Introduction
Tunnel Session Management (TSM) improves firewall traversal for real time communications for OTT VoIP applications and reduces the dependency on SIP/TLS and SRTP by encrypting access-side VoIP within standardized VPN tunnels. As calls or sessions traverse a TSM tunnel, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller (OCSBC) will route all SIP and RTP traffic from within the TSM tunnel to the core (or appropriate destination).
Oracle Communications is working with other telecom providers and vendors to standardize TSM. Within the 3GPP, TSM is called a Tunneled Services Control Function (TSCF). Currently the 3GPP Technical Requirement draft is TR 33.8de V0.1.3 (2012-05) as a standardized approach for overcoming non-IMS aware firewall issues with supporting companies including China Mobile, Ericsson, Huawei, Intel, RIM, Vodafone, and ZTE. Beyond the standard, we provide exceptional tunnel performance & capacity within the OCSBC as well as high availability, DDoS protection and our patented TSM Tunnel Redundancy to improve audio quality in lossy networks such as the Internet.
Figure 1-1 Basic TSM Setup
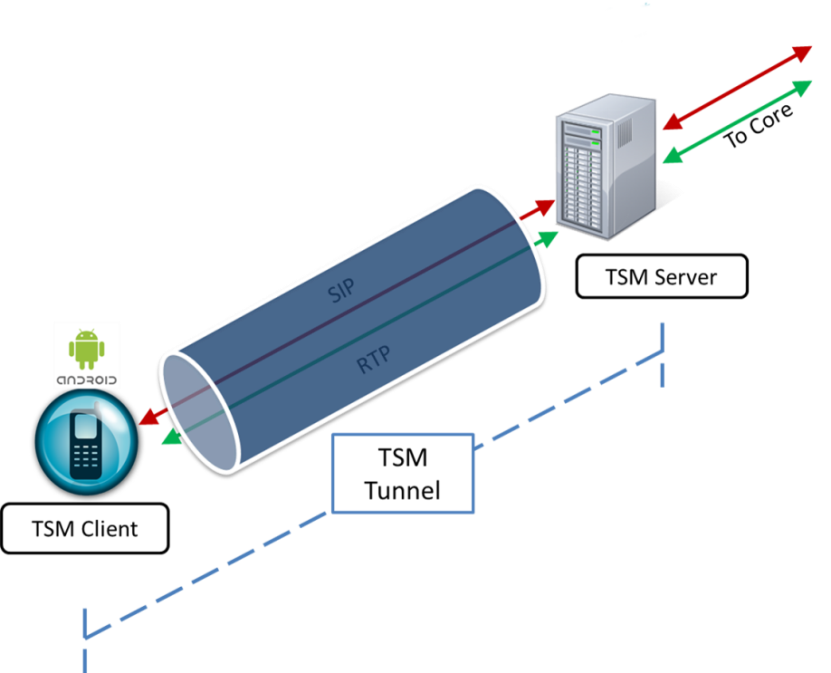
- the TSM server (often referred to as a TSCF or Tunneled Services Control Function)
- the TSM client
To deploy TSM enabled-clients such as softphones, SIP-enabled iOS/Android applications or contact center agent applications, customers and 3rd party ISVs will need to incorporate the open source TSM software libraries into their applications which will establish tunnels to the TSM server.



