15 Installing JVMD Agents with Advanced Install Options
This chapter describes how you can install JVM Diagnostics (JVMD) Agents manually in the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control environment.
In particular, this chapter covers the following:
Overview of JVMD Architecture
JVM Diagnostics is integrated with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. It primarily enables administrators to diagnose performance problems in Java applications in the production environment. By eliminating the need to reproduce problems, it reduces the time required to resolve these problems, thus improving application availability and performance. Using JVMD, administrators can identify the root cause of performance problems in the production environment, without having to reproduce them in the test or development environment.
The following diagram shows the JVMD Architecture:
Figure 15-1 JVMD Architecture
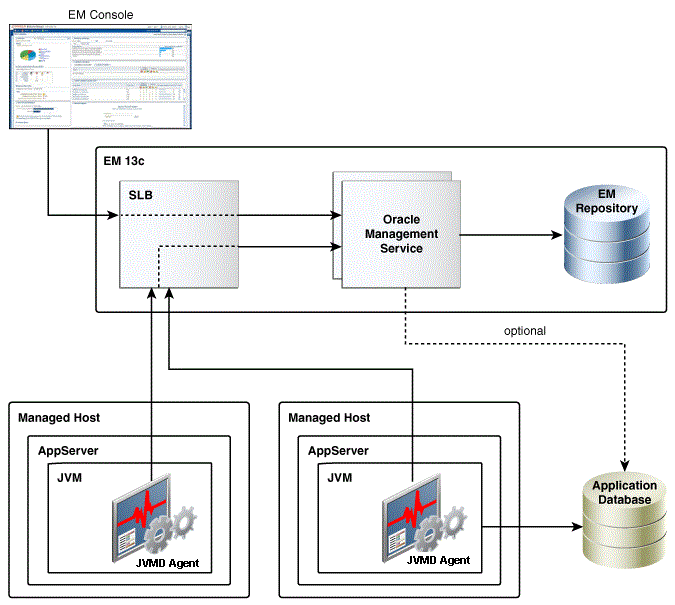
JVMD Engine is the core analytical engine of the JVMD monitoring system. Starting with Enterprise Manager 13c, JVMD Engine is deployed as an Enterprise Application Deployment (ear file) on the EMGC domain out-of-the-box. JVMD Engine runs as an Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) technology in the OMS server. JVMD Engine collects runtime data from JVMD Agents on request from the OMS, and stores the data in the repository. Multiple JVMD Engines can be configured.
JVMD Agents are the data collectors of the target JVM. JVMD Agents are deployed to managed application servers to collect JVM monitoring data related to JVM threads, stacks, heap and CPU usage, and so on, in real-time, while introducing minimal overhead.
The JVMD Agent is deployed on the targeted JVM (the one running a production WebLogic Server). It collects real-time data and transmits it to the JVM Diagnostics Engine. This data is stored in the Management Repository, and the collected information is displayed on the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control console for monitoring purposes. The communication between JVMD Engine and JVMD Agent can be secure (SSL), or non-secure.
JVMD communication between clients (also known as agents) and server (also known as manager servers or engines) is HTTPS based. The JVMD manager server hosts and ports can be found on the Engines and Agents page, under the Middleware Management option of the Enterprise Manager Setup menu. Please refer the SLB user guide to set up a pool for the corresponding JVMD manager hosts and ports. The JVMD agent deployment and download should specify the SLB host and port to achieve HA.
Most SLBs ensure source address (that is, client host) based affinity. JVMD communication inserts header field FROM-AGENT-ID, which can be used for this purpose. Please refer the SLB user guide for configuration instructions.
In 13.2GC, if the load balancer is configured to terminate at the OMS managed servers and you have defined the custom certificates, then ensure the following:
-
Custom certificates file(s) are placed in
<EMAS plugin home>/archives/jvmd/certificatesdirectory -
Custom certificates file(s) have a
.crtextension -
Custom certificates file(s) do not have a
WLSDemo_prefix -
Custom certificates file(s) are provided in above location on each OMS
Note:
AREADME.txt file is available at <EMAS plugin home>/archives/jvmd/certificates directory.Before you Begin Installing JVMD Agent
Before installing a JVMD Agent, review the points outlined in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
Prerequisites for Installing JVMD Agent
Before installing a JVMD Agent, ensure that you meet the prerequisites described in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
Deploying JVMD Agents Using Advanced Installation Options
This section describes how to deploy JVMD Agents manually.
Note:
If you have removed an agent and you want to deploy it again, you must restart JVM before deploying it.
This section consists of the following:
Deploying JVMD Agents Manually by Downloading and Deploying jamagent.war
To deploy JVMD Agents manually, follow these steps:
Note:
-
The preferred method of manual deployment of JVMD Agents is using step 1. Download jamagent.war.
-
Step 2. Deploy JVMD Agent manually section is applicable only if the Download jamagent.war fails.
-
Download jamagent.war.
To download
jamagent.warusing Cloud Control, follow these steps:-
In Cloud Control, from the Setup menu, select Middleware Management, then select Engines And Agents.
-
On the Engines And Agents page, click Download JVMD Agent. The Download JVM Diagnostics Components dialog box is displayed.
-
From the JVMD Component menu, select JVMD Agent to download
jamagent.warand then click OK. The JVM Diagnostics Agent web.xml Parameters dialog box is displayed. -
From the Available Engines menu, select an option from the list:
Select the HTTP URL if you want the JVMD Agent to connect to the JVMD Engine using a non-secure connection.
Select the HTTPS URL if you want the JVMD Agent to connect to the JVMD Engine using a secure connection.
Select Custom if you want the JVMD Agent to connect to a JVMD Engine through a Load Balancer or a firewall. Specify the host name and the port that the JVMD Agent must connect to.
For example:
HTTP:
http://sl1.us.example.com:3800HTTPS:
https://sl1.us.example.com:3801 (secure communication)
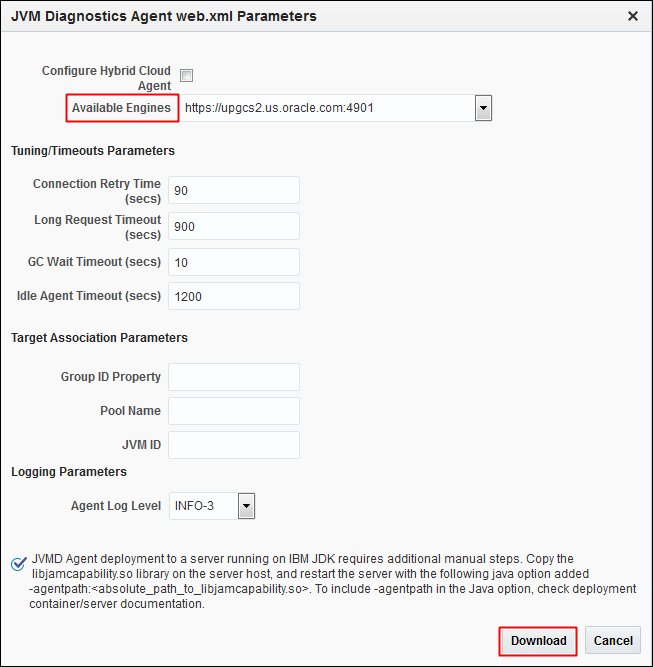
-
Click Download to download
jamagent.war.
-
-
Deploy JVMD Agent manually.
See the relevant steps below:
Deploying JVMD Agent on WebLogic Server
To deploy JVMD Agent on a WebLogic Managed Server manually, follow these steps:
-
Make a copy of the deployment profile
sample_jvmdagent_deploy.propertiesavailable in thejvmd.zipfile. Update the location of thejavadiagnosticagent.earfile, the name of the WebLogic domain, and the server information. Save the profile asjvmdagent_deploy.properties.For more information about the parameters, view the
README.txtfile present in thecustomprovfolder of thejvmd.zipfile. -
Run the following perl script available in the
customprovfolder of thejvmd.zipfile to deploy JVMD Agent on all the specified servers.perl deploy_jvmdagent.plNote:
Ensure that the deployment profile
jvmdagent_deploy.propertiesand the perl scripts are available in the same folder.
Deploying JVMD Agent on GlassFish
To deploy JVMD Agent on a GlassFish server manually, follow these steps:
-
Log in to the Glassfish Administration console.
-
In the Common Tasks section, click Applications.
-
In the Deployed Applications section, click Deploy.
-
For Location, select Packaged File to Be Uploaded to the Server, then specify the location on your local host where
jamagent.waris present. -
For Selected Targets, add the server on which you want to deploy
jamagent.war. -
Click OK.
Deploying JVMD Agent on JBoss
To deploy JVMD Agent on JBoss manually, follow these steps:
-
Log in to the JBoss Administration console.
-
Under Applications, click Web Application (WAR)s.
-
Click Add a new resource.
-
Enter the absolute path to
jamagent.warpresent on your local host. -
For both Deploy Exploded and Deploy Farmed, select No.
-
Click Continue.
To deploy JVMD Agent on JBoss manually, you can also do the following:
-
Transfer
jamagent.warto the following location:<JBOSS_HOME>/server/all/deploy -
Restart the application server.
Deploying JVMD Agent on Tomcat
To deploy JVMD Agent on Tomcat manually, follow these steps:
-
Transfer
jamagent.warto the following location:$CATALINA_BASE/webapps -
Restart the application server.
For the latest versions of Tomcat, if the
autoDeployflag is set totruein$CATALINA_BASE/conf/server.xml,you do not need to restart the application server. Tomcat will pick upjamagent.warat runtime.
Deploying JVMD Agent on Websphere
To deploy JVMD Agent on Websphere manually, follow these steps:
-
Log in to the Websphere Administration console.
-
Expand Applications, then click New Application.
-
Click New Enterprise Application.
-
For Path to the new application, select Local file system, then specify the location on your local host where
jamagent.waris present. -
Provide the context root for
jamagent.war. -
Save the configuration.
-
Start the application.
Deploying JVMD Agent on OC4J
To deploy JVMD Agent on OC4J manually, follow these steps:
-
Log in to the OC4J Administration console.
-
Click Applications.
-
Click Deploy.
-
Select Archive is present on local host. For Archive Location, specify the location on your local host where
jamagent.waris present. Click Next. -
For Application Name, enter
jamagent.For Context Root, enter/jamagent. -
Click Deploy.
Deploying JVMD Agent on a Standalone JVM
A JVMD Agent can be deployed on a standalone JVM such that the inputs are read from
web.xml,or such that you specify the inputs on the command line.To deploy a JVMD Agent on a standalone JVM such that all the inputs are read from
web.xml,run the following command from the command line:java -cp <absolute_path_to_jamagent.war> jamagent.jamrun <java_class_with_a_main_method>To deploy a JVMD Agent on a standalone JVM by specifying all the inputs on the command line, run the following command from the command line:
java -cp <absolute_path_to_jamagent.war> jamagent.jamrun <java_class_with_a_main_method> jamconshost=<jvmd_engine_host> jamconsport=<jvmd_engine_listen_port> jamjvmid=<unique_jvmd_identifier> jamtimeout=<timeout_period_in_seconds> jamloglevel=<jvmd_agent_log_level>Note:
When
jamagent.waris run using an IBM Java Development Kit (JDK), you may see the following warning in the logs:******can_tag_objects capability is not set.Copy library libjamcapability to another directory and restart Java with argument "-agentpath:<absolute_path_to_libjamcapability.so>" ******
To troubleshoot this warning, include the
libjamcapability.solibrary and restart the IBM JVM:/scratch/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer/java/bin/java -agentpath:/scratch/libjamcapability.so -cp /scratch/jamagent.war jamagent.jamrun MyFirstProgram -
Deploying JVMD Agents Manually Using deploy_jvmdagent.pl
You can deploy JVMD Agents manually, using the deploy_jvmdagent.pl script. You can run this script only in silent mode, that is, you must specify all the input details using a properties file.
To deploy JVMD Agents manually using deploy_jvmdagent.pl, follow these steps:
Deploying JVMD Agents for High Availability
If you have multiple JVMD Engines in your setup, and have configured a load balancer for them, you can deploy JVMD Agents such that they connect to the load balancer, and not to any of the individual JVMD Engines. This increases the availability of the JVMD Agents, and creates a failover mechanism, that is, even if a particular JVMD Engine goes down, the JVMD Agents remain active. For more information on configuring multiple OMS High Availability behind a SLB, see Enterprise Manager 13c Cloud Control: Configuring OMS High Availability with F5 BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager technical whitepaper.
You can deploy JVMD Agents for high availability using the Engines And Agents page, or manually.
Deploying JVMD Agents for High Availability Using the Engines And Agents Page
To deploy JVMD Agents for high availability using the Engines And Agents page, follow these steps:
-
Follow the steps mentioned in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide to deploy a JVMD Agent.
Note:
By default, the JVMD Agent connects to the load balancer using HTTPS.
-
On the JVMD Agents Configurations page, for Available JVMD Engines, select Other. Provide the load balancer host name and port.
Click Next.
-
On the Review page, review all the information, then click Deploy.
Deploying JVMD Agents for High Availability Manually
To deploy JVMD Agents for high availability manually, follow these steps:
After Installing JVMD Agents
After installing a JVMD Agent, follow the steps outlined in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.