About Static Flows
The static flow element explicitly writes entries into the IP routing table. These entries are persistent and are not deleted as calls are set up and broken down. Refer to the following diagram to understand how a static flow works.
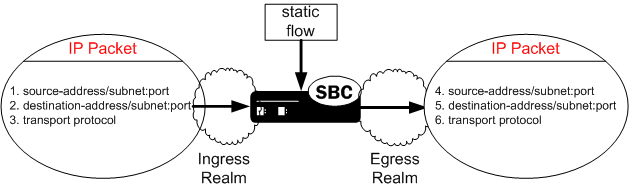
A static flow entry watches for traffic with specific criteria on a specified ingress realm; that traffic consists of the following criteria:
- The packet enters the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller on the specified ingress realm.
- The packet contains matching source address, subnet, and port criteria, field 1.
- The packet contains matching destination address, subnet, and port criteria, field 2.
- The packet contains a matching transport protocol, field 3.
If the above conditions are met, then the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller does the following:
- The IPv4 traffic is forwarded out of the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller on the specified egress realm.
- The configured source address, subnet, and port criteria are written to the exiting packet, field 4.
- The configured destination address, subnet, and port criteria are written to the exiting packet, field 5.
- The original transport protocol and its contents remain unchanged as the packet exits into the egress realm.



