Aggregate Session Constraints Nested Realms
In addition to setting session constraints per realm for SIP and H.323 sessions, you can also enable the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to apply session constraints across nested realms. When you set up session constraints for a realm, those constraints apply only to the realm for which they are configured without consideration for its relationship either as parent or child to any other realms.
You can also, however, enable the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to take nested realms into consideration when applying constraints. For example, if a call enters on a realm that has no constraints but its parent does, then the constraints for the parent are applied. This parameter is global and so applies to all realms on the system. For the specific realm the call uses and for all of its parents, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller increments the counters upon successful completion of an inbound or outbound call.
In the following example, you can see one parent realm and its multiple nested, child realms. Now consider applying these realm constraints:
- Parent Realm 1—55 active sessions
- Child Realm 1—45 active sessions
- Child Realm 2A—30 active sessions
- Child Realm 2B—90 active sessions
- Child Realm 3—20 active sessions
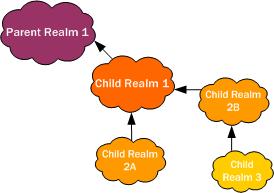
Given the realm constraints outlined above, consider these examples of how global session constraints for realms. For example, a call enters the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller on Child Realm 2B, which has an unmet 90-session constraint set. Therefore, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller allows the call based on Child Realm 2B. But the call also has to be within the constraints set for Child Realm 1 and Parent Realm 1. If the call fails to fall within the constraints for either of these two realms, then the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller rejects the call.