The Oracle Commerce Platform REST framework supports the JAX-RS standard with Jersey as the underlying implementation.
The Jersey configuration defines the components of the JAX-RS application, such as resource classes and components, filters, and additional metadata.
The following diagram shows the flow of the main REST framework components that are used when an HTTP request is made. The REST framework is initiated when a request is received by the Jersey servlet. The servlet is responsible for invoking the provider components in the correct order:
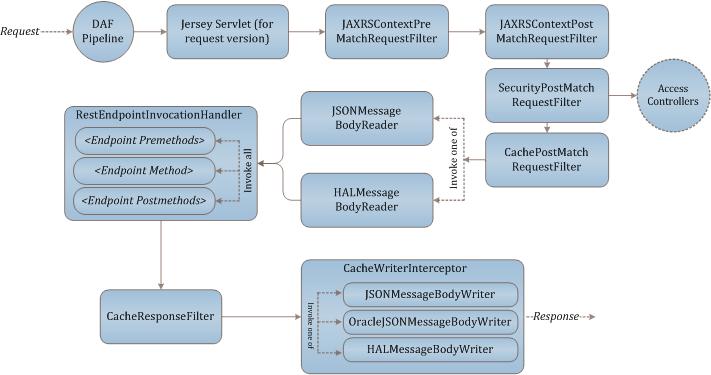
The framework supports multiple versions and/or contexts of the REST JAX-RS API. Each version and context must configure the Jersey servlet with the appropriate context root URI.
The Jersey servlet is configured in the web.xml file to reference the JAXRSApplication class which, during server startup, gets the set of providers and resources from the RestResourceRegistry Nucleus component for that version. The web.xml file also includes the appropriate validation registry. These registries provide the configuration for a specific context or version, for example, /public/v1. Each context and version of the API is configured with its own Web application and Jersey servlet, for example, /public/v1 would be a separate Web application and servlet from /public/v2 or/admin/v1.
The following is an example of a web.xml configuration:
<servlet> <servlet-name>Jersey</servlet-name> <servlet-class>atg.service.jaxrs.JerseyServletWrapper</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>atg.service.jaxrs.JerseyServletWrapper.servletClasses </param-name> <param-value>org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer, atg.service.swagger.SwaggerBootstrap</param-value> </init-param> <!-- Params for JerseyServletWrapper servlet --> <init-param> <param-name>javax.ws.rs.Application</param-name> <param-value>atg.service.jaxrs.JAXRSApplication</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>jersey.config.server.provider.classnames</param-name> <param-value>atg.service.swagger.SwaggerApiListingResource, io.swagger.jaxrs.listing.SwaggerSerializers</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <!-- Params for JAXRSApplication --> <param-name>atg.service.jaxrs.JAXRSApplication.resourceRegistryPath </param-name> <param-value>/atg/dynamo/service/jaxrs/RestResourceRegistry</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>atg.service.jaxrs.JAXRSApplication.validatorRegistryPath </param-name> <param-value>/atg/dynamo/service/validator/ValidatorRegistry</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <!-- Params for SwaggerBootstrap servlet --> <param-name>atg.service.swagger.SwaggerBootstrap.bootstrapService </param-name> <param-value>/atg/dynamo/service/swagger/SwaggerBootstrapService </param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> <async-supported>true</async-supported> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Jersey</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
When setting up the web.xml file there are four configurations that you must provide.
You must configure a
JAXRSApplicationclass that will be used as the Jersey access point for the provider and resource classes in the API.The
RestResourceRegistryNucleus component should be configured with the provider and resources for the API that are available to theJAXRSApplicationinstance. For additional information on theRestResourceRegistry, refer to the Working with REST Resource Nucleus Components section.The
ValidatorRegistrycomponent must be configured with the validator XML schema definition file that validates request input and filters the response output. For information on configuring validation, refer to the Validating Input and Filtering Output section.You should also configure the
SwaggerBootstrapServicecomponent, which scans the API and builds the Swagger definitions and documentation. For information on configuring Swagger definitions, refer to the Self Documenting with Swagger section.

