later use
-
You create control flows in the Session Design Center UI to use these business logic features.
About Using VoLTE Supplementary Services
The supplementary services listed in the IR.92 IMS Profile for voice and SMS specification define the service capabilities required to continue a multimedia call that originated in a VoLTE network. Essentially, OCECAS becomes the SIP Back-to-back User Agent (B2BUA) for the call.
OCECAS supports these supplementary services:
-
Anonymous Communication Rejection (ACR) (3GPP 24.611)
-
Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) (3GPP TS 24.607)
-
Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) (3GPP TS 24.608)
-
Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) (3GPP TS 24.607)
-
Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) (3GPP TS 24.608)
-
Communication Forwarding Unconditional (CFU) (3GPP TS 24.604)
-
Communication Forwarding on not Logged in (CFNL) (3GPP TS 24.604)
-
Communication Forwarding on Busy (CFB) (3GPP TS 24.604)
-
Communication Forwarding on not Reachable (CFNLc) (3GPP TS 24.604)
-
Communication Forwarding on no Reply (3GPP TS 24.604)
-
Incoming Call Barring of (ICB) (3GPP TS 24.611)
-
Outgoing Call Barring (OCB) (3GPP TS 24.611)
-
Barring of Outgoing International Calls (BOIC) (3GPP TS 24.661)
-
Barring of International Calls - ex Home Country (BOIC-HC) (3GPP TS 24.611)
-
Barring of Incoming Calls - When Roaming (BIC-Roam) (3GPP TS 24.611)
-
Communication Hold (CH) (3GPP TS 24.610)
-
Ad-hoc Conferencing (3GPP TS 24.605)