| User Data Repository Diameter User's Guide Release 12.4 E92984-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The Per-Connection Ingress MPS Control (PCIMC) feature limits to a configurable level the per-connection ingress message rate of each connection. Correctly configured message rate controls ensure that a single connection cannot use the majority of the resources. (No limiting is done by PCIMC for the egress message rate).
Per-Connection Capacity Management
Per-connection ingress MPS control allocates a DA-MP's ingress message processing capacity among the diameter peer connections that it hosts. Each peer connection is allocated, through user-configuration, a reserved ingress MPS message processing capacity and a maximum ingress MPS message processing capacity.
The reserved capacity for a connection is available for exclusive use by the connection. The capacity between a connection's reserved and maximum capacity is shared with other connections hosted by the DA-MP.
Per-Connection Ingress Message Coloring
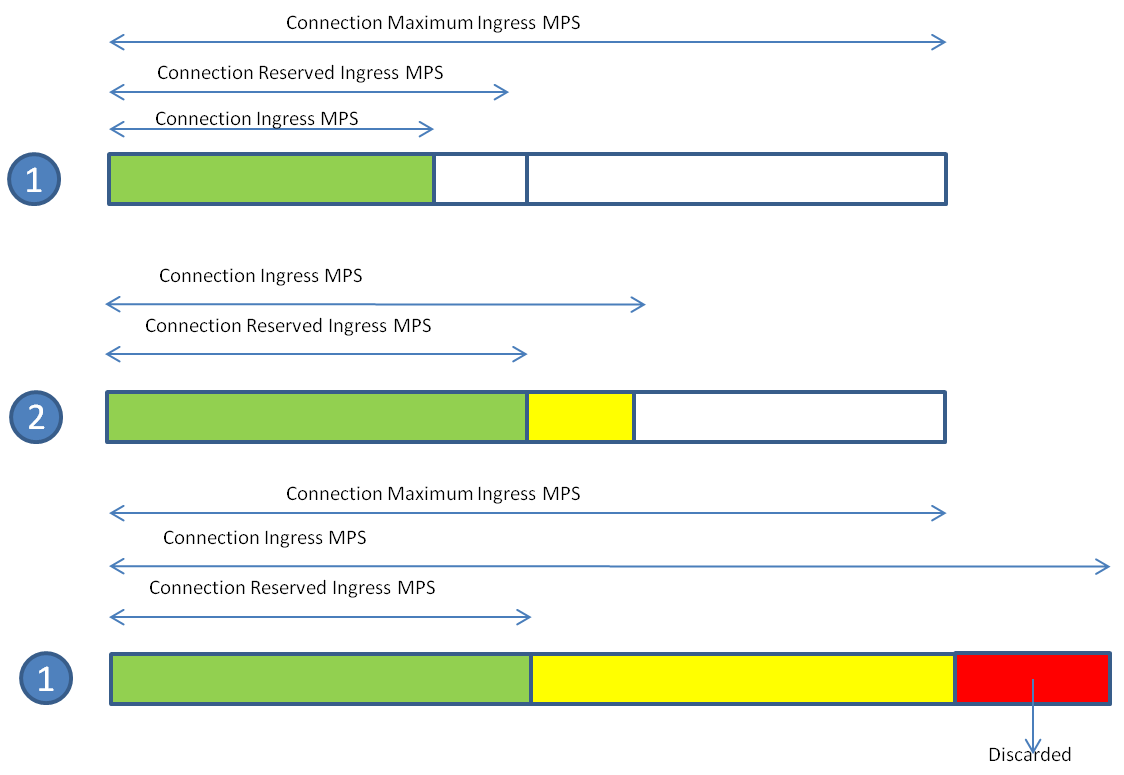
In addition to enforcing ingress message rate limits on a per-connection basis, PCIMC colors ingress messages based on the reserved and average ingress message rates. message color can be used at other traffic shedding points, such as DA-MP Overload Control.
Traffic from under-utilized connections is marked green by per-connection ingress message controls, while traffic from over-utilized connections is marked yellow. Traffic discarded by PCIMC due to capacity exhaustion (per-connection or shared) is marked red and is not considered for any subsequent processing.
Note:
If the connection's reserved ingress MPS is 0, all the messages processed by the connection are colored yellow.Figure 14-1 Per-Connection Message Coloring
Message Discard Policy
The Message Discard Policy function considers the priority of the message while discarding the message.
Each peer connection tracks the priority of the ingress message and discards the messages that exceed the maximum ingress MPS configured for the connection.
The request messages are discarded based on the configured resource exhausted action that is set as abandon the request with no answer or send answer. For a description of Resource Exhausted Action see Diameter Routing Option Sets.
Per MP Server Capacity Management
MPS rates and thresholds are used to manage ingress message MPS as it relates to the MP server as a whole.
This value provides a limit to the total reserved ingress MPS of all diameter connections assigned to the DA-MP. The value is displayed for the MP Profile assigned to the DA-MP.
This value may be greater than the MP engineered ingress MPS.
The DA MP monitors its MPS rate and limits the rate to an MP engineered ingress MPS value. If the MP engineered ingress MPS rate is exceeded, overload can occur and ingress messages can be discarded (due to MP ingress MPS limiting and MP congestion controls).
Diameter Configuration for Per-Connection Ingress MPS Control
The reserved ingress MPS cannot exceed the configured maximum ingress MPS for a given connection. A connection can be configured with a zero reserved ingress MPS value; such connections do not reserve message processing capacity.
The reserved ingress MPS for a connection cannot be used by any other connection, regardless of the load offered to other connections.
If the reserved ingress MPS capacity is set to a non-zero value, that value times the number of connections using that capacity configuration set on a given MP server must not be allowed to exceed the MP maximum reserved ingress MPS (which is equal to the MP engineered ingress MPS - the highest MPS rate at which the MP server can process ingress diameter messages).
The maximum Ingress MPS must be greater than or equal to the reserved ingress MPS. Any difference between the maximum ingress MPS and the reserved ingress MPS represents MP server resources that are shared among connections that are using the same capacity configuration set.
The configured maximum ingress MPS of a connection cannot exceed the engineered ingress MPS of the connection (the ingress MPS that a connection can process at a sustained rate without errors). If the connection has reserved ingress MPS, the configured maximum ingress MPS must be greater than or equal to the reserved ingress MPS. All connections must have a non-zero configured maximum ingress MPS; otherwise they would not be allowed to process traffic at all. (The maximum ingress MPS value in the default capacity configuration set is non-zero.)
The sum of the maximum ingress MPS configured for all connections on a MP server can exceed the MP engineered ingress MPS to the highest MPS rate at which the MP server can process ingress diameter messages.
The ingress MPS minor alarm threshold value must be less than the ingress MPS major alarm threshold value
The ingress MPS major alarm threshold must be greater than the ingress MPS minor alarm threshold.
Maintenance and Monitoring for Per-Connection Ingress MPS Control
For each connection, the MP server maintains the average number of ingress diameter messages per second read from the socket. This is the rate at which ingress diameter messages are read from the socket, not the rate at which ingress diameter messages arrive at the socket. There is no efficient means to know the rate at which messages actually arrive.
Connection Alarm
The PCIMC feature provides a connection alarm with two severities to alert the network operator when the average ingress MPS rate goes above the configured thresholds for percentage of the configured maximum ingress MPS for the connection.
The connection ingress MPS alarm is a per-connection alarm that can be configured in a connection's capacity configuration set to trigger at a minor and major capacity threshold.
The minor alarm is asserted when the MPS rate exceeds the configured ingress MPS minor alarm threshold value for the connection. The minor alarm is cleared when the MPS rate falls 5% below the ingress MPS minor alarm threshold value configured for the connection.
The major alarm is asserted when the MPS rate exceeds the ingress MPS major alarm threshold value configured for the connection. The major alarm is converted to a minor alarm when the MPS rate falls 5% below the ingress MPS major alarm threshold value configured for the connection.
An alarm cannot be abated until an abatement time delay has expired. For example, if a minor alarm is asserted, the alarm cannot be cleared until the abatement time delay has expired and the average ingress MPS for the connection is 5% below the minor alarm assert percentage.
The alarm abatement time delay affects only clearing of alarms, not asserting of alarms. Therefore, it is possible to transition rapidly from a minor alarm to a major alarm.