About Network Address Translation ALG
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller supports Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) functionality over media interfaces, collectively known as Network Address Translation (NAT) ALG. The NAT ALG feature is implemented as an extension of the static flow feature.
In some applications, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller acts as an intermediary device, positioned between endpoints located in an access network and application servers located in a backbone network. The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller ’s NAT ALG feature enables these endpoints to use non-VoIP protocols, such as TFTP and HTTP, to access servers in a provider’s backbone network to obtain configuration information.
NAT ALG parameters support RTC and can be dynamically reconfigured. The active NAT ALG configuration can be replicated on the standby SD in an HA configuration.
NAPT
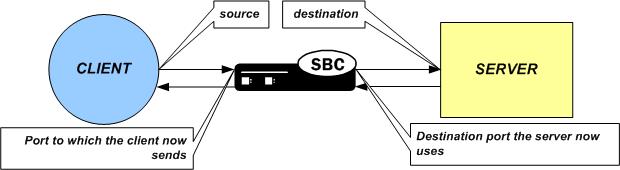
The NAPT ALG functionality is the same as that found in commercially available enterprise and residential NAT devices. The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller watches for packets entering a media interface that match source and destination IP address criteria. Matching packets are then redirected out of the egress interface, through a specified port range, toward a destination address.
TFTP
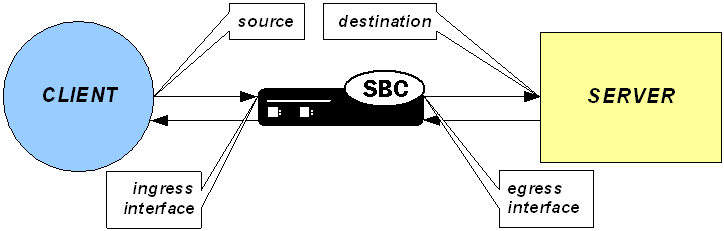
The TFTP ALG is implemented as an extension of the NAT ALG. It works slightly differently than traditional NAPT. In a TFTP session, the first packet is sent from a source endpoint to port 69 on the TFTP server. The TFTP server responds from another port. This port, from which the TFTP response originates, is used for the remainder of the TFTP session.
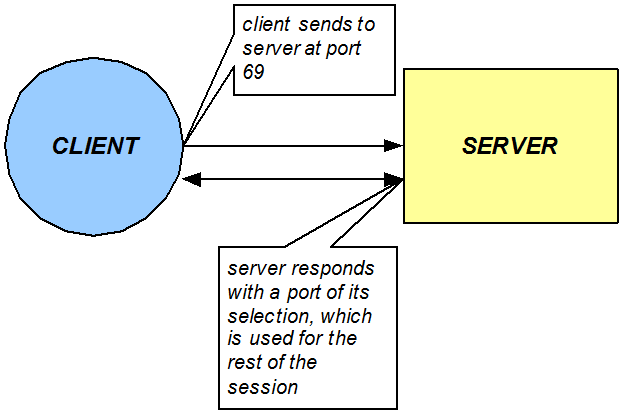
To act as a TFTP ALG, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller will latch on the first return packet from the server to learn the server's port. The ingress-side destination port of the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is changed to reflect the new communications port for the TFTP session. This process takes place without any user intervention.