4Understanding Financial Services Integration Paradigms
Understanding Financial Services Integration Paradigms
This chapter includes information about how to plan your integration.
Overview
You need to integrate your Siebel applications with other external systems for the following reasons:
You have invested in several legacy applications, back office systems, and eCommerce applications and would like to have one integrated view of all your systems.
You want to use Siebel applications as your primary application and access all other applications using Siebel applications as the front-end system.
You want to reflect changes made to your external systems in your Siebel applications and update your Siebel database with information from other applications in your enterprise.
Before you begin an integration project, identify your integration needs. You may have data in a variety of applications such as back-office solutions for Policy Administration, Claims, or accounting; e-commerce applications such as Web store fronts; and help desk applications.
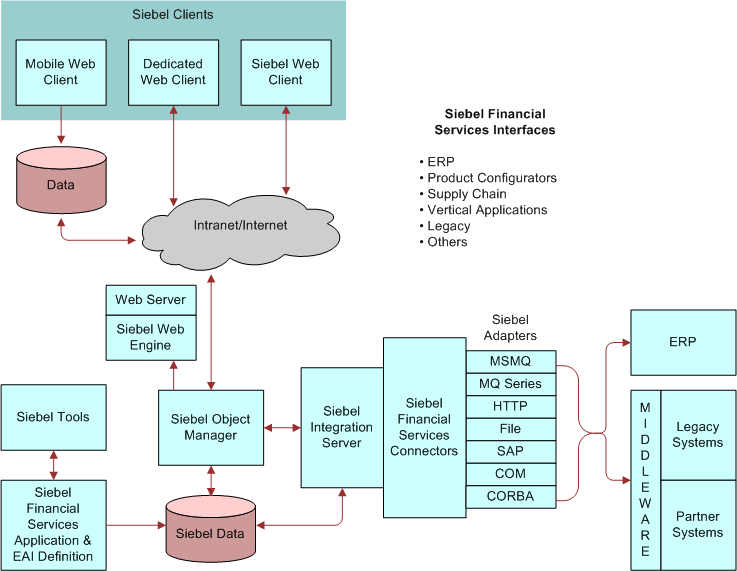
There are several ways you can approach your integration, depending on your needs. You can connect Siebel applications and your back-office or e-commerce system using prebuilt Siebel Financial Services EAI connectors. You can connect Siebel applications and an external application, using Siebel Financial Services EAI custom-built connectors. You can integrate Siebel Financial Services applications with middleware solutions. And you can integrate Siebel Financial Services applications with external applications, using a third-party EAI product.
Siebel Financial Services EAI provides solutions for each element of the EAI planning process.
Programmatic interfaces like COM and Siebel Java Beans provide a tightly-coupled integration for real time data exchange.
Adapters like MQSeries and the HTTP adapters provide a loosely-coupled mechanism for real-time integration. This means that one system needs to be aware of implementation details of the other system's integration mechanisms. A message or a document is exchanged between these systems.
For high volume batch integrations, Siebel EAI provides you with Batch Integration Manager (BIM) and Siebel Enterprise Integration Manager (EIM). BIM and EIM can replicate data between Siebel and other systems at the database layer, and both provide high performance for importing or exporting of large volume of data.
Connectors, such as the Siebel Connector for IFX XML and other prebuilt connectors, provide loosely coupled integration using XML technologies. These connectors focus on existing industry XML standards.
Siebel Integration Designer provides the infrastructure that allows you to define real-time interfaces to external systems in a variety of ways. You can use the Siebel BIM to send and receive requests for data, requests for action, and data synchronization. You can define integration workflow processes by sequencing integration requests without programming using Siebel Workflow Designer.
Design Decisions
Performing the correct analysis and making the correct decision is important for any software project but this is especially true for integration. Integrating disparate systems is a complex process because most customized applications that are created in an enterprise, and some commercially available applications, do not have a published API (Application Programming Interface). This makes seamless integration difficult, if not impossible. To add to this complexity, there are multiple infrastructures used by companies to “glue" systems together.
You need to carefully analyze the integration effort to understand your business needs and integration requirements. Before deciding to integrate your applications, you should perform a cost benefit analysis, review how you use the applications, and analyze the applications’ data structure. Some of the factors to be considered as part of this process include:
Does the data need to be shared or synchronized?
Does the data need to be transformed before it can be shared or synchronized?
Is the requirement for data real-time or batch?
Note: You will need more resources to build and maintain real-time integration than would be required by batch integration.How is the data presented to the user?
How is the data requested?
Where does the data come from?
How is the data updated?
What are the service-level or performance requirements?
Is there an existing third-party product that can help?
Siebel Financial Service EAI offers different tool sets for different types of integration requirements. Siebel Financial Services EAI is a technology that allows for data sharing, data replication, and function passing across applications. Siebel Financial Services EAI includes the following technologies:
Business Integration Manager
Virtual Business Components
Enterprise Integration Manager
Business Services
Business Object Interfaces
ActiveX Plugins
There are several approaches to integrating the Siebel application with other applications based on the Business needs. Following are some of approaches which were considered:
Synchronize Siebel data with non-Siebel data. Synchronizing Siebel data with external applications can be achieved either through the Business Integration Manager, any of the Connectors, which Siebel ships as a part of the product, Enterprise Integration Manager (EIM), or any of the Object Interfaces.
Display non-Siebel data in Siebel applets. Displaying non-Siebel data within a Siebel application can be achieved through VBC or ActiveX Plugin.
Display Siebel data in another application. Displaying Siebel data within another application without the Siebel User Interface can be achieved by plugging Siebel data as an Active-X plugin, or through a Data Service of Object interface provided by Siebel applications.
Incorporate the Siebel User Interface (UI) into another application or incorporate non-Siebel UI within Siebel applications. Siebel provides an open interface which can be adapted using COM, Active X Controls, and Java Data Beans. You can use these technologies if an external application needs to have the look and feel of the Siebel application within its own user interface or if the Siebel application needs to incorporate the user interface of an external application.
Control the Siebel application from another application. You can use Object Interfaces such as COM Servers to have another application control Siebel applications.
Export Siebel data. To export data, you can use EIM or other Object Interfaces.
The following table lists the best Siebel solution for your integration problems.
Table Best Siebel Solutions for Integration Issues
| Integration Problem | Siebel Solution |
|---|---|
High Volume Batch Interface |
Enterprise Integration Manager |
Accessing Data stored Outside of Siebel |
Virtual Business Components (VBC) |
Transactional Replication of Data |
Business Integration Manager (BIM) Siebel Financial Services Connectors |
Interface to popular financial services back office applications using XML technologies |
Siebel Financial Services Enterprise Application Integration Connectors (IFX XML, ACORD XML Connectors. Siebel Industry XML Connector, Siebel Industry XML Connector Factory APIs) |
Interface to Popular Back-Office Applications (SAP, Oracle, PeopleSoft) |
Siebel Connectors (SAP, Oracle, PeopleSoft Connectors) |
External applications to control Siebel Application or Siebel application controlling external application |
Object Interface such COM Servers (Automation and Data), Active X controls (Application and Data), and Java Data Beans |
To choose the appropriate and economical solution for your integration issue, you need to perform a step-by-step evaluation process for the following:
Transactions. List the business transactions that are executed within your Siebel implementation. These transactions should contain the information that is required for applications to integrate and work together. For example, if a company has a policy management system as one of its legacy systems but policy information initially is captured in the Siebel application, the transaction would be to add policy details in the policy management legacy system.
Applications. List the other applications you need to query or write to in order to complete the transactions. For example, in the previous case 'Policy Management System' would be the other application to integrate with the Siebel application.
Integration Points. Identify the points within the transaction flow at which the integration needs to take place (integration points). For example, populate a data warehouse with a nightly download of data. Consolidate integration points to reduce cost of ownership or verify open stock before showing the customer a product choice on a Web page. Add the transaction into the legacy system in real time as soon as a policy is added. Also identify what form of integration is required, real-time or batch, synchronous or asynchronous, tightly or loosely coupled.
Identify solutions. Identify the best solution for your integration need. There may be more than one solution in solving an integration problem. Consider the solution that is most optimal for your problem. You can use the table on Best Siebel Solutions for Integration Issues to analyze the most optimal solution for each of your integration points. For example, connector, middleware, VBC, or EIM.
Other Considerations. Determine whether you need to transform, share, or replicate your data. If you do not need to have the data in both systems but need to share it in real-time, consider VBC. Data sharing solves many of the problems associated with data replication. However, you need to consider data ownership contention and network traffic. Real-time access always carries a premium related to slow response time and the fact that it is expensive to maintain and build. Data sharing is appropriate for integration points that involve volatile or highly specialized source data such as credit card authorization, tax calculation, and so on. Other instances in which data sharing might be appropriate would be when you need to occasionally access large amounts of used data such as a credit card payment history. For details, see Access Mechanisms.
The following image illustrates available Siebel Financial Services interfaces.
Usage Models
When looking at your requirements, you should understand how you intend to use Siebel Financial Services EAI’s integration capabilities. You need to determine how the integration will behave and under what circumstances. In other words, in what way are you planning to use this integration? This is referred to as the usage model.
There are two basic usage models, real time and batch, as shown in the Siebel Financial Services Interfaces image in Design Decisions. Batch mode has a single mode, and real time has two modes, either tightly-coupled or loosely-coupled. To help you determine the appropriate usage model, ask yourself the following questions.
How do I plan to integrate Siebel Financial Services applications with other applications?
Do I want to do it in real-time or in batch mode?
If I want to do it in real-time, do I want the solution to be tightly-coupled or loosely-coupled?
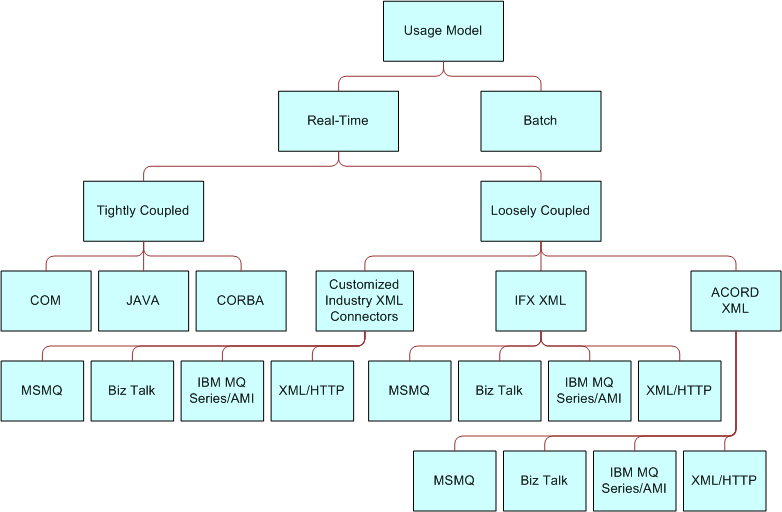
Real Time
With a real time model, you may choose to deploy Siebel Financial Services applications as a client or as a server. As a client, Siebel Financial Services applications access another program or initiate a transaction on an external system. Typical scenarios include:
Sending an insurance policy created from Siebel Financial Services applications to a 'Policy Management' system and receiving the policy status in return.
Accessing a mainframe banking application to retrieve customer bank deposits in real time and display it within the Siebel user interface.
Sending claims to independent claims agents over corporate firewalls without compromising security.
Accessing an external rating engine system to calculate a quote and then displaying the information in the Siebel system.
As a server, Siebel Financial Services applications are accessed by an external program to query, insert, update, or delete data without any initiation from the Siebel system. Typical scenarios include:
An external EJB Web application accessing a Siebel Financial Services application to retrieve contact information.
Call center software extracting customer service request information from a Siebel Financial Services application.
Batch
Batch processing typically is used for periodic uploads or downloads of large amounts of information into the Siebel database. A typical batch scenario includes:
Uploading a batch of product catalog and item information into a Siebel Financial Services application from an external system or downloading a batch of all opportunities from Siebel Financial Services applications to another database.
Downloading all the new contact and accounts for that day from the Siebel application to an external Customer Information File (CIF).
Access Mechanisms
When your business problem is accessing other applications from Siebel Financial Services applications or accessing Siebel Financial Services applications from other applications, you need to ask: Exactly what kind of data exchange do I require?
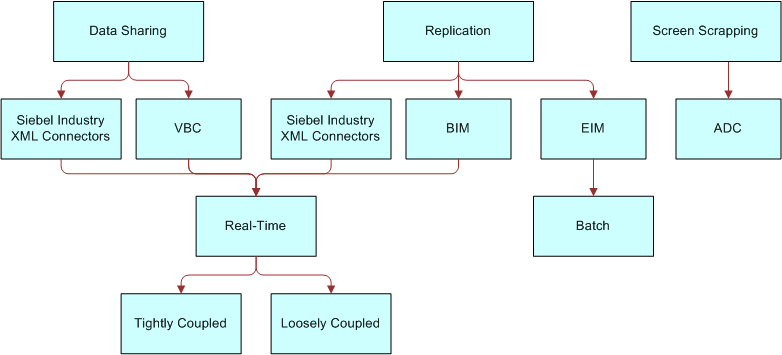
Data Sharing. You may just need to share data that exists outside of the Siebel system. For example you may have several legacy mainframe systems that you need to access with Siebel Financial Services to provide customers with comprehensive information on their insurance record. You might not want to replicate this information in the Siebel system, but may want to dynamically share this mainframe data as needed and display it within a Siebel Financial Services application. For data sharing, use VBC.
Replication. Replication of data is often useful. For example, you might want to integrate data in CIF (Customer Information File) with data in the Siebel system, keeping order status information in both systems. For mass replication of the order status information in Siebel Financial Services applications, use Siebel Business Integration Manager (BIM) and Siebel Enterprise Integration Manager (EIM).
Presentation Layer (UI) Integration. Integration at the presentation layer is useful in cases where you only need to look at the other application’s user interface (UI) and the data does not need to be retrieved. You would capture just the “screen" from the external system using ActiveX Data Controls (ADCs) and represent it natively within a Siebel Financial Services application. This is the least expensive form of integrating two applications, however, it is also the least flexible.
Screen Scrapping. Screen scrapping is another approach you may want to consider. Screen scrapping is never a good long term solution mainly due to performance considerations, cost of ownership, and lack of change management functionality within the application. It is a temporary solution available from some Siebel partners. Screen scrapping can be a very powerful tactical weapon for a project that requires shorter development time and when the project’s timeline needs to be separated from availability of legacy application or infrastructure resources.
These Siebel Financial Services solutions can be either real-time or batch. The following image shows the various access mechanism options and where they fit into the integration process.
Application Connectors
Application connectors allow for the deployment of a point-to-point connection between Siebel Financial Services applications and other applications. These applications include IBM Websphere Composer, CBTF (Core Point Bank Teller Framework), and WSBCC (Web Sphere Business Component Composer). Oracle provides solutions for prepackaged connectors either directly or through partners and third-party developers. The Siebel Financial Services Solutions image in Access Mechanisms shows the prebuilt connectors that integrate with Siebel Financial Services applications.