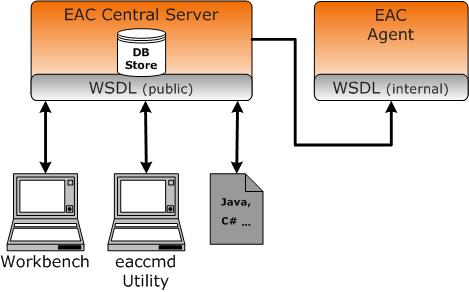
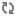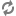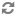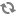The EAC is installed on each machine that runs the Guided Search software and is typically run in a distributed environment.
Depending on the role that the EAC plays in the Guided Search implementation, each instance of the EAC can take one of two roles:
You can communicate with the EAC and provide instance configuration and resource configuration information to the EAC Central Server, using any of the three methods:
Workbench. Endeca Workbench communicates through the WSDL interface to the EAC Central Server. Using Workbench you can provision, run, and monitor your application. For details, see the Oracle Commerce Workbench Help.
The command line utility,
eaccmd.eaccmdlets you script the EAC within a language such as Perl, shell, or batch.Direct programmatic control through the Guided Search WSDL-enabled interface and languages, such as Java, that support Web services.
Note
The Guided Search Deployment Template utilizes this method for communication with the EAC Central Server.
Using any of these methods, you can instruct the EAC to perform different operations in your Guided Search implementations, such as start or stop a component (for example, Forge or Dgraph), or a utility (for example, Copy or Shell environment).
The following diagram describes the EAC architecture and means of communication with it, while the sections below describe the roles of the EAC Central Server and EAC Agents: