| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.8 F11880-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.8 F11880-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
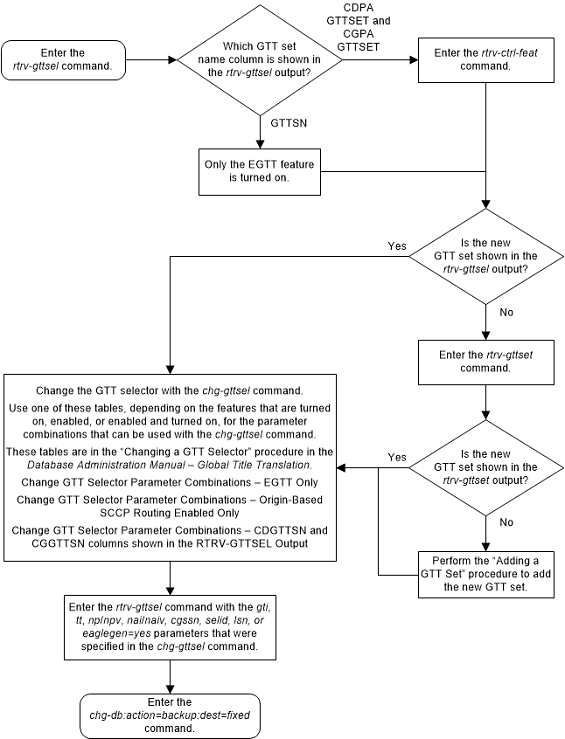
Use the following procedure to change the GTT set
assigned to a selector using the
chg-gttsel command.
The
chg-gttsel command uses these
parameters.
:gti/gtia/gtii/gtiis/gtin/gtins/gtin24 – The global
title indicator. The GTI defines the domain as shown in this list.
gti and
gtia - ANSI global title indicator
with the values 0 or 2
gtii - ITU
international (ITU-I) global title indicator with the values, 0, 2, or 4
gtiis - ITU
international (ITU-I) spare global title indicator with the values, 0, 2, or 4
gtin - ITU national
(ITU-N) global title indicator with the values 0, 2, or 4.
gtins - ITU national
(ITU-N)spare global title indicator with the values 0, 2, or 4.
gtin24 - ITU-N24
spare global title indicator with the values 0, 2, or 4.
:tt
– The global title translation type, (0-255). The same
translation type value can be specified for multiple GTI values. For example,
the translation type value 10 can be assigned to an ANSI GTI, an ITU-I GTI, an
ITU-I spare GTI, an ITU-N GTI, an ITU-N spare GTI, and an ITU-N24 GTI.
:msgtype – The SCCP message type. This parameter
allows one or more SCCP message types (UDT/UDTS/XUDT/XUDTS) for every GTT
Selector entry. This will help in screening different message types
differently.
:nai – The nature of
address indicator.
:naiv – The nature of
address indicator value. (0-127) (See
Table 4-18
for NAI/NAIV mapping)
Note:
The nature of address indicator parameters (naiv or
nai) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
naiv or
nai parameter.
Table 4-18
shows the mapping between the
naiv and the
nai parameters.
:np – The numbering plan.
:npv – The numbering plan
value. (0-15) (See
Table 4-19
for NP/NPV mapping)
Note:
The numbering plan parameters (npv or
np) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
npv or
np parameter.
Table 4-19
shows the mapping between the
npv and the
np parameters.
:gttsn – the GTT set
name.
:cdgtasn – The CDGTA GTT
set name or the value
none.
:cggtasn – The CGGTA GTT
set name or the value
none.
:cgpcsn – The CGPC GTT
set name or the value
none.
:cgssn – The CGPA SSN.
:selid – The selector ID.
:cdgttsn – The CDGTA
GTT set name or the value
none.
:cggttsn – The CGGTA
GTT set name or the value
none.
:eaglegen – Indicates
whether the GTT selector is used by messages generated by the EAGLE. If the GTT
selector is used by messages generated by the EAGLE, the entry
Eagle-Gen is shown in the
LSN column of the
rtrv-gttsel output.
:lsn – The name of the
linkset that is assigned to the GTT selector.
Table 4-18 NAIV/NAI Mapping
| NAIV | NAI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | --- | Unknown |
| 1 | Sub | Subscriber Number |
| 2 | Rsvd | Reserved for national use |
| 3 | Natl | National significant number |
| 4 | Intl | International number |
| 5-127 | --- | Spare |
Table 4-19 NPV/NP Mapping
| NPV | NP | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | --- | Unknown |
| 1 | E164 | ISDN/telephony numbering plan |
| 2 | Generic | Generic numbering plan |
| 3 | X121 | Data numbering plan |
| 4 | F69 | Telex numbering plan |
| 5 | E210 | Maritime mobile numbering plan |
| 6 | E212 | Land mobile numbering plan |
| 7 | E214 | ISDN/mobile numbering plan |
| 8 | Private | Private network or network-specific numbering plan |
| 9-15 | --- | Spare |
Figure 4-11 Change a GTT Selector