19Siebel Configurator Scripts
Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
This chapter explains how to use the Scripts view to enhance the behavior of Siebel Product Configurator. To use scripting events and methods you must be familiar with Siebel Visual Basic or Siebel eScript programming. This chapter includes the following topics:
About Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
A script is a Siebel Visual Basic or Siebel eScript program that runs when a predefined event to which it is assigned occurs during a configuration session. These events occur at specific points when opening or closing a session or processing a user request. You can also place scripts in a declarations area for use by other event-based scripts.
A script can refer to any product that has been added from the product table to a product with components. These are called component products. Scripts can also be used to set attribute values of component products and of the product with components, and of product classes. Scripts cannot be used to refer to relationships or links.
Scripts have full access to the Siebel API. You can use scripts to call Siebel business components and to provide information to back-end databases through Siebel business services. For a description of basic API methods, see Siebel Product Configurator API Reference.
In addition, several special Siebel Product Configurator methods are described in this chapter. These can be included in scripts and allow you to obtain information about the current solution. You can also use them to submit requests to the Siebel Product Configurator engine. For example, you can write a script and insert it into an event that is called each time an item quantity changes in the current solution. When the user selects or removes an item, this event is called and your script runs. The script can use Siebel Product Configurator methods to determine the amount of the item or of other items in the current solution and can submit a request to the Siebel Product Configurator engine to modify item amounts. The script could also perform special computations or update an external application based on information obtained from the Siebel Product Configurator methods.
The items and rules that comprise the product are called the declarative portion. The declarative portion cannot be modified by scripts. For example, you cannot add or delete rules from a customizable product using scripts.
Scripts are intended to add additional behaviors or features and can be used in several ways:
Arithmetic functions. You can use scripting to perform more complex mathematical operations that cannot feasibly be created using configuration rules. For example, if you are configuring a solution for a chemical manufacturing process, you can use calculations based on viscosity, average ambient temperature, and desired throughput to arrive at the correct configuration of pumps and other equipment.
External program calls. You can use scripts to make calls to external programs. For example, you can pass information about the current session to external programs.
Accessing Siebel objects. You can use all the standard features of Siebel VB and Siebel eScript, including reading and editing Siebel databases and calling Buscomps, BusObjects, and other Siebel objects.
About Siebel Product Configurator Script Processing
You can write event scripts or declarations scripts. Declarations scripts contain methods that can be called by event scripts and other declarations scripts.
A script instance is created at the beginning of the associated event and destroyed at the end of the script execution. Variables defined in the declarations section of the script are meaningful only during script execution and do not persist after the script exits. For example, if a script is called because an item has changed, its variable values do not persist. The next time an item changes and the script runs again, the values of the variables from the first script execution are not available.
The events for Siebel Product Configurator script processing are listed in the following paragraphs.
EV_CFG_INSTINITIALIZED
This event is generated once for each session after the root customizable product is instantiated and before any user requests are accepted.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_InstInitialize (RootProd) of each product present in the current solution.
The input parameter of the script is always the name of Root CP.
EV_CFG_INSTCLOSED
This event is generated once for each session after the user clicks Done to end a configuration session. After this event is generated, no further processing by the Siebel Product Configurator engine occurs.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_InstPostSynchronize(RootProd) of the root CP. The input parameter of the script is always the name of the root CP.
EV_CFG_ONCONFLICT
This event is generated when the Siebel Product Configurator engine encounters a conflict.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_OnConflict(Explanation, Resolution) of the root CP.
The input parameters of the script are:
Explanation. An input string, containing a system message explaining the conflict.
Resolution. An output string, UndoLastRequest or RemoveFailedRequests, instructing the application to undo the last changes or to make the necessary modifications to resolve the conflict and preserve the last changes.
EV_CFG_CHILDITEMSELECTED
This event is generated before the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_ChildItemSelected (SelectedItem) for the root CP.
The input parameter of the script is a PropSet, containing all the products whose quantities are about to change as elements:
<SelectedItem ObjName= "objname" OldQty= "oldqty" NewQty= "newqty">
This event is generated internally after the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution when detecting EV_CFG_ITEMCHANGED. It is issued together with EV_CFG_ATTRIBUTECHANGED.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_ChildItemChanged(ChangedItem) of the root CP.
The input Parameter of the script is a PropSet, containing all the products whose quantities have changed as elements:
<ChangedItem ObjName= "objname" OldQty= "oldqty" NewQty= "newqty">
This event is generated after the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_ItemChanged (ProdName, OldQty, NewQty) of each product whose quantities have changed.
The input parameters of the script are:
ProdName. The name of the product.
OldQty. The quantity prior to the request.
NewQty. The resulting quantity after the request.
EV_CFG_ATTRIBUTESELECTED
This event is generated before the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_AttributeSelected(ChangedItem) of each product whose attribute values are about to change.
The input parameter of the script is a PropSet containing the changed attributes as elements:
<strObjID> <strAttrName OldVal = "oldval" NewVal = "newval" > <strAttrName OldVal = "oldval" NewVal = "newval" > <strAttrName OldVal = "oldval" NewVal = "newval" > <strObjID>
This event is generated after the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution.
It triggers the execution of Cfg_AttributeChanged(ChangedItem) of each product whose attribute values have changed.
The input parameter of the script is a PropSet containing the changed attributes as elements:
<strObjID> <strAttrName OldVal = "oldval" NewVal = "newval" > <strAttrName OldVal = "oldval" NewVal = "newval" > <strAttrName OldVal = "oldval" NewVal = "newval" > <strObjID>
About Product Names in Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
Several scripting methods have product name as an argument. Product name in this context means the name of a component product you have added from the product table to a customizable product. You must specify product names in a way that makes them unique. You do this by specifying the product name, vendor name, vendor location, and attribute values.
Specify product names using the following syntax:
{ProductName; VendorName; VendorLocation}; AttributeName1=Value1;
AttributeName2=Value2; ...
Observe the following guidelines when specifying product names:
ProductName is required. All other arguments are optional.
The order of items in the name is important. ProductName must be followed by VendorName. VendorName must be followed by VendorLocation. You cannot specify ProductName followed by VendorLocation.
If ProductName is unique, you do not have to include VendorName or VendorLocation, and you do not need to enclose ProductName in braces.
Observe the following guideline when specifying the product path: do not use the sequence #1 inside the product path. This sequence is invalid. For example, the following product path does not work: $.[EXH SLCT-#1101 10X10 INLINE]#1.[CARPET, SPECIAL CUT (EX SEL10x10)]#[CARPET, SPECIAL CUT (EX SEL10x10)]
The following are examples of product names:
{ProductName; VendorName}; AttributeName=Value
ProductName; AttributeName=Value
ProductName
About Product Path in Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
The product path is the path from the root of a product with components to a component product within it. The path is a string that specifies the product with components root and all relationship names leading to the component product. All or part of the product path are arguments to several scripting methods.
The syntax for product paths is as follows:
$.[Root Product]#1.[Relationship]#[Component Product]
Observe the following guidelines for product paths:
The $ before .[Root Product] refers to a special configuration object called the basket. The basket contains all the objects in the product with components.
The #1 after [Root Product] refers to the first instance of the root product in the basket.
Use a dot (.) to specify a relationship.
Use a # to specify a component product within a relationship.
Use .xa[Attribute Name] to specify the attribute name
Use .xf[Value] to return the attribute value
Use .xf[Quantity] to return the product quantity
Use $Int.[<id>] to return the product's integration id. This is useful when multiple instances of the product exist. If it is not used and multiple instances of the product exist, the script selects at random which instance of the product it returns.
Enclose relationship names and component product names in square brackets ([ ]). Use product name syntax to specify the name of a component product.
All paths must end with a product name.
The following figure shows the structure of product with components CP1.
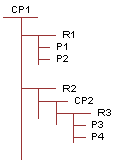
Product with components CP1 has two relationships R1 and R2. Relationship R1 contains two component products P1 and P2. Relationship R2 contains the product with components CP2. CP2 contains one relationship R3, which has two component products P3 and P4.
The product paths for this product with components are as follows:
For P1. $.[CP1]#1.[R1]#[P1]
For P2. $.[CP1]#1.[R1]#[P2]
For CP2. $.[CP1]#1.[R2]#[CP2]
For P3. $.[CP1]#1.[R2]#[CP2].[R3]#[P3]
For P4. $.[CP1]#1.[R2]#[CP2].[R3]#[P4]
Here are examples of using product paths in script methods:
To add 1 P1:
AddItem("$.[CP1]#1", "R1", "P1", "1")To add 1 P3:
AddItem("$.[CP1]#1.[R2]#[CP2]", "R3", "P3", "1")To reduce the quantity of P3 to 0:
RemoveItem("$.[CP1]#1.[R2]#[CP2].[R3]#[P3]")To set the attribute Color to Red for P1:
SetAttribute("$.[CP1]#1.[R1]#[P1]", "Color", "Red")
Siebel Product Configurator Script Events and Methods
Siebel Product Configurator constraint scripts use the following events and methods:
Cfg_InstInitialize Event
This event is called once for each session after the customizable product is instantiated and before any user requests are accepted. The customizable product selection pages do not display until all scripts associated with this event have finished.
Syntax
Cfg_InstInitialize (RootProduct as String)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
RootProduct |
String. The name of the customizable product. |
Returns
None.
Usage
Use this event to store global variables that will be reused, such as BusObjects and BusComps. This event is also useful for reading information from external sources such as forms or SmartScript.
The Cfg_InstInitialize event is always triggered for Root Customizable Products. However, it can also be triggered for child customizable products under the scenarios described here.
For example, you have the following product structure.
Root Customizable Product
|_Relationship
|_Child Customizable Product
When the default cardinality on the relationship is greater than 0 (that is, a child customizable product is initialized as part of the root customizable product) and the user customizes the root customizable product, the following events are triggered:
For the root customizable product: Cfg_InstInitialize - Root CP
For the child customizable product: Cfg_InstInitialize - Root CP
When the default cardinality on the Relationship is set to 0 (that is, a child customizable product is not initialized as part of the root customizable product) and the user customizes the root customizable product, the following event is triggered:
For the root customizable product: Cfg_InstInitialize - Root CP
If you try to add the child customizable product manually after the configuration session is loaded then Cfg_InstInitialize - Root CP is not triggered for the child customizable product.
Cfg_ChildItemChanged Event
After a user request is processed and the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution, this event is called for the product root. The event returns a property set containing all the products whose quantities have changed.
This event is also called if the user changes an item's quantity and the Request Conflict dialog box displays:
If the user selects OK in the dialog box, this submits a request that reverses the last request. Since this revises the item's baseline quantity, the event is called for the item.
If the user selects Cancel, previous conflicting requests are removed from the session. Since the current baseline values do not require revision, the event is not called for the item.
This event does not return items for which only attribute values have changed. For example, if the total number of 100 GB disk drives in a solution changes, this event returns a property set containing the 100 GB disk drive because the item quantity changed.
If the user enters or selects 10 feet as the desired value of the length attribute for power supply wiring, the returned property set does not contain power supply wiring since this is an attribute change.
In the selection pages for a customizable product, this event is called when the user selects an item. It is also called when the user increases or decreases the quantity of an item. This event is called before the Cfg_ItemChanged event.
Syntax
Cfg_ChildItemChanged (ChangedItem as Property Set)
The ChangedItem argument is passed as type PropertySet. This is a named XML element:
<ChangedItem ObjName= "objname" OldQty= "oldqty" NewQty= "newqty"/>
The properties of this XML element are defined in the following table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ObjName |
String. The item name. |
OldQty |
String. The item quantity prior to the request. |
NewQty |
String. The new baseline item quantity. |
Several Siebel API-related methods are needed to read data from the property set:
GetChildCount(). Returns the total number of changed items in the property set. Use this method to set the counter for a while-loop that reads the property set.
GetChild(n). Returns the nth record in the property set. Use this method within a while-loop to read records from the property set.
GetProperty("argument"). Returns the value of argument. Allowed arguments are ObjName, OldQty, and NewQty. Arguments must be in quotes. Use this method to read the property values from each record in the property set.
Returns
None
Usage
Use this event to determine what changes have been made to products in the solution and to submit additional requests as needed. For example, you could track the memory requirements for software the user selects and submit requests to add the correct amount of RAM to a computer configuration.
When you submit a request that changes item quantities, the submission causes the event to be called and the script runs again. Be sure to insert logic in the script that prevents an infinite loop of request submissions.
Example
The following Siebel Visual Basic example writes to a file the item name, the old quantity, and the new quantity of all the items whose quantities change in each solution.
Sub Cfg_ChildItemChanged (ChangedItem As PropertySet)
dim psItem as PropertySet
dim n as Integer
dim nCnt as Integer
dim sObjName as String
dim sOldQty as String
dim sNewQty as String
dim sMsg as String
dim hndl as Long
hndl = Freefile
REM use a relative path to open cfgtest.log
Open "..\cfgtest.log" for append as #hndl
nCnt = ChangedItem.GetChildCount()
For n = 0 to (nCnt -1)
set psItem = ChangedItem.GetChild(n)
With psItem
sObjName = .GetProperty("ObjName")
sOldQty = .GetProperty("OldQty")
sNewQty = .GetProperty("NewQty")
End With
sMsg = "ObjName = " & sObjName
sMsg = sMsg & "; OldQty = " & sOldQty
sMsg = sMsg & "; NewQty = " & sNewQty
Write #hndl, sMsg
set psItem = Nothing
Next
Close #hndl
End Sub
Cfg_AttributeChanged Event
After a user request is processed and the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution, this event is called for the product root. The event returns a property set containing all the products whose attributes have changed.
This event is also called if the user changes an item's attribute and the Request Conflict dialog box displays:
If the user selects OK in the dialog box, this submits a request that reverses the last request. Since this revises the item's baseline attribute value, the event is called for the item.
If the user selects Cancel, previous conflicting requests are removed from the session. Since the current baseline values do not require revision, the event is not called for the item.
In the selection pages for a customizable product, this event is called when the user enters or changes an attribute value.
Syntax
Cfg_AttributeChanged (ChangedAttribute as Property Set)
The ChangedAttribute argument is passed as type PropertySet. This is a named XML element:
<Id ObjName ="objname"> <AttName = "attribute name" OldVal= "old value" NewVal= "newvalue"> ... </Id>
The properties of this XML element are defined in the following table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ObjName |
String. The item name. |
AttName |
String. The attribute name. |
OldVal |
String. The attribute value prior to the request. |
NewVal |
String. The new baseline attribute value. |
Id |
String. The object ID of the item whose attribute value has changed. |
Several Siebel API-related methods are needed to read data from the property set:
GetChildCount(). Returns the total number of changed items in the property set. Use this method to set the counter for a while-loop that reads the property set.
GetChild(n). Returns the nth record in the property set. Use this method within a while-loop to read records from the property set.
GetProperty("argument"). Returns the value of argument. Allowed arguments are ObjName, OldQty, and NewQty. Arguments must be in quotes. Use this method to read the property values from each record in the property set.
GetType(). Retrieves the object ID of the item for which the attribute was changed.
Returns
None
Usage
Use this event to determine what changes have been made to product attributes in the solution and to submit additional requests as needed. For example, you could track the attributes selected for a product and submit requests based on them.
Example
The following example, writes to a file the item name, the old attribute value, and the new attribute value of all the items whose attribute values change in each solution.
{
var item;
var log = Clib.fopen("c:\\attchgd.log", "a");
var id = ChangedAttribute.GetType();
Clib.fputs(id, log);
var nCnt = ChangedAttribute.GetChildCount();
Clib.fputs(nCnt, log);
for ( var i = 0; i<nCnt; i++ )
{
item = ChangedAttribute.GetChild(i);
var attName = item.GetType();
var oldV = item.GetProperty("OldVal");
var newV = item.GetProperty("NewVal");
var s = "AttName = " + attName;
s = s + "; OldVal = ";
s = s + oldV;
s = s + "; NewVal = ";
s = s + newV;
Clib.fputs(s, log);
}
Clib.fclose(log);
}
Cfg_InstPostSynchronize Event
This event is called for the product root after the user clicks Done in the selection pages to end a configuration session. No further processing by the Siebel Product Configurator engine occurs in connection with this event. Using this event to adjust item quantities or attribute values is not recommended.
Syntax
Cfg_InstPostSynchronize (RootProd as String)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
RootProd |
String. The name of the customizable product. |
Returns
None
Usage
Use this event to add or modify line item information before it is stored. You can also use this event to modify pricing or do other activities associated with quote line items.
Cfg_ItemChanged Event
After a user request is processed and the Siebel Product Configurator engine computes a new solution, this event is called for each component customizable product whose quantity has changed. The script associated with this event must be associated with the component customizable product.
For example, CP1 is a customizable product. One of its component products is customizable product CP2. A script inserted in the Cfg_ItemChanged event in CP2 runs when the quantity of CP2 changes while CP1 is being configured.
To set up a Cfg_ItemChanged script for the component customizable product CP2 you must do the following:
Select CP2 in the product table and lock its work space.
Open the script editor and select the Cfg_ItemChanged event.
Specify CP1 as the root product for the script.
Write the script, check its syntax, and save the script.
Release a new version of CP2.
This event provides a simple way to write scripts for a customizable product that run only when that product is a component of another customizable product. This event is called after the Cfg_ChildItemChanged event.
Upgrade users: Use the Cfg_ChildItemChanged event to obtain functionality similar to the Cfg_ItemChanged event in release 6.x.
In the selection pages for a customizable product, this event is called when the user selects the component customizable product. It is also called when the user increases or decreases the quantity of that product.
Syntax
Cfg_ItemChanged (ProdName, OldQty, NewQty)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ProdName |
String. The name of the component customizable product. Use product name syntax |
OldQty |
Integer. The component customizable quantity prior to the request. |
NewQty |
Integer. The new baseline quantity for the component customizable product. |
Items
Use this event only to write scripts in customizable products that will be components of other customizable products.
Returns
Returns the component customizable product name, the quantity of it in the solution prior to the user request, and the quantity after the user request. This event does not return changes in the quantity of the products comprising a component customizable product.
Cfg_OnConflict Event
This event is called for the product root when the Siebel Product Configurator engine encounters a conflict while computing a solution. A conflict is when a user action violates a constraint. The constraint can be in the declarative portion of the product or can be a user pick.
When this event is called, if no script is defined, the application's normal conflict resolution messages display. Typically, the user must add or remove items to resolve the conflict. Users can retain the last user-pick and undo a previous user-pick, or they can undo the last user pick.
If a script is defined, you can resolve the conflict in the script. The application does not prompt the user with a conflict message. Submitting a request in a script on this event is not recommended.
Syntax
Cfg_OnConflict (Explanation, Resolution)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
Explanation |
String. Passes in the application message explaining the conflict |
Resolution |
String. Accepts as output one of the following values:
If neither of the previous arguments is passed as output, the application presents the user with the normal conflict messages. |
Returns
Returns the application error message and accepts one of two values as output. The outputs are forwarded to the Siebel Product Configurator engine and are used to resolve the conflict.
Usage
Use this event to manage conflict resolution in the background. For example, you can could create If-then statements that pass one of the outputs depending on a configuration condition in the model. If the conditions for handling the output do not exist, then passing no value causes the normal conflict resolution message.
OnAttributeSelected Event
This event is triggered when an attribute has been selected and the model update is about to occur.
Syntax
Cfg_AttributeSelected (SelectedAttribute)
Returns
None
OnChildItemSelected Event
This event is triggered before the Item is added to the Instance.
Syntax
Cfg_ChildItemSelected (SelectedItem)
Returns
None
GetInstanceId Method
This method returns the row ID of the product root in the source object, such as the quote or order line item. The row ID of the product root will be different for each quote or order.
Syntax
GetInstanceId() as String
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
None |
Items
Not applicable.
Returns
Returns the row ID of the customizable product root.
GetCPInstance Method
This method returns the entire structure of a customizable product as a property set.
Syntax
GetCPInstance(ps)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ps |
Can be created with TheApplication().NewPropertySet(); |
Items
Not applicable.
Returns
Returns the structure of the customizable product as a property set. Depending on the structure of the customizable product, the property set can be complex. To learn how to access the property set, use the following JavaScript code to dump the property set to a file. You can then study the property set structure to determine how to access it using a script.
/*
Use the PropertySetToFile(PropSet, fileName, title) API in your script.
Note that fileName must be double slashed, as demonstrated in the example below:
PropertySetToFile(InputsPS, "..\\temp\\testPSexport.txt", Inputs into " +
MethodName);
This will write the property set to a text file in the Siebel temp directory.
*/
function PropertySetToFile (PropSet, fileName, title)
{
var file = Clib.fopen(fileName, "at");
LogData(("\n---------------------------------------------------"), file);
LogData(("Start Process " + Clib.asctime(Clib.gmtime(Clib.time()))), file);
LogData(title, file);
LogData("PROVIDED PROPERTY SET", file);
WritePropertySet(PropSet, file, 0);
Clib.fclose(file);
return (CancelOperation);
}
function WritePropertySet(PropSet, file, Level)
{
if ((Level == "") || (typeof(Level) == "undefined")){
Level = 0;
}
var indent = "";
for (var x = 0; x < Level; x++){
indent += "\t";
}
var psType = PropSet.GetType();
var psValue = PropSet.GetValue();
LogData((indent + "Type: " + psType + " Value: " + psValue), file);
var propName = PropSet.GetFirstProperty();
while (propName != ""){
var propValue = PropSet.GetProperty(propName);
LogData((indent + propName + " = " + propValue), file);
propName = PropSet.GetNextProperty();
}
var children = PropSet.GetChildCount();
for (var x = 0; x < children; x++){
LogData(( indent + "CHILD PROPERTY SET " + x), file);
WritePropertySet(PropSet.GetChild(x), file, (Level + 1));
}
}
function LogData(DataString, file)
{
try {
Clib.fputs((DataString + "\n"), file);
Clib.fflush(file);
}
catch (e){
// no action
}
}
GetObjQuantity Method
This method returns the quantity of the specified component product in the current solution.
Syntax
GetObjQuantity (ProdName) as Integer
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ProdName |
String. The name of the component product. Use product name syntax to identity the component product. |
Items
Can be used only for component products within the customizable product.
Returns
Quantity of the component product in the current solution as an integer. If multiple instances of the component exist, the quantity of all instances are added together and the sum is returned. For example if there are two instances of an item one with quantity five and the other with quantity three, the return is eight.
Example
This script fragment obtains the quantity of 10 GB Drive (vendor = Sony) in the current solution and assigns it to the variable iItemQty.
Dim iItemQty as Integer
iItemQty = GetObjQuantity("{10 GB Drive; Sony}")
AddItem Method
This method creates a new instance of an item and adds the specified quantity to the solution. For example, Item A exists in the solution and has quantity three. You use AddItem to add two more Item A to the solution. The new solution will contain two instances of Item A, one with quantity three, and one with quantity two.
Syntax
AddItem (ParentObjPath, RelName, ProdName, Quantity) as Integer
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ParentObjPath |
String. The product path to, but not including, the relationship in which the component product resides. Use product path syntax to specify the path. If the component product is located at the product root, then specify the product root as the ParentObjPath. |
RelName |
String. The name of the relationship containing the component product you want to add. If the component product is located at the product root, then specify the customizable product name as the RelName. |
ProdName |
String. The name of the product you want to add. Use product name syntax to specify the product name. |
Quantity |
String. The amount of the product you want to add. |
Items
Can be used only for component products within the customizable product.
Returns
Returns the integration id of the item added if the add was successful. Returns 0 if the add fails.
Example
For an example of using AddItem, see About Product Path in Siebel Product Configurator Scripts.
RemoveItem Method
This method reduces the quantity of the specified item to 0 in the current solution. If multiple instances of an item have the same path, the Siebel Product Configurator engine randomly picks one of the instances and removes it.
Syntax
RemoveItem (ObjPath) as Integer
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ObjPath |
String. The full path of the component product you want to remove. Use product path syntax to specify the path. |
Items
Can be used only for component products within the customizable product.
Returns
Returns 1 if the item removal was successful. Returns 0 if the removal fails.
Example
For an example of using RemoveItem, see About Product Path in Siebel Product Configurator Scripts.
SetAttribute Method
This method sets the value of an attribute for an item in the customizable product. This method can also be used to set attribute values for attributes of the customizable product.
If multiple instances of an item have the same path, the Siebel Product Configurator engine randomly picks one instance and changes its attribute values. Users can reference a particular instance of a product by using $Int.[<id>] to specify the integration id in the product path.
Syntax
SetAttribute (ObjPath, AttName, AttVal) as Integer
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ObjPath |
String. The full path of the component product. For attributes of the customizable product, specify the product root. Use product path syntax to specify the path. |
AttName |
String. The name of an attribute of the component product or customizable product. |
AttValue |
String. The value to which you want to set the attribute. |
LICflag |
Optional input. String. This property is applicable for LOV Domains. It specifies whether the value passed to the method is the LOV display value or the LOV language independent code (LIC). Set it to 'Y' if you are supplying the LIC value. |
For LOV domains, the AttValue must be one of the values in the list of values. Validation expressions defined for LOV domains are ignored.
For range of value domains, the AttValue must be within the domain defined by the validation expression.
Items
Can be used only for component products within the customizable product.
Returns
Returns 1 if setting the attribute was successful. Returns 0 if setting the attribute failed.
Example
For an example of using SetAttribute, see About Product Path in Siebel Product Configurator Scripts.
GetAttribute Method
The GetAttribute method gets the value of an attribute for an item in the customizable product. This method can also be used to get attribute values for attributes of the customizable product.
If multiple instances of an item have the same path, the Siebel Product Configurator engine randomly picks one instance. Users can reference a particular instance of a product by using $Int.[<id>] to specify the integration id in the product path.
Syntax
Get Attribute (ObjPath, AttName) as String
Input Arguments
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ObjPath |
The full path of the component product. For attributes of the customizable product, specify the path of the root product. Use product path syntax to specify the path. |
AttName |
The name of an attribute of the component product or customizable product. |
Items |
The name of component products. Can be used only for component products within the customizable product. |
Output
This API returns a string. If it is successful, the string contains the Language Independent Code (LIC) value of the attribute. If it is not successful, the string is empty.
Examples
Ptype = GetAttribute("$.[Life Insurance]#1", "PlanType")
AttVal = GetAttribute("$.[RootProd1]#1.[Rel1]#[ChildProd1]", "attr1");
AttVal = GetAttribute ("$Int.[12-4JEFK]", "Color");
BatchRequest Method
This method is used to stack multiple configuration requests into a single request, improves performance because it is not necessary to initialize the constraint engine for each request.
For example, when a user exits Siebel Product Configurator, you want to automatically add items A, B, remove item C and set attribute values for newly added items A and B. Without the BatchRequest method, the constraint engine is called for each configuration request such as AddItem, RemoveItem and SetAttribute. With the BatchRequest method, you can write a script that makes a single call to the constraint engine to compute the solution, which improves performance.
Syntax
BatchRequest (InputArgs, OutputArgs)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
InputArgs |
A collection of property sets. Each child property set contains a Siebel Product Configurator script request along with its required set of parameters. Optionally, each child property set can contain alias properties that may be used as a replacement for product paths. There are two type of alias properties:
Optionally, any child request can use the ItemAlias property instead of the product path. The user can use any name as the value of the alias. |
OutputArgs |
A property set that contains the Integration IDs returned by the AddItem script request and any errors that might have occurred during this BatchRequest execution. |
Example
This example shows one way that you can use batch request. It assumes the product is set up as follows:
T-Shirt|_Team T-Shirt (relationship)|_Short sleeve shirt (component product) with Attribute: Color (dropdown values: Please Specify, Red, Blue)| |_Accessories (relationship)| |_Matching Hat (component product)| |_Matching Bag (component product) with Attribute: Type (dropdown value: Please Specify, Duffel, Tote)|_Long Sleeve Shirt (component product)
The following script adds 10 red short sleeve shirts along with 10 matching hats and 15 blue short sleeve shirts along with one matching duffel bag
function Cfg_InstInitialize (RootProduct)
{
var parentPropset = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var outPropset = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset1 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset2 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset3 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset4 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset5 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset6 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var childPropset7 = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
//Add 10 short sleeve shirts
childPropset1.SetProperty("RequestType", "AddItem");
childPropset1.SetProperty("OutItemAlias","RedShirtAlias");
childPropset1.SetProperty("Parent Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1");
childPropset1.SetProperty("PortName","Team T-Shirt");
childPropset1.SetProperty("Name","Short sleeve shirt");
childPropset1.SetProperty("Quantity","10");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset1);
//set Red color
childPropset2.SetProperty("RequestType","SetAttribute");
childPropset2.SetProperty("ItemAlias","RedShirtAlias"); // picks particular instance
//childPropset2.SetProperty("Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1.[Team T-Shirt]#[Short sleeve
shirt]"); // picks random instance
childPropset2.SetProperty("Name","Color");
childPropset2.SetProperty("Value","Red");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset2);
//Add 10 Matching Hats
childPropset3.SetProperty("RequestType", "AddItem");
childPropset3.SetProperty("ItemAlias","RedShirtAlias"); // picks particular instance
//childPropset3.SetProperty("Parent Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1.[Team T-Shirt]#[Short sleeve
shirt] "); // picks random instance
childPropset3.SetProperty("PortName","Accessories");
childPropset3.SetProperty("Name","Matching Hat");
childPropset3.SetProperty("Quantity","10");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset3);
//Add 15 short sleeve shirts
childPropset4.SetProperty("RequestType", "AddItem");
childPropset4.SetProperty("OutItemAlias","BlueShirtAlias");
childPropset4.SetProperty("Parent Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1");
childPropset4.SetProperty("PortName","Team T-Shirt");
childPropset4.SetProperty("Name","Short sleeve shirt");
childPropset4.SetProperty("Quantity","15");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset4);
//set Blue color
childPropset5.SetProperty("RequestType","SetAttribute");
childPropset5.SetProperty("ItemAlias","BlueShirtAlias"); // picks particular instance
//childPropset5.SetProperty("Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1.[Team T-Shirt]#[Short sleeve
shirt]"); // picks random instance
childPropset5.SetProperty("Name","Color");
childPropset5.SetProperty("Value","Blue");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset5);
//Add 1 Matching Bag
childPropset6.SetProperty("RequestType", "AddItem");
childPropset6.SetProperty("ItemAlias","BlueShirtAlias"); // picks particular instance
//childPropset6.SetProperty("Parent Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1.[Team T-Shirt]#[Short sleeve
shirt] "); // picks random instance
childPropset6.SetProperty("OutItemAlias","BlueDuffelBag");
childPropset6.SetProperty("PortName","Accessories");
childPropset6.SetProperty("Name","Matching Bag");
childPropset6.SetProperty("Quantity","1");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset6);
//Set Bag Type = Duffel
childPropset7.SetProperty("RequestType","SetAttribute");
childPropset7.SetProperty("ItemAlias","BlueDuffelBag"); // picks particular instance
//childPropset7.SetProperty("Path","$.[T-Shirt]#1.[Team T-Shirt]#[Short sleeve
shirt].[Accessories]#[Matching Bag]") // picks random instance
childPropset7.SetProperty("Name","Type");
childPropset7.SetProperty("Value","Duffel");
parentPropset.AddChild(childPropset7);
BatchRequest(parentPropset, outPropset) ;
}
Creating Siebel Product Configurator Event Scripts
Event scripts run when defined events are called during a configuration session. You create an event script by selecting an event method and writing the script within it.
Event scripts can call methods and objects defined in the Siebel API. They can also call methods assigned to the declarations area.
To create an event script
Navigate to the Administration - Product screen.
Select and lock the desired product or product class.
Navigate to the Scripts view for the Work Space version.
In the Scripts list, add a new record and complete the necessary fields, described in the following table.
Field Comments Name
Select the desired event.
If this is not the first script for this event, overwrite the event name with a script name. All scripts for a customizable product must have a unique script name.
Program Language
If this is the first script you are creating for this product, select Visual Basic or eScript.
If this is not the first script, and select the same programming language used for previous scripts.
Root Product
Select the current customizable product.
Enter the script in the area in the Script Definition form.
The Script Definition form is located after the Scripts list.
When you have finished entering the script, click Check Syntax.
If there are errors, they will display at the start of the Customizable Product Scripts form. Correct any errors before saving the script.
In the Script Definition form, click Save.
Creating Siebel Product Configurator Declarations Scripts
Declaration scripts are methods that you want to make available to event scripts or other declaration scripts. Declaration scripts are stored in a common area accessible by event scripts. Declaration scripts can call methods and objects defined in the Siebel API.
Use declaration scripts to write methods that are common to more than one event script. Instead of repeating the method in each event script, you can write one declaration script and call it from within the event scripts that use it.
To create a declarations script
Navigate to the Administration - Product screen.
Select and lock the desired product or product class.
Navigate to the Scripts view for the Work Space version.
In the Scripts list, add a new record and complete the necessary fields, described in the following table.
Field Comments Name
Choose "(declarations)."
If this is not the first declarations script, overwrite "(declarations)" with a script name. All scripts for a customizable product must have a unique script name.
Program Language
If this is the first script you are creating for this product, select Visual Basic or eScript.
If this is not the first script, and select the same programming language used for previous scripts.
Root Product
Select the current customizable product.
Enter the script in the area in the Script Definition form.
The Script Definition form is located after the Scripts list.
When you have finished entering the script, click Check Syntax.
If there are errors, they will display at the start of the Customizable Product Scripts form. Correct any errors before saving the script.
In the Script Definition form, click Save.
From the Scripts view menu, select Validate.
This starts a configuration session. Verify that the new script works correctly.
Reviewing the Siebel Product Configurator Script Log File
If a method within a script fails or the script contains syntax errors, you can obtain valuable diagnostic information by reviewing the script log.
To review the script log file
Navigate to
\log\cfgscript.log. It is located in the Siebel installation directory.Open the file with a text editor.
Locate the entries for the date and time the script ran.
About Managing Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
You can manage scripts in the following ways:
Editing Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
You can edit scripts by selecting the script in the Scripts view. If you edit declaration scripts, verify that the changes do not adversely affect event scripts.
To edit a script
Navigate to the Administration - Product screen.
Select and lock the desired product or product class.
Navigate to the Scripts view for the Work Space version.
Highlight the script you want to edit.
The script displays in Script Definition form, located after the list of scripts.
In the Script Definition form, edit the script.
When you have finished editing the script, click Check Syntax.
If there are errors, they will display at the start of the Customizable Product Scripts form. Correct any errors before saving the script.
In the Script Definition form, click Save.
Deleting Siebel Product Configurator Scripts
After deleting a script, test the customizable product in validation mode to verify that the product works correctly.
To delete a script
Navigate to the Administration - Product screen.
Select and lock the desired product or product class.
Navigate to the Scripts view for the Work Space version.
In the Scripts list, select the script you want to delete.
In the Scripts list, click Delete.
Open the Scripts view list menu and click Validate.
This starts a configuration session. Verify that the customizable product functions correctly.