An LDAP data source uses a tree-like structure, called a directory information tree (DIT), for storing, organizing, and retrieving data objects (or entries) from a database. Organizing entries into a DIT makes the information faster and easier to look up which is crucial for time sensitive processing.
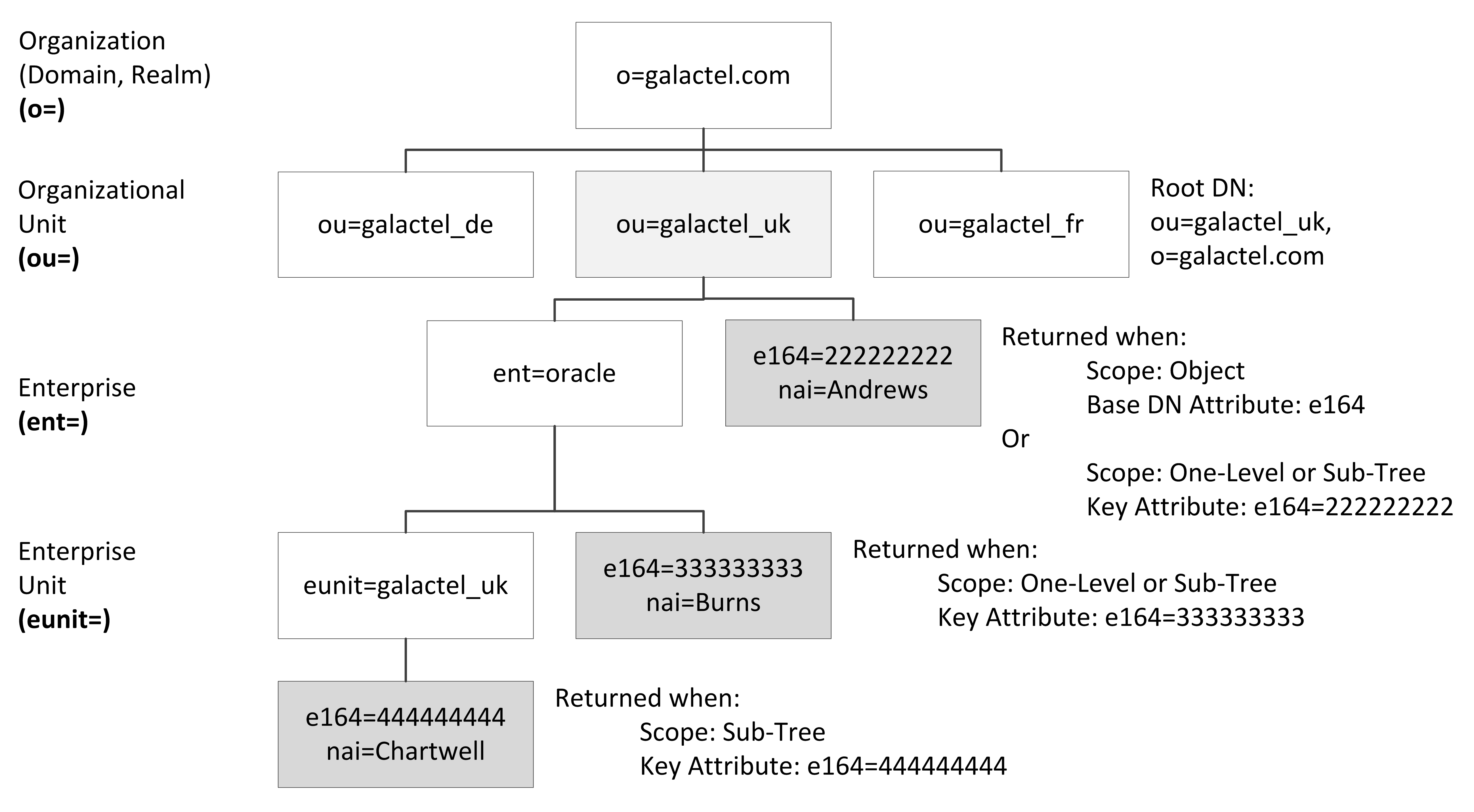
In Figure 1, the example database structure has a realm (or domain) of o=galactel.com, which encompasses all subscribers in the system. The subscribers may then be organized by organizational unit; for example, by country ou=galactel_uk. Within an organizational unit, the subscribers could be further subdivided into enterprises and enterprise units. A data lookup locates a subscriber's information based on the key attribute used to index the information, for example the NAI or the E.164 (MSISDN). An example of a DN for a specific subscriber's record is e164=222222222, ent=oracle, ou=galactel_uk, o=galactel.com.
The Search Criteria tab of the Edit Data Source dialog provides a method of restricting a record search to a particular section of the DIT. By specifying the Root DN (for example, ou=galactel_uk,o=galactel.com) and the Scope, you can either broaden or narrow the LDAP database search. See Defining LDAP Search Criteria for more information.
See Configuring an LDAP Data Source for details on configuring an LDAP data source.