A widget is a Flash-based display of the results of a dataset report, allowing users to visualize data in different ways than traditional reports displayed as Grid/Graphs do. Widgets are sophisticated visualization techniques that can combine with rich interactivity to enable users to understand their data more effectively. You can use a variety of widget types, such as Gauge, Heat Map, and Interactive Stacked Area widgets. Although each type of widget looks different and is used in a unique way, the main purpose of all widgets is the same: to provide document analysts with a visual and interactive look into their data.
To create a widget that is correctly displayed in the application, you must place and position the correct number of report objects on the Grid/Graph.
When you add a Cylinder widget to a document in Editable Mode, it looks similar to a standard Grid/Graph. In the object selector of the Formatting toolbar ![]() , the widget is considered a type of Grid/Graph when it is selected.
, the widget is considered a type of Grid/Graph when it is selected.
In the image below, the new Cylinder widget is shown on the right. The Dataset Objects panel is displayed on the left to give you an idea of the dataset and dataset objects with which the designer is working.
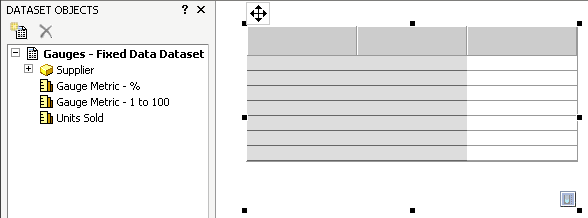
To define the widget, dataset objects such as attributes and metrics must be placed on the Grid/Graph. To successfully define a Cylinder widget, one attribute must be placed on the Grid/Graph's rows and one metric must be placed on the columns, as shown below. The Supplier attribute is placed on the rows and the Units Sold metric is placed on the columns.
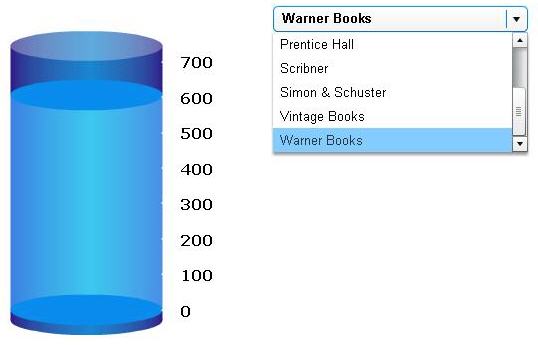
A selector alongside the widget is very useful. In this case, the selector will be used by a document analyst to switch between different suppliers (the attribute elements of the Supplier attribute).

The selector is designed as follows:
The DHTML Style is the Drop-down style.
The Target is the Cylinder Grid/Graph. In this case, this is Grid/Graph33, the name of the widget. The target ensures that the Grid/Graph is updated accordingly when an item is selected from the drop-down list.
The Source is the Supplier attribute. The source provides the attribute elements from the Supplier attribute to populate the selector.
The Cylinder widget presents a vertical cylinder with liquid in it; the level of the liquid within the cylinder depicts a specific metric value. In this case, the metric value is the number of units sold. Notice also that the look and feel of the selector changes in the application.
To display the number labels on the right of the cylinder, right-click the cylinder and select Properties. By default, the minimum and maximum values for a Cylinder widget are 0 to 100. Since the metric values are much larger on this report, you should change the maximum value to something like 700, to accommodate the largest metric values on the report.
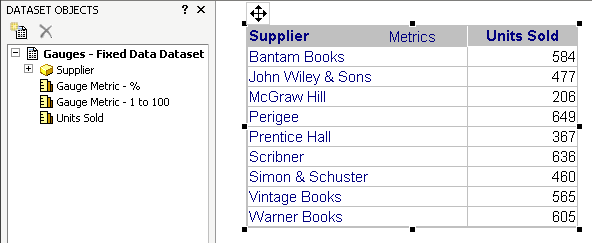
Another convenient addition to the widget/selector combination shown above is a grid version of the report. For this example, you might add the grid report shown in the Dataset Objects panel above. The grid report allows you and document analysts to see how one attribute element's value compares against other values. You can also sort the grid report and pivot objects on it. In this example, the full grid report allows you to see how one supplier's revenue compares with other suppliers. To add a grid report next to the widget, simply drag the report from the Dataset Objects panel and drop it next to the widget..
The following list briefly summarizes each type of widget that you can use in a document.
Bubble Grid: The Bubble Grid widget contains metric values that are plotted as bubbles of different colors and sizes; the colors and sizes of the bubbles represent the values of two distinct metrics on the Grid\Graph.
Cylinder: The Cylinder widget displays a vertical cylinder with fluid in it. The level of the fluid within the cylinder is a visual representation of a single metric value.
Data Cloud: The Data Cloud widget consists of a list of attribute elements. The font size of each attribute element represents a metric value for that element. These metric values represent the values of the first metric on the Grid/Graph.
Date Selection: A calendar selector that allows you to select which dates you want to see data about in an RS dashboard. You are able to see all of the dates of each month in the widget, which makes selecting dates easier.
Fish Eye: The Fish Eye Selector magnifies an item when you hover the cursor over it. It allows you to choose from a large list of attribute elements, metrics, or images without having to see all of the elements, metrics, or images.
Funnel: The Funnel widget can be used for a wide variety of business purposes, including application management, click management, pipeline analyses for sales forecasts, and sales process analysis.
Gauge: The Gauge widget displays a needle that moves within a range of numbers displayed on its outside edges. An example of a gauge is a car's speedometer.
Graph Matrix: The new Graph Matrix widget allows you to display data using different graph types, format the graphs, then slice the data to customize the display of the widget. To create a Graph Matrix widget, create a Visual Insight (VI) dashboard with a Graph visualization, then convert the VI dashboard to a document.
Heat Map: The Heat Map widget combines colored rectangles, each representing an attribute element, which allow you to quickly grasp the state and impact of a large number of variables at once.
Interactive Bubble Graph: The Interactive Bubble Graph widget allows you to visualize the trends of three different metrics for a set of attribute elements.
Interactive Stacked Graph: The Interactive Stacked Graph widget is a combination of a check box list and area graph. The graph allows a user to see the contribution of various metric series to the change in value of a larger set of data.
Media: The Media widget allows you to present a variety of media, such as video, audio, images, or website content, on your RS dashboard. You can include media in the widget to provide background information about data or instructions on how to use the RS dashboard.
Microcharts: The Microcharts widget conveys information in such a way that the user can, at a glance, determine the trend of a metric over time or how a metric is performing compared to forecasted figures.
RSS Reader: The RSS Reader widget helps provide a 360-degree view of your business by allowing you to compare and contrast data in your RS dashboard with information from external news feed sources.
Thermometer: The Thermometer widget displays a thermometer set to a certain temperature level. The temperature level within the thermometer is a visual representation of a single metric value.
Time Series Slider: The Time Series Slider widget allows a document analyst to choose which section of the graph to view at a time.
Waterfall: The Waterfall widget consists of a group of clustered bars displayed from left to right. The X-axis contains either attribute elements or metrics, depending on where the attributes and metrics are placed on the Grid/Graph in Design Mode or Editable Mode. The Y-axis displays a range of values based on the metrics on the Grid/Graph.
Weighted List Viewer: The Weighted List Viewer widget provides attribute and metric values with threshold colors applied to them from top to bottom. The color bands on the grid reflect the range of values of the first metric on the Grid/Graph. The stacked contribution bar graph on the left that depicts the relative contribution or percent-to-total calculation of a metric. This bar reflects the values of the second metric on the Grid/Graph.
Selectors allow a user to display different metrics or different elements of attributes, custom groups, or consolidations in a Grid/Graph (the target of the selector). Targets can be automatically maintained in a layout. This means that when you add a Grid/Graph or widget, the Grid/Graph or widget is the target of all selectors in the same panel or document section as the Grid/Graph or widget.
_____________________________
Copyright © 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Legal Notices