Calculating Benefits
This topic provides an overview of benefits calculation and discusses how to:
Calculate legal benefits.
Calculate complementary benefits.
When payees are on temporary disability leave (IT), they are eligible for these benefits:
The legally mandated benefit (Subsidio).
PeopleSoft Global Payroll for Spain calculates legal benefits by multiplying the employee's daily base (Base Reguladora Diaria) by the number of leave days, and then applying a percentage to this base. The percent applied varies according to the benefit being calculated and the number of days the employee is on leave.
A complementary benefit (Prestación Complementaria) defined by the employer. The calculation for complementary benefits depends on the base that you selected on the Complementary Benefits page.
The legal benefit is calculated by earning elements with a calculation rule of Unit x Rate x Percent. The correct percent varies depending on the benefit type and day of the leave (see tables in this topic). The rate is the daily base for IT, AT, or maternity or risk during pregnancy that is taken from the previous period to the begin date of the absence. For new employees hired during the month, the system calculates a theoretical daily base that would apply if the employee had worked for the whole month. The unit is the number of days that the employee is on leave and must be entered on the Absence Event Entry page.
Note: For IT benefits, employees are eligible only when they have contributed to Social Security for at least 180 days in the past five years. The person who enters the absence event must validate that the employee is eligible for the benefit. If an employee is not eligible for the benefit, select the Lacking Period Indicator check box on the Additional Data page of the Absence Event ESP (GPES_ABS_EVENT) component so that the system does not pay the benefit.
IT Legal Benefit
For temporary disability leave (IT), the legally mandated benefit is defined as a percentage of the benefits base—with the percentage varying according to the number of days the employee is on leave. The current percentages (and the benefits base to which the percentages are applied) are shown in this table:
|
From Day in IT |
To Day in IT |
Percentage |
Benefit Base |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
4 |
20 |
60 |
CC Base |
|
21 |
540 |
75 |
CC Base |
Two benefit phases exist. From day 4 to day 15 of the benefit, the employer is responsible for making payments to the employee. Beginning with day 16 and continuing to day 180, Social Security subsidizes the benefit. Although the company serves as the direct provider of the benefit during the entire benefit period, Social Security reimburses the company for any payments made after day 15 under a system known as Pago Delegado. This table shows who is responsible for the benefit paid during each phase:
|
From Day in IT |
To Day in IT |
Who Pays? |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
3 |
No benefits paid |
|
4 |
15 |
Company |
|
16 |
540 |
Social Security |
If the IT absence continues after 540 days it can be extended by Social Security. If that happens, enter an end date for the first IT event, and enter a new row for absence event IT PRORROGADA with an original begin date that is the same begin date as the original IT event. This benefit is paid directly by Social Security.
AT Legal Benefit
For employees on disability leave for work-related injury, the current legally mandated benefit is defined as 75 percent of the benefits base throughout the entire benefit period. The current percentage, as well as the benefits base to which the percentage is to be applied, are shown in this table:
|
From Day in AT |
To Day in AT |
Percentage |
Benefit Base |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
540 |
75 |
CP Base |
By law, the Mutual Insurance Company is responsible for paying the AT benefit through the entire benefit period. Although the company acts as the direct provider of the benefit, Social Security reimburses the company for any payments made under a system known as Pago Delegado. This table shows who is responsible for the benefits paid:
|
From Day in AT |
To Day in AT |
Who Pays? |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
540 |
Social Security |
If the AT/EP absence continues after 540 days it can be extended by Social Security. If that happens, enter an end date for the first AT/EP event, and enter a new row for absence event AT/EP PRORROGADA with an original begin date that is the same begin date as the original AT/EP event. This benefit is paid directly by Social Security.
Maternity/Paternity Leave, Risk During Pregnancy or Lactancy, and Minor Care Legal Benefits
Maternity, pregnancy risk, and minor care benefits consist of 100 percent of the daily regulatory base: CC for maternity/paternity, and CP for risk during pregnancy or lactancy and minor care. Social Security is responsible for paying benefits beginning with the first day of leave. As a consequence, this benefit is not processed by PeopleSoft Global Payroll for Spain and these benefits never appear on the payslip. However, the system calculates legal benefits to calculate the complementary benefits for maternity and risk during pregnancy that are defined on the Complementary Benefits page.
This table summarizes the benefit amount and benefit period for maternity:
|
From Day in MATERNITY/PATERNITY |
To Day in MATERNITY/PATERNITY |
Amount |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Depends on number of children born. |
100 % of daily common contingencies base. |
This table summarizes the benefit amount and benefit period for pregnancy risk:
|
From Day in Risk During Pregnancy or Lactancy |
To Day in Risk During Pregnancy or Lactancy |
Amount |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
No limits |
100 % of daily professional contingencies base. |
This table summarizes the benefit amount and benefit period for minor care:
|
From Day in Risk During Pregnancy or Lactancy |
To Day in Risk During Pregnancy or Lactancy |
Amount |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
No limits |
100 % of daily professional contingencies base for the non-worked period. |
Part-time Maternity and Paternity
Maternity and paternity leave can be taken on a part-time basis in which an employee works part of the day and is absent for the other part. For part-time maternity and paternity, you enter MATERNIDAD PARCIAL or PATERNIDAD PARCIAL absence events. In addition, you need to enter the number of partial hours for the absence events. If an absence starts or ends in the middle of the month it will cause an element segmentation of the payroll calculation.
Special Maternity Leave Benefits
There are two special cases that affect maternity leave benefits:
The birth, adoption, or foster care of two or more children simultaneously.
A working mother does not comply with the minimal contribution period.
For multiple simultaneous births, adoptions or foster care, the payee is eligible for a special subsidy for each additional child after the first. The amount of the subsidy for each additional child is the same as it is for the first child (100% BRD) and is paid in one lump sum six weeks after the birth or adoption. To indicate that a payee is eligible for the multiple maternity subsidy, select MLT in the Absence Reason field and enter the number of children on the Additional Data page of the Absence Event ESP (GPES_ABS_EVENT) component.
For working mothers who do not comply with the minimal contribution period, the system pays a subsidy of either 100% IPREM (Indicador Público de Renta de Efectos Múltiples) or 100% BRD, whichever is smaller. The duration of this subsidy is 42 natural days from the birth. To indicate that a working mother should receive this subsidy, select the Lacking Period Indicator check box on the Additional Data page of the Absence Event ESP (GPES_ABS_EVENT) component.
Image: Example of MATERNIDAD absence event with absence reason of MLT
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Additional Data tab of the Absence Event Entry page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
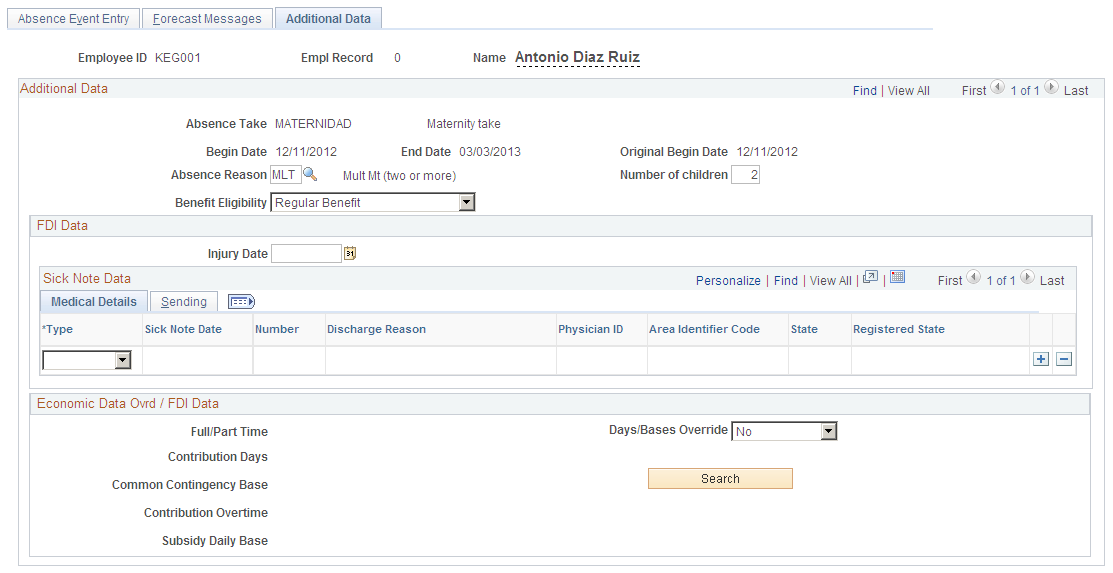
Note: For both special maternity leave benefits, the corresponding absence take is still MATERNIDAD.
See Additional Data Page.
To define complementary benefits (Prestaciónes Complementarias), set up the following items on the Complementary Benefits page:
Funding Base used to calculate complementary benefits. This could be:
Social Security Common Contingencies or Professional Contingencies base. This is the default base.
Employee's gross daily salary.
Any other daily accumulator that you have defined.
Absence period.
Total percentage to be paid for each period.
The complementary benefit uses an earning element with a calculation rule of Unit x Rate x Percent. The correct percent is retrieved by a formula based on the benefit percentages defined on the Complementary Benefits page. The rate is the daily base for IT, AT, and maternity or risk during pregnancy, which is either based on the previous period without absence (if the default base is used) or another base defined on the Complementary Benefits page. The unit is the number of days that the employee is on leave and must be entered on the Absence Event Entry page.
Then another earning (PRSTCN CMPIT, PRSTCN CMPAT, PRSTCN CMPMT, PRSTCN CMPRE, or PRSTCN CMPCM) gets the difference between the previous earning and the value corresponding to the Subsidio IT, Subsidio AT, Subsidio MT, or Subsidio RE.