Overview
DNS ALG service provides an application layer gateway for use with DNS clients. DNS ALG service allows a client to access multiple DNS servers in different networks and provides routing to/from those servers. It also supports flexible address translation of the DNS query/response packets. These functions allow the DNS client to query many different domains from a single DNS server instance on the client side of the network.
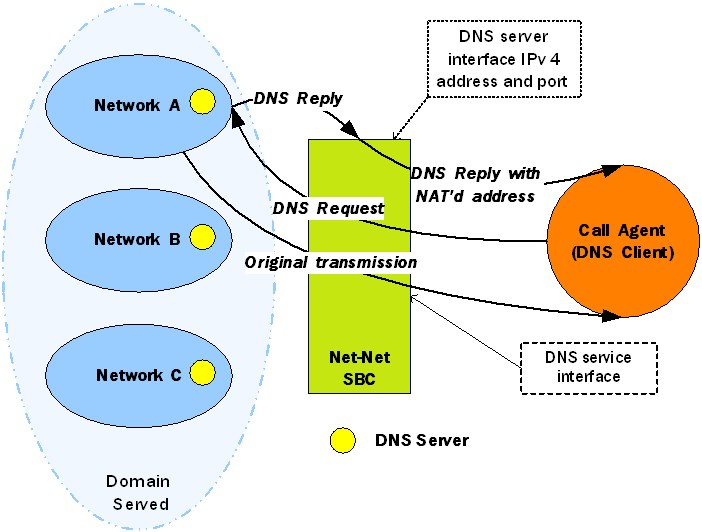
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller’s DNS ALG service is commonly used when a DNS client (such as a call agent) needs to authenticate users. In this case, the DNS client that received a message from a certain network would need to authenticate the endpoint in a remote network. Since the DNS client and the sender of the message are on different networks, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller acts as an intermediary by interoperating with both.
In the following diagram, the DNS client has received a message from an endpoint in Network A. Since the DNS client is in a different realm, however, the DNS client receives the message after the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller has performed address translation. Then the DNS client initiates a DNS query on the translated address. The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller forwards the DNS request to the DNS server in Network A, using the domain suffix to find the appropriate server. Network A’s DNS server returns a response containing its IPv4 address, and then the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller takes that reply and performs a NAT on the private address. The private address is turned into a public one that the DNS client can use to authenticate the endpoint.