1 Sales Audit Overview
In retail, the sales audit function describes the process of reviewing the Point-of-Sale (POS) and Order Management System (OMS) transaction data for accuracy. Sales Audit provides a simplified sales audit process while ensuring the integrity of audited data and smooth integration with other retail applications. The retail sales audit function also allows for balancing out cashiers, cash registers, or an entire store day. This process validates the totals from POS and OMS against the calculated totals of transactions. If these totals are not equal, you can report this variance as an over or short value.
Sales Audit is a part of the Merchandise Operations Management (MOM) product group, which helps retailers to reduce shrinkage, reduce integration costs, improve internal control, increase productivity, and improve visibility to sales. Using real time inventory information, this system calculates need based on set parameters for any product, store or other category. It also manages foundation data, purchasing and cost, inventory, price, and financial processes.
Purpose and Benefits of Sales Audit
Sales Audit accepts POS and OMS data and provides audited data to downstream applications such as, Retail Management System (RMS), Retail Analytics (RA), Retail Store Inventory Management (SIM), and General Ledger applications. It allows a single entry point for sales data from external systems into Oracle Retail applications and other financial systems. It accepts and validates transaction data while detecting and correcting errors according to pre-defined rules which are both system defined and user defined. It allows users to view and audit data at the store/day level or the cashier/register level selected by the user. This process results in correct data that you can export to other applications.
Sales Audit reduces shrinkage because it provides regular comparisons of inventory levels and sales. It can isolate irregularities at the point of sale. It reduces the cost of integration between sales audit functionality and other applications such as the Oracle Retail Merchandising System (RMS) and Oracle Retail Analytics (ORA). Audited POS and OMS data, exported from Sales Audit, provides a single version of data across downstream solutions. It can support reporting and analysis to help reduce losses.
Automatic Audit Process
Automatic auditing is done in Sales Audit using batch programs. The goal of the automatic audit process is to accept transaction data from point-of-sale (POS/OMS) applications and move the data through a series of processes that culminate in clean data. Sales Audit uses several batch-processing modules to perform the following activities:
-
Import POS/OMS transaction data from the RTLog.
-
Perform initial validation of data during upload of data from the RTLog to Sales Audit.
-
Produce totals using user-defined totaling calculation rules that are user reviewable during the interactive audit.
-
Validate transaction and total data with user-defined audit rules and generate errors whenever data does not meet the criteria. The user reviews these errors during the interactive audit.
-
Create and export files of clean data in formats suitable for transfer to other applications.
-
Update the Sales Audit database with adjustments received from external systems on previously exported data.
Interactive Audit Process
Auditors use the interactive audit process to view and correct errors. This process is done after the automated audit is completed. This process allows the auditors to view errors at summary or detail level, fix or override errors, update the totals and close the store/day. In addition, it is also possible to review and edit data of missing transactions or transactions that have passed automated audit, add transactions and delete invalid or missing transactions.
Understanding the Sales Audit Process
The Sales Audit process includes the following procedures:
-
Setting up Sales Audit – For more information, see ”Download/Upload from Spreadsheets” in the Oracle Retail Sales Audit Do the Basics User Guide.
-
Generating totals – For more information, see ”Define Totals” in the Oracle Retail Sales Audit Foundation Data User Guide.
-
Defining audit rules – For more information, see ”Define Audit Rules” in the Oracle Retail Sales Audit Foundation Data User Guide.
-
Importing data – For more information, see the Oracle Retail Sales Audit Operations Guide.
-
Auditing transaction data – This manual describes how Sales Audit audits transaction data.
-
Exporting data – For more information, see the Oracle Retail Sales Audit Operations Guide.
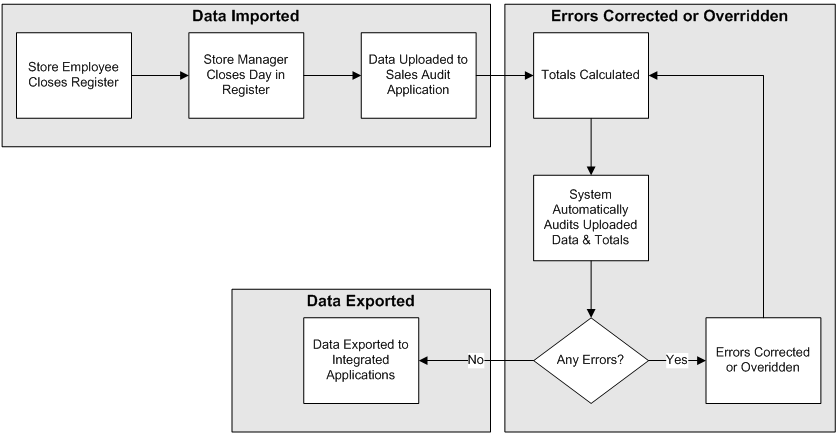
Audit Process Flow
The audit process performs the following steps:
-
At the end of the day or by trickle-poll method, transactions are transmitted from the store to the head office. This data includes order initiation, order complete, and order return transactions from both OMS and POS.
-
The duplicate records received from OMS and POS are filtered within Sales Audit.
-
The transmitted transactions are loaded to the database, totaled, audited, and reviewed.
-
Any errors that are generated as part of the validation process must be corrected or overridden.
-
Once the audit is complete, the data is exported.
Auditing Process Followed by the Auditor
As a Sales Audit auditor, your responsibility is to review all exception errors related to your stores and either correct or override these errors.
The following is a standard auditing workflow for a auditor within Sales Audit:
-
Find and select the store/day containing and navigate to either Balancing Level Summary or Store Day Summary.
-
Use the Store Day Summary to review and audit the following:
-
Error List
-
Miscellaneous totals
-
Over short totals
-
Missing transactions
-
Import and export log
-
-
Use the Cashier/Register Level Summary to review and audit the following:
-
Error list
-
Miscellaneous total
-
Over short total
-
-
You can also perform data analysis such as, reviewing the audit trails. You can use the following screens for the analysis:
-
Transaction Search
-
Item Summary
-
Tender Summary
-
Transaction Audit Trail
-
Total Audit Trail
-
General Ledger Transactions
-
Import/Export Log
-
Bank ACH Maintenance
-
Store ACH Maintenance
-
Note:
Once all errors are corrected or overridden, sales audit sets the store/day audit status to Audited. The store/day audit is then available for export to an external application.