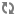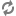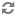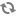You add a Delimited File data source by specifying delimited text files to crawl, delimiter information, and optional information about column names and whether columns contain multi-assign values.
Each new line in a delimited text file results in one corresponding Endeca record after crawling. Columns and column fields become properties and property values.
By default, the Delimited File data source reads the header row of a file and uses the header values as column names. In cases where a delimited file does not have a header row of column names, you can specify column names manually using the Column Names option.
The data source supports both single-assign and multi-assign values. (See the configuration options below.)
To add a new Delimited File data source:
Select Delimited File from the list and click Add.
The Data Source tab displays.
In Name, specify a unique name for the data source to distinguish it from others in the CAS Console.
You can create a data source name with alphanumeric characters, underscores, dashes, and periods. All other characters are invalid for a name.
In Path to Input File(s), specify an absolute path to the delimited files you want to crawl.
Wildcards may be used in the filename but not in the path preceding the filename.
Example of local folders on Windows:
Example of syntax for network drives:
In Record Id Column, specify the name of the column that you want to map to the record ID property in the generated records.
The values of this column must be unique across all files being crawled.
In Delimited Character, specify a single character that delimits the fields in the records. The default delimiter is a comma ( , ).
In Quote Character, specify a single character that escapes occurrences of the delimited character within a field. The default quote character is a quote ( " ).
Optionally, in Column Names, click Add for each column in the file and name it as appropriate for the column value. Specify column names in the order in which they appear in a delimited text file. This optional configuration is typically only necessary in cases where a delimited file does not contain a header row. If Column Names are unspecified, the data source treats the first row of the file as the header row and uses the column names as MDEX property names.
Optionally, in Multi-Assign Delimiter Character, specify a single character that delimits multi-assign values within a multi-assign column. If you specify a value and omit adding any Multi-Assign Columns, the data source parses all columns in the file as if they may contain multi-assign values.
In this example, the pipe character ( | ) delimits multi-assign values named
Value2a,Value2b, andValue2cwithin a multi-assign column namedHeader2:Header1,Header2,Header3 Value1,Value2a|Value2b|Value2c,Value3
Optionally, in Multi-Assign Columns, click Add for each column in the file that contains multi-assign values and name it as appropriate for the column value.
Optionally, in Trim Whitespace, select true to trim the leading or trailing whitespace from the data stored in columns of the delimited file. The default value is true.
Optionally, in Character Encoding, specify the character encoding of the delimited file that is being crawled. If unspecified, the default value is UTF-8.
The data source displays Acquisition Steps where you can add manipulators, revise the data source configuration if necessary, or start acquiring data from the data source.
At this point, you can add manipulators, acquire data from the data source, and monitor its status.