Purpose: Use the Customer Maintenance programs to maintain existing customer information and create new customer records without creating orders. You use the Customer Maintenance programs when you need to:
• Enter customer address changes
• Construct a demographics profile
• Create a contract price for a short-term sale
• Change a customer's tax status, payment type, etc.
• Add a customer service action note
• Review a customer's ordering history
In this chapter:
Purpose: There are four customer types:
• Sold-to
• Ship-to
• Bill-to
You need to understand the customer types in order to work with Customer table maintenance.
Sold-to customers: A sold-to customer is a person who places an order. Name, address, and mailing information for sold-to customers is in the Customer Sold-to table only.
Note: The Customer Engagement Customer Integration includes only sold-to customers.
Ship-to customers: A ship-to customer is a person who receives an order. The system generates a temporary ship-to record for every sold-to customer when you enter an order. You can create permanent ship-to customers through Customer Ship-to when you enter an order.
• Permanent ship-to customers are customers who request a ship-to address different from their sold-to address. The Customer Ship-to table stores permanent ship-to customer information.
• Temporary ship-to customers are customers who receive the shipped order but do not place the order or pay for the order (for example, gift recipients). The Order Ship-to Address table stores temporary ship-to customer information.
Bill-to customers: A bill-to customer is a person who pays for an order. A bill-to customer record is required when the person who pays for the order is different than the sold-to customer.
You can assign bill-to customer addresses through Order Entry if the system control value Create/Assign Bill To Customers in Order Entry (A76) is selected.
The system generates bill-to records for business-to-business customers. Business-to-business customers are customers who ship to a consistent address, have a permanent account, and are commercial in nature.
You can define a business-to-business customer by selecting the Commercial flag for a customer. Once you have established a bill-to customer account, the account remains permanently in the Bill-to customer table.
The figure below illustrates the relationships between the customer types.
 |
(Sold-to) customer places, receives, and pays for order. Payment methods: Cash, Check, Credit Card |
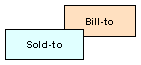 |
(Sold-to) customer places and receives order, but someone else receives the bill. Payment methods: Credit Card |
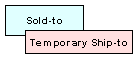 |
(Sold-to) customer places and pays for order, but directs shipment to another (Temporary Ship-to) person. Payment methods: Cash, Check, Credit Card |
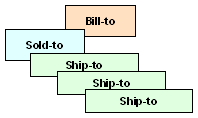 |
(Sold-to) customer orders for one or more (Permanent Ship-to) locations, and directs bill to a separate (Bill-to) accounting function. Payment methods: Credit Card |
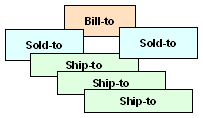 |
One or more (Sold-to) customer orders for one or more (Permanent Ship-to) receiving locations, but each Sold-to directs their bills to a single (Bill-to) accounting function. Payment methods: Credit Card |
Rules to remember: The following is a list of guidelines to keep in mind when working with the different customer types.
• Every order has at least a sold-to customer
• The system creates a bill-to record if the person paying for the order is different from the person placing the order
• More than one permanent ship-to record can exist under a single sold-to, if the sold-to regularly places orders to be shipped to different locations
For more information: See Creating and Updating Customers for options related to creating and working with each customer type.
| Creating and Updating Customers | Contents | SCVs | Search | Glossary | Reports | Solutions | XML | Index | Selecting Customers |

CS03_01 OMSCS 18.1 April 2019 OTN