BEA AquaLogic Service Bus Encoding Handling
|
|
|
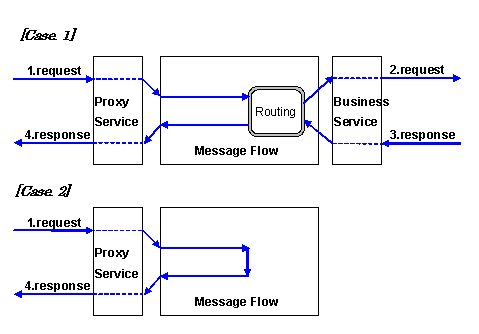
BEA AquaLogic Service Bus has been designed, as its unique product feature requires, to flexibly cope with various encodings (*1) of messages sent from various systems. When linking with the systems that employ multibyte characters, it is essential to know how AquaLogic Service Bus handles the encoding. With the AquaLogic Service Bus that handles multiple transports, the implementation has been done to adapt to as different transport rules as possible, but this may lead to unnecessary differences among transports; this is not a simple situation. This document describes how each transport handles encodings. When you read this document, having the following chart in mind will help you understand the description. Case 1 shows the example of routing from inside the message flow to other services, and Case 2 shows a flow without any routing.
(*1) However, the encodings that AquaLogic Service Bus can handle are only those supported by Java.
With HTTP/HTTPS transport, the encoding at the scene of receiving the messages from outside will be selected from one of following, according to the priority, and then processed.
Also the encoding when a message is sent out to outside services is selected from one of following, according to the priority.
The priority is shown in the following table.
| Proxy Service request | Business Service request | |
| 1. Content-Type/charset attribute 2. Request encoding set value 3. Default : iso-8859-1 | 1. Request encoding set value 2. (At $body update) Generic encoding : UTF-8 3. Encoding of source message | |
| Proxy Service response | Business Service response | |
| 1. Response encoding set value 2. (At $body update) Generic encoding : UTF-8 3. Encoding of source message | 1. Content-Type/charset attribute 2. Response encoding set value 3.Default : iso-8859-1 |
For the details of context variables such as $body, see Message Context in Products Documentation.
In e-mail transport, when a proxy service receives an e-mail, the encoding of the message is selected from following, according to the priority, and then processed.
Also the encoding at sending from business service is selected from following, according to the priority, and then processed.
The priority is shown in the following table.
| Proxy Service request | Business Service request | |
| 1. Content-Type/charset attribute 2. Request encoding set value 3. Default : iso-8859-1 | 1. Request encoding set value 2. (At $body update) Generic encoding : UTF-8 3. Encoding of source message |
With file and ftp transport, both the encoding at file reading by proxy service and the encoding at writing by business service are selected according to the following priority and processed.
With JMS transport, both the encoding at cue/topic reading by proxy service and the encoding at writing by business service are selected according to the following priority and processed.
The encoding processing at JMS transport is done only when ByteMessage I/F of JMS is used.
|
|
|
|