Search for a Record
The Search button at the top of the report page allows you to find a specific record within a Monitor and Trace report. It also allows you to specify criteria on which to perform the search.
After defining a search criteria in the Search Filter dialog box, clicking Search automatically populates the report page with the records that match the specified criteria specified. The search performs the filtering process of criteria dependent on the report page from which you are running the search.
Note:
A SIP Monitor and Trace global search can find items in the SIP headers, as well.The system saves the search criteria until you click Reset in the dialog box, or until you log out of the HTTP session.
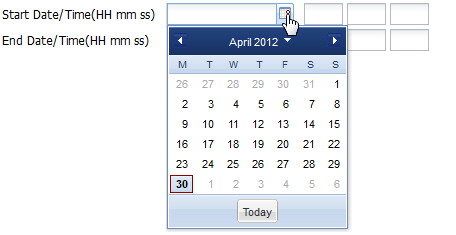
Perform a Search
You can specify a value for any or all of the fields in the Search box. The search process searches for records with all of the values you specify and displays only the records with these values. If you perform a “Global Search”, and specify values in other fields, the search process searches the other specified fields first and then filters on the “Global Search” field.
If you specify a “*” in a search string, the search is performed on that exact string. For example, if you search for “123*45”, the search shows results for all strings containing “123*45”.
You can use quotes (“ “) to specify a search. For example, you can enter Smith and the search finds all of the records that match Smith, such as: John Smithfield<sip:sipp@192.168.1.70:5070>;tag=12260SIPpTag001.
If you enter a space before or after a quotation mark, (for example, “Smith “), the search returns no data.
Specify Additional Identifiers
To specify additional identifiers:
- In the Session Id field, enter the ID of the call session you want to search. Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, 22-3412@172.16.34.1.
- In the In Call ID field, enter the ID of the incoming call (phone number and source IP address). Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, 25-3412@172.16.34.10.
- In the Out Call ID field, enter the ID of the outgoing call (phone number and IP address). Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, 14-3412@172.14.54.6.
-
In the State (with result code) field, enter the status of the call session with the result code for which you want to search. Valid values are (case-sensitive):
-
INITIAL-<result code>
-
EARLY-<result code>
-
ESTABLISHED-<result code>
-
TERMINATED-<result code>
-
FAILED-<result code>
Result codes can range from 1xx to 5xx. For example, terminated-200, or failed-400.
-
-
In the Notable Event field, select the notable event for which you want to search. Valid values are:
-
any-event - search displays any notable event that was stored in memory.
-
short-session - search displays only records that indicate a short-session duration has occurred.
-
local-rejection - search displays only records that indicate a local-rejection has occurred.
-
- To search on additional parameters, click on the Additional Search Options down arrow to expand the dialog box.
Specify Additional Search Options
To specify additional search options:
- In the “In Realm” field, enter the name of the realm for which the incoming call belongs. Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, access.
- In the “Out Realm” field, enter the name of the realm for which the outgoing call belongs. Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, backbone.
- In the “In SA” field, enter the name of the session agent (SA) on the incoming call session. Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, SA1.
- In the “Out SA” field, enter the name of the session agent (SA) on the outgoing call session. Valid values are alpha-numeric characters. For example, SA2.
- In the “In Source Addr” field, enter the source IP address of the SA that accepted the incoming call session. IP Address must be entered in dotted decimal format (0.0.0.0). For example, 172.45.6.7.
- In the “Out Dest Addr” field, enter the destination IP address of the SA that accepted the outgoing call session. IP Address must be entered in dotted decimal format (0.0.0.0). For example, 172.64.56.7.
- In the In Network Interface field, enter the incoming core network interface that connects the Net-Net ECB to your network. IP Address must be entered in dotted decimal format (0.0.0.0). For example, 192.45.6.7.
- In the Out Network Interface field, enter the outgoing network interface that connects your Net-Net ECB to the outside network. IP Address must be entered in dotted decimal format (0.0.0.0). For example, 192.45.6.8.
- Click <Search> to perform the search with the values you specified. A list of the records that the search process filtered, display in the window. The GUI saves the search specifications until you click <Reset> in the search dialog box, OR until you log out of the GUI.