2 Preparing for Oracle Database Appliance Installation and Deployment
Complete these setup tasks before Oracle Database Appliance is delivered.
Tasks:
- Registering Your Support Identifier on My Oracle Support
Add your hardware Support Identifier (SI) to your My Oracle Support account profile. - Planning Oracle Database Appliance Configuration Options
Determine how many CPU cores you want to enable, determine your database configuration options, and gather the system information for your Oracle Database Appliance Bare Metal deployment configuration. - Gathering System Requirement Information
Use these checklists to collect information before deploying Oracle Database Appliance.
Registering Your Support Identifier on My Oracle Support
Add your hardware Support Identifier (SI) to your My Oracle Support account profile.
Your hardware SI is supplied when you purchase Oracle Database Appliance. If you acquire new software licenses, then you must also register your new software SIs. The SI registration process can take up to 24 hours to complete.
Note:
You cannot obtain support or software from Oracle without registered SIs.
Planning Oracle Database Appliance Configuration Options
Determine how many CPU cores you want to enable, determine your database configuration options, and gather the system information for your Oracle Database Appliance Bare Metal deployment configuration.
Note:
Do not use Oracle Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) to create databases on Oracle Database Appliance. Only use Oracle Appliance Manager for database configuration. Deploying Oracle Database instances using Oracle Appliance Manager ensures that these databases are properly configured, optimized, and supported on Oracle Database Appliance.- Selecting Operating System Groups and Users
Determine how you want to configure your operating system groups and users and whether or not you want to allow operating system role separation. - Selecting Database Deployment Options
See the Oracle Database editions that are available for deployment. - Selecting Database Shapes for Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance software includes preconfigured templates, known as shapes, that incorporate Oracle best practices with optimization for different classes of databases.
Selecting Operating System Groups and Users
Determine how you want to configure your operating system groups and users and whether or not you want to allow operating system role separation.
About Operating System Groups and Users
Role separation enables you to configure groups and users to provide separate groups for operating system authentication.
Without role separation, a single user owns all of the Oracle installations. All of the databases are installed under a single user. Role separation enables you to have separate users for Oracle and Oracle Clusterware. You can install multiple databases without sharing operating system authentication for system privileges. In addition, each Oracle software installation is owned by a separate installation owner, to provide operating system user authentication for modifications to Oracle Database binaries.
Note:
Any Oracle software owner can start and stop all databases and shared Oracle Grid Infrastructure resources, such as Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) or Virtual IP (VIP). The job role separation configuration enables database security, it does not restrict user roles in starting and stopping various Oracle Clusterware resources.With Oracle Grid Infrastructure role separation, separate operating system groups provide operating system authentication for Oracle ASM system privileges for storage tier administration. This operating system authentication is separated from Oracle Database operating system authentication. In addition, the Oracle Grid Infrastructure installation owner provides operating system user authentication for modifications to Oracle Grid Infrastructure binaries.
You can configure the appliance with one of four combinations of operating system users, groups, and roles. The default users are the Oracle Database installation owner (oracle) and Oracle Grid Infrastructure installation owner (grid). The default groups are oinstall, dbaoper, dba, asmadmin, asmoper, and asmdba
Default Configuration: Two Users with Six Groups
The default configuration is a combination of two operating system roles for users with six groups.
To configure two users, oracle user with the Oracle User (oracleUser) role and the grid user with the gridUser role, allow operating system role separation.
To configure six groups, oinstall, dbaoper, dba, asmadmin, asmoper, and asmdba, do not select the option to customize users and groups.
Note:
When you select the default configuration in the Web Console, the users and groups do not appear in the interface.Two Custom Users with Six Custom Groups
You can customize the configuration to create two custom users and six custom groups.
To configure two users, allow operating system role separation. The users are populated with the default values, oracle and grid, which you can edit.
To configure six groups, select the option to customize users and groups. The groups are populated with the default values, which you can edit. The default groups are oinstall, dbaoper, dba, asmadmin, asmoper, and asmdba.
The figure shows an example of a custom configuration with the default values populated.
Figure 2-1 Two Custom Users with Six Custom Groups
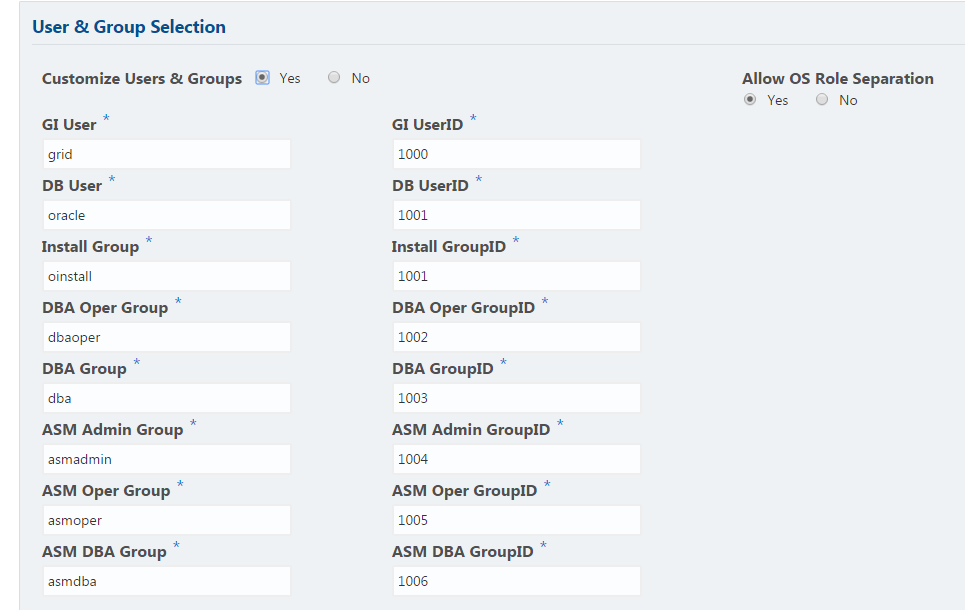
Description of "Figure 2-1 Two Custom Users with Six Custom Groups "
Single Custom User with Six Custom Groups
You can customize the configuration to create a single operating system database user and with six custom groups. The database user can deploy both the grid infrastructure and RDBMS (relational database management system) stacks. You can edit the user name and user ID and you can customize the group names and IDs. Use this option when you deploy SAP.
To configure a single oracle database user with the Oracle User (oracleUser) role, do not allow OS role separation.
To configure six groups, select the option to customize users and groups. The following default groups are populated: oinstall, dbaoper, dba, asmadmin, asmoper, and asmdba. You can customize the groups.
Single User with Two Groups
To configure a single oracle user with the Oracle User (oracleUser) role, do not allow OS role separation.
To configure two groups, oinstall and dba, do not select the option to customize users and groups.
Parent topic: Planning Oracle Database Appliance Configuration Options
Selecting Database Deployment Options
See the Oracle Database editions that are available for deployment.
Oracle Appliance Manager installs Oracle Database software on mirrored disks that are internal to Oracle Database Appliance. You specify the database edition in the Web Console during the initial deployment. You cannot use both Oracle Database Enterprise Edition and Standard Edition on the same appliance.
The following Oracle Database editions are available:
-
Oracle Database Enterprise Edition
Oracle Database Enterprise Edition provides the performance, availability, scalability, and security required for mission-critical applications such as high-volume online transaction processing (OLTP) applications, query-intensive data warehouses, and demanding Internet applications.
-
Single-instance Oracle Database Enterprise Edition home
-
Oracle Database options are available
-
-
Oracle Database Standard Edition 2
Oracle Database Standard Edition 2 delivers unprecedented ease of use, power, and performance for workgroup, department-level, and Web applications.
-
Oracle Database Standard Edition
Oracle Database Standard Edition delivers the unprecedented ease of use, power, and performance of Standard Edition One, with support for larger machines and clustering of services with Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC).
-
Oracle Database Standard Edition One
Oracle Database Standard Edition One delivers unprecedented ease of use, power, and performance for workgroup, department-level, and Web applications.
Note:
Review the Oracle Database licensing guide for supported options and products.Parent topic: Planning Oracle Database Appliance Configuration Options
Selecting Database Shapes for Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance software includes preconfigured templates, known as shapes, that incorporate Oracle best practices with optimization for different classes of databases.
Because of differences in CPU counts, memory size, and other resources available with different Oracle Database Appliance models, some shapes are not supported on all models.
Each Oracle Database shape has different workload profile and performance characteristics:
-
Memory requirements, which are calculated from the System Global Area (SGA), and Program Global Area (PGA) sizes
-
Processing requirements, which are calculated from the number of processes
-
Logging requirements, which are based on log buffer size, and online redo log size
Oracle Database Appliance shapes are tuned for the size of each database instance workload and are designed to run on a specific number of cores.
Note:
Oracle strongly recommends that you use the Oracle Database Appliance shapes. These shapes implement best practices, and are configured specifically for Oracle Database Appliance.
Parent topic: Planning Oracle Database Appliance Configuration Options
Gathering System Requirement Information
Use these checklists to collect information before deploying Oracle Database Appliance.
- List of Information You Need Before Deployment
Collect security, storage, and network information required to prepare for deploying Oracle Database Appliance. - Checklist for System Details
Use the checklist to gather system information that you need to obtain for Oracle Database Appliance. Record the values for your system. - Checklist for Custom Network Address Configuration
Use the checklist to identify the IP addresses required for Oracle Database Appliance.
List of Information You Need Before Deployment
Collect security, storage, and network information required to prepare for deploying Oracle Database Appliance.
Review your security requirements for root passwords, determine your storage requirements and network administration requirements, and complete any required configuration before your Oracle Database Appliance hardware is delivered.
Security Requirements
-
What root password should you use for Oracle Database Appliance? Root passwords should comply with your system security requirements.
-
Secure operating systems are an important basis for general system security. Ensure that your operating system deployment is in compliance with common security practices.
Storage Administration Requirements
Storage administration is integrated into Oracle Database Appliance. No additional storage configuration is required.
Oracle Database Appliance includes integrated storage for operational files (operating system, Oracle Grid Infrastructure home, Oracle Database homes, tools), user data (database files), and log files (database redo logs). Operational files are stored on mirrored internal system disks in each server. Data and database redo log files are stored on shared disks in the storage shelf.
The Oracle Database Appliance X6-2-HA storage shelf contains ten 1.6 TB SSDs (partitioned to 1.2 TB to improve performance) for data, which are configured as a DATA ASM disk group. Four 200 GB SSDs are used for the database redo logs, which are configured as a REDO ASM disk group.
Note:
Disk hardware capacity is measured using the formula that 1 KB equals 1,000 bytes; software storage requirements are based on 1 KB equals 1,024 bytes.
Network Administration Requirements
Ensure that the names and addresses that you provide for network configuration are configured in your Domain Name System (DNS) servers. The addresses that you provide are configured in the /etc/hosts file to provide IP name and address resolution, even if a DNS server is not available.
You have the option to connect either to a copper, or to a fiber public network. Ensure that your network planning is based on the correct type of public network.
Oracle recommends that you resolve addresses using a DNS server, so that you can use Single Client Access Names (SCANs). Having a single name to access the cluster enables the client to use the EZConnect client and the simple JDBC thin URL to access any Oracle Database running in the cluster, independent of the active servers in the cluster. The SCAN provides load-balancing and failover for client connections to these databases. The SCAN works as a cluster alias for Oracle Databases in the cluster.
If you deploy without using a DNS server, then you can add a DNS server later, and add SCANs. If you add SCANs, then you must specify additional VIP addresses for those SCANs.
A correctly configured Oracle Database Appliance requires at least six public addresses on the same subnet for the nodes:
-
A public IP name and address for each node
-
A virtual IP name and address for each node
-
Two addresses that resolve to the SCAN for the cluster.
All names must conform to the RFC 952 standard, which permits alphanumeric characters and hyphens ("-"), but does not allow underscores ("_").
Provide an IP address for the public interface for each node. This interface is bond0, or Eth1 on Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform, (a bond of Eth2 and Eth3), which is used for the host IP address for the node.
Use bond1 and bond2 for management, backup, disaster recovery, or other options where you require a network interface. Be prepared to provide a netmask and a gateway for each interface, as both are required when you configure network connections for Oracle Database Appliance. If you select a Custom installation, then provide names and addresses for the bond1 optional interface.
Also determine answers to the following questions:
-
Do you have a Network Time Protocol (NTP) service configured for each server, so that the local system time for each server is synchronized?
If you have NTP servers, and you want to synchronize time between Oracle Database Appliance nodes using NTP, then be prepared to provide the addresses for the servers. If you do not provide addresses for NTP servers, then Oracle Grid Infrastructure software configures time synchronization between nodes using Cluster Time Synchronization Service (CTSS).
-
Do you want to plug in the public IP address cables to redundant switches, so that you can avoid a single point of failure for Oracle Database Appliance? Oracle recommends that you use redundant switches for High Availability.
Parent topic: Gathering System Requirement Information
Checklist for System Details
Use the checklist to gather system information that you need to obtain for Oracle Database Appliance. Record the values for your system.
Table 2-1 Checklist for System Configuration Information for Oracle Database Appliance
| System Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
Host Name |
The name for the Oracle Database Appliance System. The name must conform with the RFC 952 standard, which allows alphanumeric characters and hyphens ( - ), but does not allow underscores ( _ ). The name should not begin with a numeral or hyphen and should not end in a hyphen. Oracle recommends that you use all lowercase characters for the host name. |
|
Domain Name |
Your domain name. For example: |
|
Master Password |
The password set for the root password of the system, OS users, database users, and pdbadmin. The password is also used to set the database |
|
DNS Server |
(Optional) DNS server details. |
|
NTP Server |
(Optional) Network Time Protocol (NTP) service details. |
|
Region |
The region where you plan to operate the Oracle Database Appliance system. |
|
Timezone |
Select the time zone where you plan to operate the Oracle Database Appliance system. |
|
Database Edition |
Select an Oracle Database edition, either Enterprise Edition or Standard Edition. You cannot mix editions. The database edition you select determines the database editions that you create in the appliance. To change editions, you must redeploy Oracle Database Appliance. |
|
Backup Location |
Determine the backup location setting. The setting determines how the NVMe Disks are partitioned between DATA and RECO. Select External, Internal, or Custom:
|
|
Percentage of Storage Reserved for Data |
If you select a Custom backup location, determine the amount of reserves for DATA storage. The percentage must be a whole number between 10 and 90. |
|
Diskgroup Redundancy |
If the machine has 4 NVMe, select normal redundancy (two way mirror) or high redundancy (three way mirror). If the machine has 2 NVMe, redundancy is automatically set to normal and this field does not appear. |
|
Network Information |
Obtain network information:
|
|
Initial Database Details (if you want to create one during deployment) |
|
Parent topic: Gathering System Requirement Information
Checklist for Custom Network Address Configuration
Use the checklist to identify the IP addresses required for Oracle Database Appliance.
Note:
Oracle does not recommend changing the default Host Private Address. You cannot change the private network after deploying the appliance.Table 2-2 Default IP Address Requirements for Oracle Database Appliance
| Type of IP | IP Address Default Values | Your Values As Applicable |
|---|---|---|
|
Client Access Network |
No default |
No default |
|
Additional Network |
No default |
No default |
|
Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) |
No default |
No default |
|
Host Private Addresses |
192.168.16.24 |
Not applicable: the private addresses are defined before deployment and should not be changed |
Parent topic: Gathering System Requirement Information