3Customizing Siebel Object Interfaces
Customizing Siebel Object Interfaces
This chapter describes how to customize Siebel object interfaces. It includes the following topics:
Process of Customizing a Siebel Object Interface
To customize a Siebel object interface, perform the following tasks:
Determining the Type of Siebel Object Interface You Must Use
This task is a step in Process of Customizing a Siebel Object Interface.
This topic describes how to determine the type of Siebel Object Interface you must use.
To determine the type of Siebel Object Interface you must use
In the following table, examine the Usage column, and then choose the row that most closely matches your requirements.
To identify the type of Siebel Object Interface you must use, examine the other columns in the following table, in the row that you identified in the preceding step.
Table Determining the Type of Siebel Object Interface You Must Use
| Usage | Web Client Automation Server | Mobile Web Client Automation Server | COM Data Control | COM Data Server | Siebel Java Data Bean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Control the Siebel client from an external application. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
Access Siebel business objects without using the Siebel client. |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Run objects on the Siebel Server. |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Run objects in the Siebel client in a mobile environment. |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Use Caution If You Customize a Siebel Object Interface
Oracle does not support the following items:
Functions developed through custom programming
Specific performance characteristics of third-party software
Oracle defines a Siebel business object or a Siebel object interface at the sole discretion of Oracle. Oracle reserves the right to modify the behavior, properties, and events of a Siebel business object or a Siebel object interface at any time without notice.
Setting the Connect String
The connect string is a text string that describes the URL that is required to connect to a server component on the Siebel Server. It specifies the protocol and the details of the Client Application Manager service on the Siebel Server. The Siebel client or a program that is external to Siebel CRM must use this string to connect to the Siebel Server.
Format of the Connect String Parameter
The connect string uses the following format:
host="siebel.transport.encryption.compression://host:port/EnterpriseServer/ AppObjMgr_lang" lang="lang_code"
For example:
SiebelApplication.Login "host=""siebel://host/EnterpriseServer/SCCObjMgr_enu"" "lang="ENU"", "CCONWAY", "CCONWAY"
The following table describes how to set each variable in the connect string.
Table Variable Substitutions You Can Use to Log In to a Siebel Server
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
transport |
Use the default value, tcpip, or leave empty. |
encryption |
Use one of the following values:
|
compression |
Use one of the following values:
|
host |
Use the name of the computer where you installed the Siebel Server. |
port |
Enter the number for the SCBroker port. The default value is 2321. Modify this value only if you also modify the default value when you install the Siebel Server. For information about load-balancing with SCBroker, see Siebel Deployment Planning Guide, Siebel System Administration Guide, and Siebel Installation Guide for the operating system you are using. |
EnterpriseServer |
Enter the name of the Siebel Enterprise Server. |
AppObjMgr |
Enter the name of the Application Object Manager that the Siebel client must access. You can enter a custom server component or one of the following predefined server components:
For more information, see Siebel System Administration Guide. |
The format of the connect string is optional. You can enter only the transport variable and use a period (.) to separate it from siebel. For example:
siebel.tcpip://host/siebel/AppObjMgr_lang
If you specify any of the other variables, then you must use a period (.) as a placeholder for each variable that you do not specify. For example:
siebel...zlib://myhost/siebel/SCCObjMgr_enu
Examples of Using the Connect String
This topic includes examples of using the connect string.
Example Connect String for COM Data Control in Server Mode
The following example includes a connect string for COM Data Control that operates in server mode:
'COM Data Control : SERVER Mode lstr = "host=" + """siebel://frashid/Siebel/SSEObjMgr_enu""" 'Format of the connect string is '"host=" + """siebel://host/enterprise/App. Object Mgr_lang""" lng = "lang=" + """ENU""" retval = siebDataCtl.Login(lng + lstr, "username", "password")
Example Connect String for COM Data Control in Local Mode
The following example includes a connect string for COM Data Control that operates in Local Mode:
'COM Data Control : LOCAL Mode lstr = "cfg=" + """C:\Siebel\8.1\Client_2\BIN\ENU\siebel.cfg,ServerDataSrc""" 'Format of the connect string is '"cfg=" + """Absolute path of the CFG file, DataSource""" 'Datasource = ServerDataSrc or Local or Sample lng = "lang=" + """ENU""" retval = siebDataCtl.Login(lng + lstr, "username", "password")
If in Local Mode, then COM Data Control must reside on the same computer as the Siebel Mobile Web Client.
Example Connect String for COM Data Control When Using Siebel VB
The following example includes a connect string for COM Data Control that uses Siebel VB. The Char(34) code indicates a double quote:
ConnStr = "host =" & char(34) & "siebel://HOST/ENTERPRISE_SERVER/SCCObjMgr_enu/ SIEBEL_SERVER" + char(34) & " Lang = " & char(34) & "LANG" & char(34)
Using Load Balancing with the Connect String
You can use Siebel native load balancing across Siebel Servers with the following Siebel object interface: Siebel Java Data Bean
To use load balancing with the connect string
Modify the predefined connect string so that it directs requests to an appropriate virtual host.
This host includes specific Siebel Servers. Each Siebel Server includes the required object manager.
Specify the path to the file that defines the virtual host.
Connect String That Uses Load Balancing with Siebel Java Data Bean
A connect string that uses native Siebel load balancing with Siebel Java Data Bean uses the following format:
host="siebel://VirtualHost/EnterpriseServer/AppObjMgr_lang"
If you use Java code to connect to the Siebel Server, then Siebel CRM reads virtual host definitions from the following property in the siebel.properties file:
siebel.conmgr.virtualhosts
The siebel.properties file must reside in the classpath of the Java Virtual Machine.
For information about using virtual hosts in the siebel.properties file, see Transports and Interfaces: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.
Accessing a Siebel Object Interface
This task is a step in Process of Customizing a Siebel Object Interface.
This topic describes how to access a Siebel Object Interface.
To access a Siebel Object Interface
To access a Siebel object interface, do one of the following:
These topics assume you use Microsoft Visual Basic to access the interface.
Accessing the Web Client Automation Server
This topic describes how to access the Web Client Automation Server. For more information, see Mobile Web Client Automation Server.
To access the Web Client Automation Server
Run the Siebel Enterprise Server Installer.
The Siebel Enterprise Server Installer installs the Web Client Automation Server by default.
Start Microsoft Visual Basic.
Choose Standard EXE.
Choose the Project menu, and then the References menu item.
In the list box, choose SiebelHTML 1.0 Type Library.
Add the required code.
For more information, see Example of Accessing the Web Client Automation Server.
Example of Accessing the Web Client Automation Server
The following example includes the code you use in Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 to access the Web Client Automation Server:
Private Sub Command1_Click()
'Siebel Application Object
Dim siebApp As SiebelHTMLApplication
Dim siebSvcs As SiebelService
Dim siebPropSet As SiebelPropertySet
Dim bool As Boolean
Dim errCode As Integer
Dim errText As String
Dim connStr As String
Dim lng As String
'Create The SiebelHTML Object
Set siebApp = CreateObject("Siebel.Desktop_Integration_Application.1")
If Not siebApp Is Nothing Then
'Create A New Property Set
Set siebPropSet = siebApp.NewPropertySet
If Not siebPropSet Is Nothing Then
Set siebPropSet = Nothing
Else
errCode = siebApp.GetLastErrCode
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText "Property set creation failed." & errCode & "::" &
errText
End If
'Get A Siebel Service
Set siebSvcs = siebApp.GetService("Workflow Process Manager")
If Not siebSvcs Is Nothing Then
Set siebSvcs = Nothing
Else
errCode = siebApp.GetLastErrCode
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText "Could not Get Siebel Service." & errCode & "::" &
errText
End If
Set siebApp = Nothing
End If
End Sub
Accessing the Mobile Web Client Automation Server
This topic describes how to access the Mobile Web Client Automation Server. For more information, see Mobile Web Client Automation Server.
To access the Mobile Web Client Automation Server
Install the Siebel Mobile Web Client.
Siebel CRM installs the Mobile Web Client Automation Server by default when you install the Siebel Mobile Web Client.
Start Microsoft Visual Basic.
Choose Standard EXE.
Choose the Project menu, and then the References menu item.
In the list box, choose Mobile Web Client Automation Server.
Add the required code.
For more information, see Example of Accessing the Mobile Web Client Automation Server.
Example of Accessing the Mobile Web Client Automation Server
The following example includes the code you use in Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 to access the Mobile Web Client Automation Server:
Private Sub Command1_Click()
'Siebel Application Object
Dim siebApp As SiebelWebApplication
Dim siebBusObj As SiebelBusObject
Dim siebBusComp As SiebelBusComp
Dim siebSvcs As SiebelService
Dim siebPropSet As SiebelPropertySet
Dim bool As Boolean
Dim errCode As Integer
Dim errText As String
Dim connStr As String
Dim lng As String
'Create The Siebel WebApplication Object
Set siebWebApp = CreateObject("TWSiebel.SiebelWebApplication.1")
If Not siebWebApp Is Nothing Then
'Create A Business Object
Set siebBusObj = siebWebApp.GetBusObject("Contact")
If Not siebBusObj Is Nothing Then
'Create a Business Component
Set siebBusComp = siebBusObj.GetBusComp("Contact")
Else
errCode = siebWebApp.GetLastErrCode
errText = siebWebApp.GetLastErrText
siebWebApp.RaiseErrorText "Business Object Creation failed." & errCode & "::" &
errText;
End If
'Create A New Property Set
Set siebPropSet = siebWebApp.NewPropertySet
If Not siebPropSet Is Nothing Then
Set siebPropSet = Nothing
Else
errCode = siebWebApp.GetLastErrCode
errText = siebWebApp.GetLastErrText
siebWebApp.RaiseErrorText "Property Set Creation failed." & errCode & "::" &
errText;
End If
'Get A Siebel Service
Set siebSvcs = siebWebApp.GetService("Workflow Process Manager")
If Not siebSvcs Is Nothing Then
Set siebSvcs = Nothing
Else
errCode = siebWebApp.GetLastErrCode
errText = siebWebApp.GetLastErrText
siebWebApp.RaiseErrorText "Could not Get Siebel Service." & errCode & "::" &
errText;
End If
If Not siebBusComp Is Nothing Then
Set siebBusComp = Nothing
End If
If Not siebBusObj Is Nothing Then
Set siebBusObj = Nothing
End If
Set siebWebApp = Nothing
End If
End Sub
Accessing the Siebel COM Interface
This topic describes how to access the Siebel COM Interface.
To access the Siebel COM Interface
in the Siebel application configuration (CFG) file, set the EnableOLEAutomation parameter to TRUE.
Use the object browser of your COM programming tool to determine the correct format for the object interface method.
For more information, see Example of an Object Browser.
Example of an Object Browser
The following image includes an example of the object browser in Microsoft Visual Basic 5.0, which is a COM programming tool. The format window at the bottom displays the method signature for the method chosen in the Object Browser window. This signature includes information about the method, such as the inputs, data types, and the information the method returns.
Accessing the COM Data Server
This topic describes how to access the COM Data Server. For more information, see COM Data Server.
To access the COM Data Server
Install the Siebel Mobile Web Client.
Siebel CRM installs the COM Data Server by default when you install the Siebel Mobile Web Client.
In the Siebel application configuration (CFG) file, set the DataSource parameter to the Siebel database where Siebel CRM must connect.
Start Microsoft Visual Basic.
Choose Standard EXE.
Choose the Project menu, and then the References menu item.
In the References dialog box, in the Available References window, click Siebel Data BusObject Interfaces.
Do not add a check mark to the Siebel Data BusObject Interfaces.
In the Siebel Data BusObject Interfaces section, note the name of the folder that contains the sobjsrv.tlb file.
In the Available References window, make sure the Siebel Data BusObject Interfaces item contains a check mark, and then click OK.
Add the required code.
For more information, see Example of Accessing the COM Data Server.
Example of Accessing the COM Data Server
The following example includes the code you use in Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 to access the COM Data Server. You must write and run this code outside of Siebel Tools. For example, in Microsoft Visual Basic:
Private Sub Command1_Click()
'Siebel Application Object
Dim siebApp As SiebelApplication
Dim siebBusObj As SiebelBusObject
Dim siebBusComp As SiebelBusComp
Dim siebSvcs As SiebelService
Dim siebPropSet As SiebelPropertySet
Dim bool As Boolean
Dim errCode As Integer
Dim errText As String
Dim connStr As String
Dim lng As String
Dim cfgLoc As String
ChDrive "C"
ChDir "C:\Server\siebsrvr\bin"
'Create The COM Data Server Object
Set siebApp = CreateObject("SiebelDataServer.ApplicationObject")
If Not siebApp Is Nothing Then
'''COM Data Server
cfgLoc = " C:\Siebel\8.1\Server\BIN\ENU\siebel.cfg,ServerDataSrc"
siebApp.LoadObjects cfgLoc, errCode
If errCode = 0 Then
'Log in to the Siebel Server
siebApp.Login "username", "password", errCode
If errCode = 0 Then
'Creat A Business Object
Set siebBusObj = siebApp.GetBusObject("Contact", errCode)
If errCode = 0 Then
'Create a Business Component
Set siebBusComp = siebBusObj.GetBusComp("Contact")
Else
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText("Business Object Creation failed: " & errCode & "::" &
errText);
End If
'Create A New Property Set
Set siebPropSet = siebApp.NewPropertySet(errCode)
If errCode = 0 Then
Set siebPropSet = Nothing
Else
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText("Property Set Creation failed: " & errCode & "::" &
errText);
End If
'Get A Siebel Service
Set siebSvcs = siebApp.GetService("Workflow Process Manager", errCode)
If Not siebSvcs Is Nothing Then
Set siebSvcs = Nothing
Else
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText("Could not Get Siebel Service: " & errCode & "::" &
errText);
End If
If Not siebBusComp Is Nothing Then
Set siebBusComp = Nothing
End If
If Not siebBusObj Is Nothing Then
Set siebBusObj = Nothing
End If
Else
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText("Login Failed: " & errCode & "::" & errText);
End If
Else
errText = siebApp.GetLastErrText
siebApp.RaiseErrorText("Load Objects Failed: " & errCode & "::" & errText);
End If
Set siebApp = Nothing
End If
End Sub
Accessing the COM Data Server with Microsoft Visual Studio
This topic describes how to create a simple COM client in Microsoft Visual C++and the Microsoft Foundation Class (MFC) library that accesses the Siebel Data Server.
To access the COM Data Server with Microsoft Visual Studio
In Microsoft Visual C++, choose the File menu, New, and then the Project menu item.
Choose the MFC AppWizard (exe) project type.
In the Project name field, enter SiebelCOM, and then click OK.
In the MFC AppWizard, choose the Dialog-based option and then click Next.
In the What Other Support Would You Like to Include frame, do the following:
Make sure the Automation option contains a check mark.
Make sure the ActiveX Controls does not contain a check mark.
Click Next.
Click Next.
Click Finish, and then click OK.
The Application Wizard creates the MFC code that you use for this project, including the headers and libraries that COM automation requires. For more information about the MFC libraries, see the documentation for Microsoft MSDN Visual Studio.
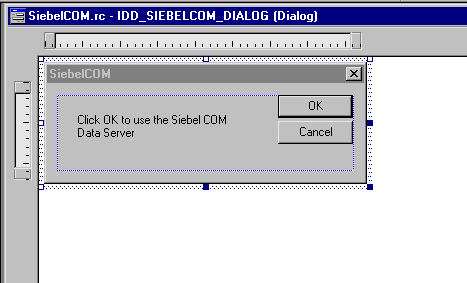
Modify the new dialog box.
Microsoft Visual C++ displays a new dialog box. To resize and modify the text in this dialog box, right-click the label in the dialog box and edit the properties. Modify the dialog box so that it resembles the following illustration.
Choose the View menu, ClassWizard, and then the Automation menu item.
Click Add Class, and then click From a Type Library.
Navigate to the
SIEBSRVR_ROOT\bin folder, and then choose sobjsrv.tlb.In the Confirm Classes dialog box, make sure all Siebel classes are chosen, click OK, and then click OK again to close the Class Wizard.
Add code to communicate with the Siebel COM Server.
In the workspace window, click the FileView tab.
Expand the Source Files folder and the Header Files folder.
Double-click the SiebelCOMDlg.h file.
In the code window, add the following code to the SiebelCOMDlg.h file. Add only the code that uses bold typeface:
#if _MSC_VER > 1000 #pragma once #endif // _MSC_VER > 1000 #include "sobjsrv.h" // Include Siebel wrapper classes class CSiebelCOMDlgAutoProxy; /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // CSiebelCOMDlg dialog class CSiebelCOMDlg : public CDialog{ DECLARE_DYNAMIC(CSiebelCOMDlg); friend class CSiebelCOMDlgAutoProxy; SiebelApplication sApp; // Declare Siebel object //Construction public: CSiebelCOMDlg(CWnd* pParent = NULL); //standard constructor virtual ~CSiebelCOMDlg();Choose Open from the File menu, and then choose the SiebelCOMDlg.cpp file.
Add the following code to the OnInitDialog procedure. Add only the code that uses bold typeface:
CDialog::OnInitDialog(); ... // TODO: Add extra initialization here // Start the Siebel Data Server if (!sApp.CreateDispatch(_T("SiebelDataServer.ApplicationObject))) { AfxMessageBox("Cannot start Siebel Data Server."); EndDialog(-1); // Fail } else { AfxMessageBox("Siebel Data Server initialized."); } return TRUE; // Return TRUE unless you make a control active ...In the same file, add the following code to the OnOK procedure.
To add this code correctly, do the following:
Make sure that the line that begins with sApp.LoadObjects references the location of the Siebel application configuration (CFG) file you intend to use.
In the line that begins with sApp.Login, make sure you use a valid logon name and password.
Add only the code that uses bold typeface.
void CSiebelCOMDlg::OnOK() { short sErr; // Load configuration file // Make sure that the following line references the correct file sApp.LoadObjects(C:\Siebel\8.1\Server\BIN\ENU\siebel.cfg", &sErr); if(sErr) { AfxMessageBox("LoadObject failed."); return; } else { AfxMessageBox("CFG file loaded."); } // Log in as SADMIN sApp.Login("SADMIN", "SADMIN", &sErr); if(sErr) { AfxMessageBox("Login failed."); return; } else { AfxMessageBox("Logged in to Siebel database."); } // Get Account business object LPDISPATCH lpdBo; lpdBo = sApp.GetBusObject("Account", &sErr); if(sErr) { AfxMessageBox("GetBusObject failed."); return; } else { AfxMessageBox("Account business object returned."); } SiebelBusObject Bo(lpdBo); // Get Account business component LPDISPATCH lpdBc; lpdBc = Bo.GetBusComp("Account", &sErr); if(sErr) { AfxMessageBox("GetBusComp failed."); return; } else { AfxMessageBox("Account business component returned."); } SiebelBusComp Bc(lpdBc); // Get the name of the first account if (sErr) return; Bc.ClearToQuery(&sErr); if (sErr) return; Bc.SetSearchSpe("Name", "*", &sErr); if (sErr) return; Bc.ExecuteQuery(ForwardOnly, &sErr); if (sErr) return; Bc.FirstRecord(&sErr); if (sErr) return; // Display the account name in a message box CString csAcctName; csAcctName = Bc.GetFieldValue("Name", &sErr); AfxMessageBox(csAcctName); Bc = null; lpdBc = null; Bo = null; lpdBo = null; return; if (CanExit()) CDialog::OnOK(); }
Test your work:
Start the Siebel client.
Make sure you use the same Siebel application configuration (CFG) file and login arguments that you specified in the code.
Navigate to the Accounts screen, and then the All Accounts view.
Verify that at least one account is visible in the Account list applet.
If at least one account is not visible, then create one.
Exit the Siebel client.
Open the Siebel application configuration (CFG) file you specified in the code and make sure the DataSource parameter indicates the correct Siebel database source.
In Microsoft Visual C++, choose the Build menu, and then the SiebelCOM.exe menu item.
If Microsoft Visual C++ displays an error or warning in the output window, then correct the error and repeat this step.
Choose the Build menu, and then the Execute SiebelCOM.exe menu item.
Wait for Microsoft Visual C++ to display the following message:
Siebel Data Server initialized.
Click OK.
The Siebel application displays the following series of messages:
CFG file loaded. Logged in to Siebel database. Account business object returned. Account business component returned.
The Siebel application displays the name of the first account in the All Accounts view.
Accessing COM Data Control
This topic describes how to access COM Data Control. A call to COM Data Control is in process. For more information, see How Siebel CRM Uses Memory and Resources with the Mobile Web Client Automation Server.
To access COM Data Control
Install COM Data Control.
Use the Siebel Enterprise Server Installer. Make sure the EAI Siebel Connectors option contains a check mark. For more information, see the Siebel Installation Guide for the operating system you are using.
Start Microsoft Visual Basic.
Choose Standard EXE.
Choose the Project menu, and then the References menu item.
In the References dialog box, in the Available References window, make sure the Siebel Business Object Interfaces Type Library item contains a check mark.
To open the Object Browser, click OK.
Determine the correct format for the object interface method.
You must use the CreateObject method and the Login method. You cannot use an object interface method that returns an active Siebel object because no Siebel objects are currently active. You must use your own Siebel objects.
Verify that you can view the Siebel objects.
Add the required code.
For more information, see Example of Accessing COM Data Control.
Example of Accessing COM Data Control
The following example includes the code you use in Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 to access COM Data Control:
Sub CreateDataControl()
Dim errCode As Integer
Set SiebelApplication = CreateObject("SiebelDataControl.SiebelDataControl.1")
SiebelApplication.Login "host=""siebel://hostname/EnterpriseServer/AppObjMgr""",
"CCONWAY", "CCONWAY"
errCode = SiebelApplication.GetLastErrCode()
If errCode <> 0 Then
ErrText = SiebelApplication.GetLastErrText
SiebelApplication.RaiseErrorText ErrText;
Exit Sub
End If
set OpptyB0 = SiebelApplication.GetBusObject("Opportunity",errCode)
set OpptyBC = OpptyBO.GetBusComp("Opportunity", errCode)
End Sub
To determine values to substitute for the variables in the login string, see Setting the Connect String.
Example of Using Siebel Server ASP Script to Access COM Data Control
To set off an ASP script in HTML code, you use the following format:
To indicate the beginning of the ASP script, you use the less than symbol and the percent symbol (<%).
To indicate the end of the ASP script, you use the percent symbol and the greater than symbol (%>).
The following example code starts COM Data Control from a Siebel Server ASP script:
<%
Dim SiebelApplication, BO, BC, ConnStr, logstat
Dim strLastName, strFirstName, errCode, errText
Set SiebelApplication = CreateObject("SiebelDataControl.SiebelDataControl.1")
' Test to see if object is created
If IsObject(SiebelApplication) = False then
Response.Write "Unable to initiate Siebel Session.
Else
connStr = "host=" & Chr(34) & "siebel.tcpip.none.none://hostname:2321/
EntServer/ObjMgr" & Chr(34) & " lang=" & Chr(34) & "lang" & Chr(34)
logstat = SiebelApplication.Login ConnStr, "SADMIN", "SADMIN"
response.write("Login Status: " & logstat)
Set BO = SiebelApplication.GetBusObject("Employee")
Set BC = BO.GetBusComp("Employee")
End If
%>
Accessing the Siebel Java Data Bean
A Java client that uses the Siebel Java Data Bean to connect to the Siebel Server requires JAR files. These files allow the Java language to access the objects and methods of the Siebel Object Interface. These files are specific to the version of the Siebel application. Do not use these JAR files with other versions. For more information, see About the Siebel Java Data Bean Object Interface.
To access the Siebel Java Data Bean
Add the following JAR files to the CLASSPATH:
Siebel.jar
SiebelJI_lang.jar
To install the Siebel Java Data Bean interface, do one of the following:
Use the Siebel Enterprise Server Installer. Make sure the EAI Siebel Connectors option contains a check mark. For more information, see the Siebel Installation Guide for the operating system you are using.
Install Siebel Tools. The Oracle Universal Installer installs the Siebel Java Data Bean interface by default when you install Siebel Tools.
Start a new SiebelDataBean Java object.
To call the Login method for the object you started in the preceding step, use the following code:
SiebelDataBean l_sdb = new SiebelDataBean(); l_sdb.login(<parameters>);
You must use the Login method. You cannot use an object interface method that returns an active Siebel object because no Siebel objects are currently active. You must use your own Siebel objects. For more information, see step 2 in Accessing the Siebel COM Interface.
Example of Accessing the Siebel Java Data Bean
The following example code accesses the Siebel Java Data Bean. You can use a Java IDE to compile and run this code:
import com.siebel.data.*;
import com.siebel.data.SiebelException;
public class DataBeanDemo
{
private SiebelDataBean m_dataBean = null;
private SiebelBusObject m_busObject = null;
private SiebelBusComp m_busComp = null;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DataBeanDemo demo = new DataBeanDemo();
}
public DataBeanDemo()
{
try
{
// instantiate the Siebel Java Data Bean
m_dataBean = new SiebelDataBean();
// log in to the Siebel Server
// SiebelServerhost = the name or IP address of your Siebel Server
// SCBPort = listening port number for the SCBroker component (default 2321)
m_dataBean.login("Siebel://SiebelServerhost:SCBPort/enterpriseServer/
AppObjMgr_enu", CCONWAY, CCONWAY, "enu");
// get the business object
m_busObject = m_dataBean.getBusObject("Opportunity");
// get the business component
m_busComp = m_busObject.getBusComp("Opportunity");
// log off
m_dataBean.logoff();
}
catch (SiebelException e)
{
System.out.println(e.getErrorMessage());
}
}
}
Using Single Sign-on (SSO) with Siebel Java Data Bean
If you use single sign-on (SSO) with Siebel Java Data Bean, then you must include the following items in the login:
Login ID of an employee as the username.
The value of the TrustToken parameter in the connect string. To determine the value for the TrustToken, examine the TrustToken parameter in the Siebel application configuration (CFG) file. For more information, see Setting the Connect String.
For example:
m_dataBean.login("Siebel://gatewayserver:2321/enterpriseServer/SCCObjMgr_enu",
SADMIN, HELLO,"enu");
where:
SADMINis an employee.The TrustToken parameter is HELLO in the LDAPSecAdpt section of the Siebel application configuration (CFG) file.
Customizing the Parameters a Third-Party Application Uses to Connect Through the Siebel Java Data Bean
You can customize the parameters that a third-party application uses when it connects to a Siebel application through the Siebel Java Data Bean.
To customize the parameters a third-party application uses to connect through the Siebel Java Data Bean
Open the siebel.properties file.
This file is located in your classpath, which is an operating system environment variable that a Java program references. The siebel.properties file can exist in any location. The CLASSPATH environment variable must include an entry for this file so that the Java Virtual Machine can find the file when it starts.
Set the properties.
For more information, see Properties of the Siebel Properties File.
Properties of the Siebel Properties File
The following table describes the properties of the siebel.properties file.
Table Properties of the Siebel Properties File
| Property Type | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
Siebel Connection Manager |
siebel.conmgr.txtimeout |
The transaction timeout in milliseconds. The default value is 600000, which is 10 minutes. The maximum value is 2,147,483,647, which is approximately 25 days. |
siebel.conmgr.poolsize |
The connection pool size. For more information, see Determining the Total Number of Open Connections. |
|
siebel.conmgr.sesstimeout |
The transaction timeout in seconds on the Siebel client. The default value is 2700, which is 45 minutes. The maximum value is 2,147,483,647, which is approximately 68 years. |
|
siebel.conmgr.retry |
The number of open session retries. The default value is 3. |
|
siebel.conmgr.jce |
Sets the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE):
For more information, see Encrypting Communication Between the Java Data Bean and the Siebel Server. |
|
Siebel created code for Java EE Connector Architecture and Java Data Bean |
siebel.connection.string |
The Siebel connection string. |
siebel.user.name |
The user name to log in to the Object Manager. |
|
siebel.user.password |
The password to log in to the Object Manager. |
|
siebel.user.language |
The preferred language for the user. |
|
siebel.user.encrypted |
Determines if Siebel CRM encrypts the username and password. |
|
siebel.jdb.classname |
The default Java Data Bean (JDB) classname. |
|
Java System Properties |
file.encoding |
The character encoding on the Siebel client. For example, cp1252, utf8, unicodeBig, or cp942. Java system properties are not Siebel properties. |
Example of the Siebel Properties File
The following code is an example of the siebel.properties file:
siebel.connection.string = siebel.tcpip.rsa.none://test.siebel.com/siebel/ sseobjmgr_enu/test siebel.user.name = User1 siebel.user.password = password siebel.user.language = enu siebel.user.encrypted = false siebel.conmgr.txtimeout = 3600 siebel.conmgr.poolsize = 5 siebel.conmgr.sesstimeout = 300000 siebel.conmgr.retry = 5 siebel.conmgr.jce = 1
Determining the Total Number of Open Connections
The connection pool maintains a set of connections to a specific server process. The default value for the siebel.conmgr.poolsize property is 2. The maximum value is 500.
The siebel.conmgr.poolsize property and the Min MT Server parameter on the object manager determine the total number of open connections. Each MT server process is a Windows process that includes a connection pool. The total number of open connections is the value in the siebel.conmgr.poolsize property multiplied by the value in the Min MT Server parameter.
For example, if the siebel.conmgr.poolsize is 2, and if the Min MT Server parameter is 3, then the total number of open connections is six.
Customizing Character Encoding for the Siebel Java Data Bean
The character encoding of the Siebel Server and the character encoding of the Siebel client must be the same. This allows the Siebel client and the Siebel Server to communicate correctly. If the Siebel client and the Siebel Server default character encoding cannot be the same, then you can modify the Siebel client character encoding.
To customize character encoding for the Siebel Java Data Bean
To set the file.encoding system property to the proper character encoding, do one of the following:
Set it for the entire Java Virtual Machine on the command line. For example:
java -Dfile.encoding=ascii java_application
Set it in the environment variable. For more information, see your particular Java Virtual Machine.
Set it for a particular Java component. Add the following line to the Java component:
System.setProperty("file.encoding", CodePageValue);where:
CodePageValueis a Siebel value that specifies character encoding for the Java Data Bean.
The following information lists character encoding mappings you can use for the Java Data Bean. The Siebel Value column contains the codes you can specify in the CodePageValue variable.
Table Character Encoding Mappings You Can Use for the Java Data Bean
| Java Value | Siebel Value |
|---|---|
ascii |
1 |
cp1252 |
1252 |
iso8859_1 |
1252 |
iso8859-1 |
1252 |
unicodebig |
1201 |
unicodelittle |
1200 |
utf8 |
65001 |
big5 |
950 |
cp942 |
932 |
cp942c |
932 |
cp943 |
932 |
cp943c |
932 |
cp949 |
949 |
cp949c |
949 |
cp950 |
950 |
cp1250 |
1250 |
cp1251 |
1251 |
cp1253 |
1253 |
cp1254 |
1254 |
cp1255 |
1255 |
cp1256 |
1256 |
cp1257 |
1257 |
cp1258 |
1258 |
gbk |
936 |
ms874 |
874 |
ms932 |
932 |
ms936 |
936 |
ms949 |
949 |
ms950 |
950 |
sjis |
932 |
tis620 |
874 |
Encrypting Communication Between the Java Data Bean and the Siebel Server
To encrypt communication between the Siebel Java Data Bean and the Siebel Server, you can use the Rivest, Shamir and Adleman (RSA) encryption libraries. For information about platforms you can use with encryption, see Siebel System Requirements and Supported Platforms on Oracle Technology Network.
To encrypt communication between the Siebel Java Data Bean and the Siebel Server
Enable encryption in the Object Manager server component that you use for the communication between the Java Data Bean and the Siebel Server.
For more information, see Siebel System Administration Guide.
Set the encryption parameter of the connect string in the Siebel Java Data Bean to rsa.
For example:
siebel.tcpip.rsa.none://gateway/enterprise/ObjMgr
where:
gatewayis the name of the gatewayenterpriseis the name of the enterpriseObjMgris the name of the Object Manager
Encrypting Communication on a Platform That the RSA Libraries Do Not Support
To use encryption on a platform that the RSA libraries do not support, Oracle uses the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) v1.2.1 specification. JCE provides a way to encrypt, create the encryption key, create the key agreement, and handle Message Authentication Code. With JCE, you can use some other qualified cryptography library as a service provider. For information about developer resources for Java technology, see the following Web site:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/java-sun-com-138872.html
To encrypt communication on a platform that the RSA libraries do not support
Download and install the JCE v1.2.1 software, policy files, and documentation.
For information about installing and configuring your Java Virtual Machine for use with JCE, see the following Web site:
http://java.sun.com/products/archive/jce/
Note that you can only use a static specification of JCE providers with the Siebel Java Data Bean.
Modify the java.security file to specify your provider of choice.
Make sure the classpath variable includes the necessary provider JAR files.
Set the siebel.conmgr.jce property in the siebel.properties file to 1.
Login Errors You Might Encounter When You Use the Siebel Java Data Bean
The Siebel Java Data Bean might return a login error that is similar to the following:
Siebel Exception thrown invoking login Method. Code--1. Message-Logon request 75 was abandoned after 2ms connection.
Any of the following items can cause this error:
An Object Manager process is down.
A hardware reset is required. For example, Object Manager hardware, router, switch, and so forth.
There is a problem with an operating system setting or the operating system network.
There is a network failure.
There is a network address translation timeout.
Using the Siebel Java Data Bean with Multiple Threads
Multiple threads of a single process must not access a common instance of the Siebel Java Data Bean. If a process with multiple threads must use the Siebel Java Data Bean, then each thread must create a separate instance of the Siebel Java Data Bean.
Do not reuse an instance of any other object that the Siebel Java Data Bean makes available across multiple threads of the same process. This requirement includes the following objects:
SiebelBusObject
SiebelBusComp
SiebelService
SiebelPropertySet
Customizing Object Interface Events and Extension Events
This topic describes object interface events and extension events. It includes the following topics:
For more information, see the following topics:
Overview of Object Interface Events and Extension Events
An object interface event is a type of object interface method that Siebel Engineering creates. A Siebel object includes a set of events that correspond to different points of execution during the lifetime of the object. An event acts as a placeholder in this Siebel object. It replies to a method that executes on the object.
Some object interface events allow you to associate custom code with a Siebel application. This code is available in Server Script or Browser Script. If the Siebel application starts the event, then Siebel CRM calls the custom code and the predefined Siebel code that is associated with the event.
You can use the following types of object interface events:
Preoperation event. Occurs before the predefined Siebel operation runs. The PreDeleteRecord event is an example of a preoperation event. This event occurs before the DeleteRecord event occurs. To modify the behavior of a predefined Siebel application, you can use a preoperation event. For example, to perform custom validation on a record that Siebel CRM is about to delete, you can use the PreDeleteRecord event. If the validation fails, then you can instruct Siebel CRM to cancel the DeleteRecord operation.
Postoperation event. Starts after Siebel CRM finishes executing the preoperation event. The DeleteRecord event is an example of a postoperation event. For example, Siebel CRM starts the DeleteRecord event after it finishes executing the PreDeleteRecord event. The postoperation event handler is rarely scripted, but you can use it for some postoperation events, such as posting a notice to a log if the event completes successfully.
Format of the Object Interface Event
The object interface event uses the following format:
ObjectReference_EventName (arguments) As RetValue
where:
ObjectReferenceis the variable name of the object where Siebel CRM calls the event.EventNameis the event that Siebel CRM calls.
Customizing the Outcome of an Object Interface Event
A preoperation event handler exists for every Siebel operation event handler. You typically place a script in the preoperation event. The PreInvokeMethod event results in the most important outcome. In a PreInvokeMethod event, you can call an object interface method that substitutes the predefined Siebel code.
To customize the outcome of an object interface event
Attach a script to the preoperation event handler.
Customizing How Siebel CRM Continues an Operation
This topic describes how to customize the way Siebel CRM continues an operation.
To customize how Siebel CRM continues an operation
To process data before the default event method runs, set the return value for this predefined event to ContinueOperation.
The return value for a preoperation event is ContinueOperation. It configures the calling Siebel object to continue processing the remaining operations that Siebel CRM associates with the event.
If you handle a custom method in a preevent, then that event must return CancelOperation or you must handle the custom method somewhere in the process. For important caution information, see Caution About Using the Cancel Operation Event Handler.
Caution About Using the Cancel Operation Event Handler
Including the CancelOperation return value configures the Siebel application to cancel the remaining operations that Siebel CRM associates with the event.
CancelOperation does not stop the code in a script that follows CancelOperation, but it does prevent Siebel CRM from running any predefined code that is associated with the method or event that is running. If you handle the method or event entirely through scripting, and if you must prevent the predefined code from executing, then the method or event must return CancelOperation.
For information about how Siebel CRM handles a predefined business service method, see How Siebel CRM Handles a Predefined Business Service Method.
Example of Using Siebel VB to Create a Validation
The following Siebel VB example creates a validation that queries a specific field to determine if the object interface event completed successfully or completed with a run-time error:
Function BusComp_PreSetFieldValue (FieldName As String,
FieldValue As String) As Integer
' code to check if a quote discount > 20%
' if it is, notify user and cancel the operation
Dim value as Integer
Dim msgtext as String
If FieldName = "Discount" then
value = Val(FieldValue)
If value > 20 then
msgtext = "Discounts greater than 20% must be approved"
TheApplication.RaiseErrorText msgtext ' cancels the run
Else
BusComp_PreSetFieldValue = ContinueOperation
End if
End If
End Function
Note the If statement in the following pseudocode:
If condition is true call custom code raise error text to cancel operation Else returnValue = ContinueOperation End If
In this If statement, Siebel CRM runs the custom code only if the condition is true:
If the condition is true, then Siebel CRM uses the custom code instead of the predefined code.
If the condition is not true, then the event handler returns ContinueOperation, and Siebel CRM uses the predefined code.
You can also use the following alternative If statement:
returnValue = Continue Operation
If condition is true
call custom code
End If
Note that with a PreInvokeMethod event, you use the method name to determine if the script conditionally runs. For example, consider the following code in Siebel eScript:
if (methodName == "PushOpportunity")
Example of Using Siebel eScript to Create a Validation
The following Siebel eScript example creates a validation that queries a specific field to determine if the object interface event completed successfully or completed with a run-time error:
function BusComp_PreSetFieldValue (FieldName, FieldValue)
{
var iReturn = ContinueOperation;
//code to check if a quote discount > 20%
//if it is, notify user and cancel the operation
var varvalue;
var msgtext;
if (FieldName == "Discount")
{
varvalue = ToNumber(FieldValue);
if (varvalue > 20)
{
msgtext = "Discounts greater than 20% must be approved";
TheApplication().RaiseErrorText(msgtext); // cancels the run
}
else
{
iReturn = ContinueOperation;
}
}
}
Using Tracing to Determine When an Event Occurs
Many different events can occur if a view becomes current or if a script calls an object, so a simple way to determine when various events occurs does not exist. It is recommended that you use tracing to determine when events occur.
To use tracing to determine when an event occurs
To determine the exact order of events, use the Application_Start event to enable tracing when the Siebel application starts.
In Siebel VB, use the following code:
TheApplication.TraceOn "filename, type, selection" TheApplication.Trace "Event_Name has fired."
In Siebel eScript, use the following code:
TheApplication().TraceOn("filename, type, selection"); TheApplication().TraceOn(" Event_Name has fired.");Add the following code in each event handler for the object:
TheApplication.Trace "Event_Name fired."Make sure you add this code to each of the following items:
Each relevant event, such as insert, delete, write, business component, and so forth
Each relevant preevent handler
Perform a few simple inserts, updates, and deletes.
Make a note of each message as Siebel CRM displays it.
Your notes will list the order that Siebel CRM uses to start events on the view or for the object.
Configuring Error Handling
This topic describes how to configure error handling.
COM Error Handling
The errCode parameter is the last parameter for every COM Data Server interface method. It is not available in the following object interfaces:
COM Data Control
Mobile Web Client Automation Server
Web Client Automation Server
Siebel Java Data Bean
Examples of Configuring Error Handling
This topic includes examples of configuring error handling.
Example of Configuring Error Handling for the COM Data Server
The following code is an example of error handling only for the COM Data Server:
GetBusObject (BusObjectName as string, errcode as integer) -> businessObject
Example of Configuring Error Handling for COM Data Control and Mobile Web Client Automation Server
The following code is an example of error handling for COM Data Control and Mobile Web Client Automation Server:
GetBusObject (BusObjectName as string) -> businessObject
Example of Configuring Error Handling for Siebel Java Data Bean
The SiebelException object handles errors in Siebel Java Data Bean. You can use the getErrorCode method and getErrorMessage method with the SiebelException object. The SiebelException object is defined in the com.siebel.data.SiebelException file. This file is a class file in one of the.jar files included in any java project that must communicate with Siebel CRM. For example:
...
import com.siebel.data.SiebelException;
import com.siebel.data.SiebelDataBean;
...
SiebelDataBean mySiebelBean=null;
try
{
mySiebelBean = new SiebelDataBean();
mySiebelBean.login("Siebel://SOMSERVER/somsiebel/AppObjMgr/", "CCONWAY",
"CCONWAY","enu");
}
catch (SiebelException e){
// Exception handling code
System.out.println (e.getErrorMessage ());
mySiebelBean = null; //avoid using mySiebelBean if login is unsuccessful
}
...
The ellipsis (...) in this code indicates code that was removed from the example in this book for brevity.
For more object interface methods on the SiebelException object, see the Siebel Java Data Bean JavaDoc that Oracle Universal Installer installs when you install Siebel Tools. Note that Oracle Universal Installer installs the JavaDoc only if you install the Siebel Java Integration option. It installs a zipped file that contains the JavaDoc in the Tools_ROOT\CLASSES folder.
Error Message Tracking
For error message tracking in ActiveX, you can use exceptions or object interface methods. This topic describes the methods that you can use.
Enable Exceptions Method
The EnableExceptions method allows Siebel CRM to use native COM error handling. If the method is about to fail due to error, then Siebel CRM creates a COM exception and does not return the method. The COM host receives the control instead. Siebel CRM might display the error message, which is the default behavior for Microsoft Internet Explorer or Siebel VB. You cannot use script to modify this behavior.
The following code is an example of using the EnableExceptions method:
EnableExceptions(enable as integer)
Get LastErrCode Method and GetLastErrText Method
After Siebel CRM runs an object interface method, you can do the following:
To determine if Siebel CRM returned an error from the previous operation, you can call the GetLastErrCode method.
To return the text of the error message, you can call the GetLastErrText method.
For example:
GetLastErrCode() ' returns errCode As Integer GetLastErrText() ' returns text As String