


|

|
|
|
|
Notes on Using MBCS (Multi-Byte Character Set) in WebLogic Server 6.1
Introduction
Changes, and key features regarding I18n/L10n in WebLogic Server 6.1:
Changes from WebLogic Server 6.0
Specifing the Charset for an HTTP Request for a Request URL using the <input-charset>
In WebLogic Server 6.0, the encoding for an HTTP request was specified using weblogic.httpd.inputCharset in web.xml.
i) - - Please specify the following in web.xml: <context-param> <param-name>weblogic.httpd.inputCharset./*</param-name> <param-value>SJIS</param-value> </context-param>
In WebLogic Server 6.1, the encoding for an HTTP request is specified using the <charset-params> in weblogic.xml.
ii) - - Please specify the following in weblogic.xml: <input-charset> <resource-path>/*</resource-path> <java-charset-name>SJIS</java-charset-name> </input-charset>
For more information, see the "Notes on Using Servlet/JSP" section.
request.setCharacterEncoding() Support
In Weblogic Server 6.1, you can use the request.setCharacterEncoding() method to specify the character set for an HTTP request from a client. This method has been added in compliance with the Servlet 2.3 specification. This method is not available in Weblogic Server 6.0.
This method offers the same capabilities as <input-charset>. <input-charset> can be used in both Weblogic Server 6.0 and Weblogic 6.1.
The difference between <input-charset> and request.setCharacterEncoding() is that when using the <input-charset>, you can specify the encoding for each path of the requested URLs. When using the setCharacterEncoding(), you can specify the encoding of each call.
If you specify the encoding using the <input-charset> and then call the setCharacterEncoding() method, the encoding of setCharacterEncoding() will take precedence.
For more information, see the "Notes on Using Servlet/JSP" section.
pageEncoding Directive Support
In Weblogic Server 6.1, you can use the pageEncoding directive. This directive has been added in compliance with the JSP 1.2 in the page tag. The pageEncoding specifies the encoding of the JSP file itself.
The WebLogic Server JSP container or JSP compiler reads itfs JSP files using the character set specified by the pageEncoding. So you can specify the character set for a JSP file (using pageEncoding) and the character set WebLogic Server outputs to a client (using ContentType/Charset) separately. In Weblogic 6.0 which follows the JSP 1.1 specification, both the encoding of the JSP file and what character set WebLogic Server outputs to a client were both determined by ContentType/Charset.
For more information, see the "Notes on Using Servlet/JSP" section.
SAX 2 Support
The version of the WebLogic Server built-in XML parser has been upgraded from Xerces 1.2.0 to Xerces 1.3.1 so that you can use SAX 2. Some problems when parsing an XML file that contains Japanese have been fixed with Xerces 1.3.1.
Notes on Using the Administration Console
About the Language at Startup
The language displayed when the Administration Console first starts is the preference language specified in your Web browser. For example, if you are using the Japanese version of Windows and Internet Explorer, the Administration Console will be displayed in Japanese when it first starts. If you want to change the language displayed first to English, you can change it by setting the preference language in your browser to English.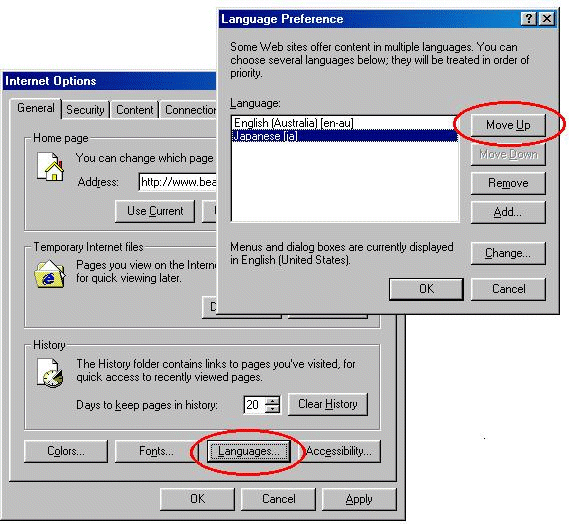
Switching the Language after Startup ( Only for the English and Japanese)
Select the desired language from the Language drop-down list on the Preferences page at the home page for the Console.
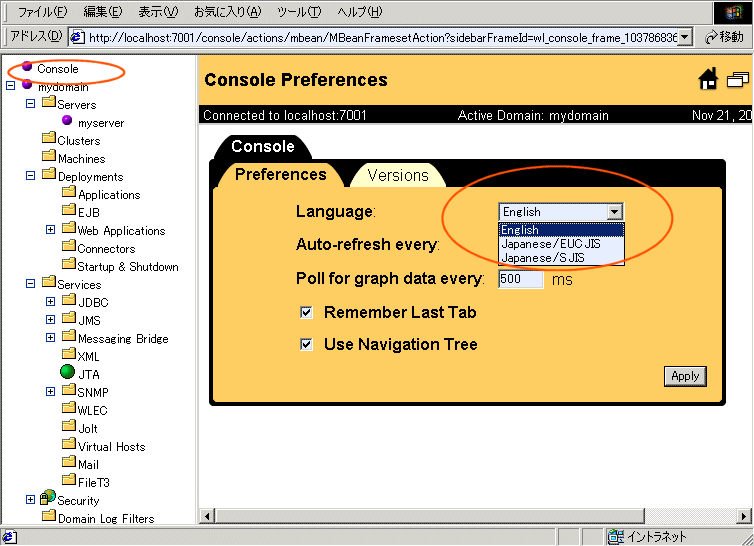
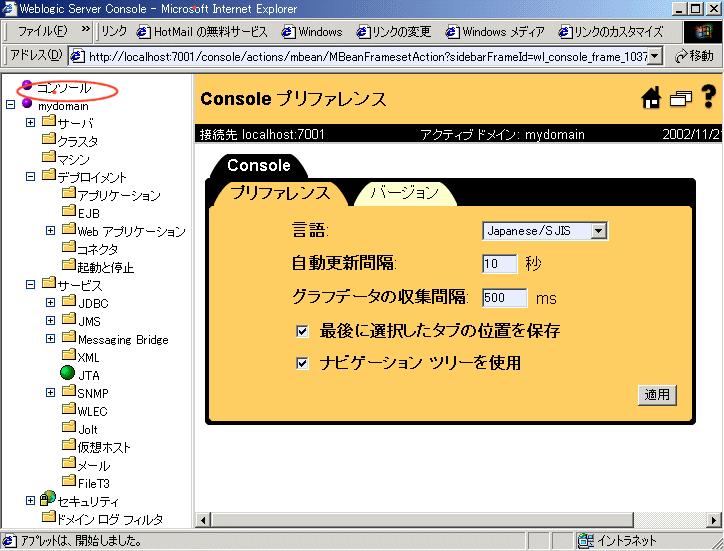
If you change the console's language to Japanese, the console will display in Japanese. Please note however it may be necessary to click the refresh button on your browser in order for the left pane of the console to also display in Japanese.
WebLogic Server Management
Encoding in WebLogic Server and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
There are many places in Weblogic Server to set the encoding. For example, you can specify the encoding that Weblogic Server outputs to a client by setting the ContentType/Charset. You can specify the encoding for a JDBC connection when using weblogic jDriver using the weblogic.codeset property. These and many more are discussed in this document.
Note that there is no relationship between the encoding that you specify for a particular scope and the default encoding for the Java VM on which WebLogic Server runs. If the Java VM is running in the English locale, there still is no problem in providing services using MBCS JSP files. However, the handling of the following strings are dependent on the Java VM default encoding.
These strings work with the Java VM default encoding for each platform (the encoding specified by the file.encoding Java system property). For example, the language and encoding of the log message which WebLogic Server outputs to a terminal console is dependant on the encoding specified in the Java VM.
The file.encoding java system property is based on the platform environment and the system locale. If you want to switch the language and encoding of the WebLogic Server log message, then you need to switch the system locale accordingly. You cannot switch the Java VM default encoding dynamically once the VM has been started. Make sure of the following settings before you restart WebLogic Server.
For Windows 2000/Windows NT
Select English(U.S) or your own language from the Regional option in the Control Panel. This allows the server to use CP1252 or the codepage for your language as the default encoding.
For UNIX
Specify the locale supported by your platform in the LANG environment variable.
Below are the settings of the server encoding for Japanese and the LANG environment variable:
|
Table 1-1 Settings of the server encoding and the LANG environment variable
|
|
Platform |
Encoding |
LANG environment variable |
|
Solaris |
EUCJIS SJIS |
ja or ja_JP.eucJP ja_JP.PCK |
|
HP |
EUCJIS SJIS |
ja_JP.eucJP ja_JP.SJIS |
Please refer to the following URL for other locales.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4/docs/guide/intl/encoding.doc.html
If you'd like to specify EUCJIS on Solaris, then the LANG setting should be like:
LANG=ja
How to Check the Server Encoding
The Java VM default encoding becomes the WebLogic Server default encoding. You can check the encoding by referring to the log message from the Administration Console. Here are the steps:
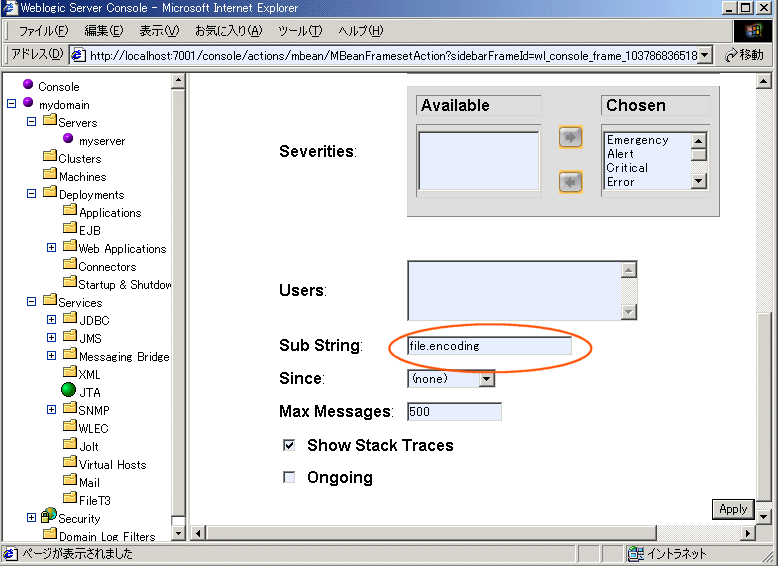
The displayed encoding is the server encoding.
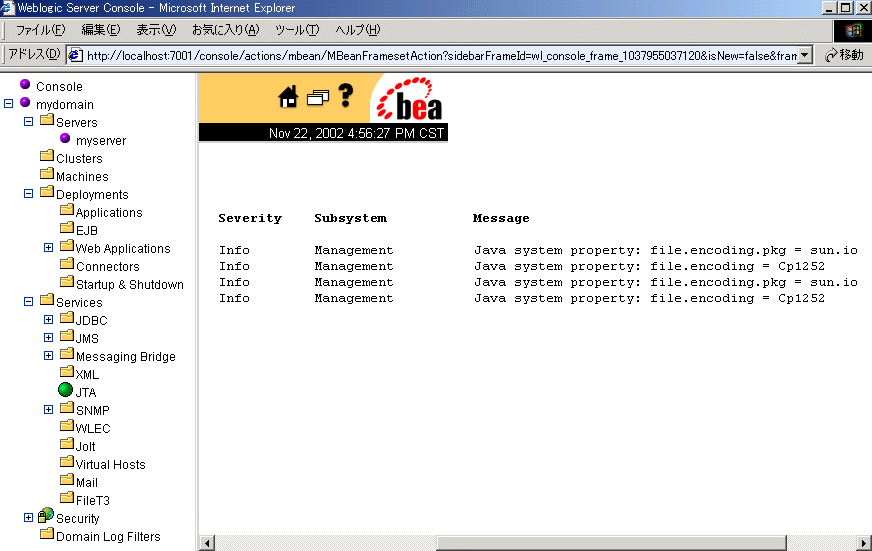
Notes on Configuring Administration and Managed Servers
In WebLogic Server 6.1, you must set the same encoding for all the servers in a domain.
If a server whose encoding is different from the others exists within the domain, that server log will not be displayed correctly.
Notes on Configuring Clusters
Set the same encoding for all the servers in a cluster.
Notes on Using Servlets and JSPs
Encoding Conversion, Standards, Scope and Preference
WebLogic Server 6.1 is a Java application program. All strings are handled internally as Unicode strings. On the other hand, various charsets are used for HTML pages. In WebLogic Server, the encoding conversion between Unicode and the HTML charsets is performed using the Java encoding converter when handling HTML data.
In WebLogic Server 6.1, some of the ways that you set the encoding are defined by the J2EE specification. Others are WebLogic proprietary specifications. You need not specify all of them. Read the following description, and combine the most appropriate encoding settings for your environment.
Encoding Settings
What happens if I set the encoding with two different parameters that affect the same scope?
Basically, the more specific definition of scope will take priority. For example, if Shift_JIS is set as the default encoding for the JSP container, and EUC-JP is specified in the page tag of a specific JSP, then the encoding specified in the page tag will take priority (i.e. EUC-JP will be used).
Another example: If you specify the encoding for requests applicable to a given request URL pattern (using the <input-charset>) and also specify the encoding of a specific request (using the setCharacterEncoding() method), the encoding of setCharacterEncoding() will take precedence. Again, the encoding with the more specific definition will take priority.
It is recommended that you use the same particular encoding throughout your application.
Or set the encoding you primarily wish to use to cover a wide scope like at the JSP container level. Then for areas that require special encoding handling, set the encoding on a more specific level such as the JSP or servlet itself.
Specifying the Encoding
Regarding the below, note that if you do not specify any encoding for the HTTP request and HTTP response then ISO-8859-1 encoding will be used.
For Servlets
For JSPs
For Servlets and JSPs
The following sections describe details on each setting of Servlet and JSP.
For Servlets
Specifying the Encoding for an HTTP Response --- response.setContentType()
To specify the encoding for an HTML page generated by a Servlet, use the setContentType() method. You must call the setContentType() before getting a writer.
res.setContentType("text/html;charset=Shift_JIS");PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
Specifying the Encoding for an HTTP Request ---- request.setCharacterEncoding or <input-charset>
Now you have finished the setting of the encoding for an HTTP response which is data sent from WebLogic Server to a client using the above. Then, the following describes how to set the encoding for an HTTP request when sending data from a client to WebLogic Server.
There are two ways to specify the encoding for an HTTP request:
request.setCharacterEncoding("Shift_JIS");String pval = request.getParameter(pname);
For example, you can set it so that encoding for request URLs are obtained as follows:
Again, in WebLogic Server 6.1 this is set in weblogic.xml. However, In WebLogic Server 6.0 it is set in web.xml. Also, the element names and so on have changed. So when migrating from WebLogic Server 6.0, the weblogic.xml and web.xml files will require modification.
The <input-charset> format is as follows.
Write the <charset-params> for the target Web application in the deployment descriptor (weblogic.xml) as shown below.
In the <charset-params> element (which is embedded in the <weblogic-web-app> element), write the request URL path for which you want to specify the encoding and the encoding which you want to specify for the HTTP request in the IANA name.
For information about mapping between a Java encoding name and an IANA character set, see the "Mapping Between a Java Encoding and an IANA Character Set (Setting in weblogic.xml)" section.
Below is an example of a single web-app that handles multiple encodings. In the below example, the encoding for "/*" is set to Shift_JIS and the encoding for "/rus/jo/*" to ISO-8859-1. The later definition is more specific and hence will take priority.
<charset-params>
<input-charset>
<resource-path>
/*
</resource-path>
<java-charset-name>
Shift_JIS
</java-charset-name>
</input-charset>
</charset-params>
<charset-params>
<input-charset>
<resource-path>
/rus/joe/*
</resource-path>
<java-charset-name>
ISO-8859-1
</java-charset-name>
</input-charset>
</charset-params>
For more information about this setting, see the next section in the "Assembling and Configuring Web Applications".
If you specify both 1 and 2, 1 is enabled.
For JSPs
Specifying the Encoding for a JSP File --- pageEncoding Directive in the page Tag (Optional)
To specify the encoding the WebLogic Server 6.1 JSP container or JSP compiler uses to read a JSP file, specify the pageEncoding directive in the page tag as follows.
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=Shift_JIS" pageEncoding="Shift_JIS" %>
The pageEncoding directive has been added in accordance with the JSP 1.2 specification.
Specifying the Encoding for Page Output ---- contentType Directive in the page Tag
To specify the encoding for page output, specify the contentType directive in the page tag as follows.
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=Shift_JIS" %>
When the pageEncoding directive is not set, the contentType directive is used for the encoding for reading a JSP file. This allows you to continue to use the JSP files used in WebLogic Server 6.0 or earlier in WebLogic Server 6.1.
If the JSP container finds the content type setting, it will stop parsing the JSP file, switch the file reader to this new-specified encoding, and parse the JSP page from the beginning again. If more than one contentType is specified in one file and each specification is different, a parsing error occurs.
Therefore, if different encodings are specified in a file that is included statically, an error occurs. If the file is included dynamically, an error will not occur but garbled characters will be generated. (See the "Difference between the Static include Tag and the Dynamic include Tag, and Specifying the Encoding Using the page Tag" section.)
Specifying the Encoding for an HTTP Request ---- request.setCharacterEncoding or <input-charset>
You can specify the encoding for an HTTP request in a JSP the same way as in a Servlet. See the "For Servlets" section.
Specifying the Encoding for java complier (Optional)
If you don't want to specify the pageEncoding directive for each JSP file, you can specify the "encoding" JSP parameter in "weblogic.xml". Doing so will add the -encoding option to the java compiler.
<jsp-descriptor> <jsp-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value> SJIS </param-value> </jsp-param> </jsp-descriptor>
If your java compiler doesn't support the -encoding option, you can specify the "compilerSupportsEncoding" as false (default is true) to generate an ASCII java file.
<jsp-descriptor> <jsp-param> <param-name>compilerSupportsEncoding</param-name> <param-value>false</param-value> </jsp-param> </jsp-descriptor>
For both Servlets and JSPs
Mapping Between a Java Encoding and an IANA Character Set (Setting in weblogic.xml)
When you specify the encoding using the setContentType() method or the contentType directive in the page tag, use an IANA character set name. But, when you handle the encodings in WebLogic Server 6.1 which is a Java application, these values must be Java encoding names. WebLogic Server 6.1 has the default mappings also internally and normally uses them. The default mappings also include mapping which are not defined in IANA, but are conventionally used in the Content-Type for HTML.
Example : x-sjis ----> MS932
See "Appendix A: WebLogic Specific Default IANA-Java charset Mapping" for all mapping information.
Note: In Java, the IANA character set, Shift_JIS is handled as MS932 (JDK 1.1.8 or later).
This allows you to use the MS932-specific characters (@,A and so on) with the default setting.
You can overwrite the default mappings by defining a <charset-mapping> in weblogic.xml. In the below example, Shift_JIS is mapped to SJIS.
In this example, Shift_JIS is mapped to SJIS.
<charset-params>
<charset-mapping>
<iana-charset-name>
Shift_JIS
</iana-charset-name>
<java-charset-name>
SJIS
</java-charset-name>
</charset-mapping>
</charset-params>
Note the above mappings are weblogic-specific.
Note: Why the acceptCharset in the HTTP header is not used to determine the encoding for the GET/POST in the HTTP request.
The "acceptCharset" which is defined in the request header of the HTTP protocol specifies the list of the encodings the client can accept as the encoding for the response to the request. Therefore, it is not used to specify the encoding for the request itself.
Instead, in WLS, you can specify the encoding for the GET/POST request for a particular content on the server side by defining the <input-charset> in weblogic.xml. In addition, in WLS 6.1, if there is no <input-charset>, the encoding for the GET/POST request is handled as the VM default encoding.
Therefore, if you don't specify the encoding in the <input-charset> on a Windows NT Japanese version, the GET/POST strings are handled as MS932.
Workaround to Encode an HTTP Request with ISO-8859-1 encoding
If ISO-8859-1 is specified as the encoding for an HTTP Request in the <input-charset>, you can still obtain an HTTP Request using a different encoding using the following workaround.
new String(request.getParameter(itemQ[i]).getBytes ("8859_1"), "SJIS")Static vs. Dynamic Includes, Encoding Differences
Static Include
<%@ include file="relativeURL" %>
In this case, all the included files are loaded and got together in one file before JSP compile is performed, and therefore, if the encoding is specified for the include file, the included file will be handled as the file using the same encoding as the include file, even though it is not specified its encoding.
In addition, if the encoding specifications are different between the included file and the include file, a JSP compiling error occurs.
Dynamic Include
<jsp:include page="{ relativeURL | <%= expression %>}" flush="true" />With Dynamic includes, the page is not included when it is loaded, and left in the tag state. The page will be included when the JSP is executed. Therefore, the encoding set in the JSP that does the including will not apply to the included file(s). Hence, you must also specify the encoding in the included file.
Notes on Using JDBC
Setting Up the Environment for Using WebLogic jDriver for Oracle
To use the weblogic.jdbc.oci.Driver, set up the environment as follows. Note that you need to set the jDriver license.
Specify the path to the bin directory of Oracle and that to the bin directory of WebLogic Oracle Oci driver native library.
%WL_HOME%_bin_oci816_8;d:_oracle_ora81_bin
Both the encodings for the NLS_LANG and the weblogic.codeset which is a connection property for the jDriver for Oracle must be always the same. For example, for Japanese, it should be like:
NLS_LANG = japanese_japan.ja16sjis
For information about the relation between the NLS_LANG and the weblogic.codeset, see the "Codeset Support" section in the chapter "Advanced Oracle Features" of the Installing and Using WebLogic jDriver for Oracle. If you can specify the following encodings: ja16sjis for the Oracle database, japanese_japan.ja16sjis for the NLS_LANG, and MS932 for the weblogic.codeset, the character sets used on a Windows platform can be stored in the Oracle database.
Now, you can use the WebLogic Server jDriver for Oracle without using connection pools from WebLogic Server. For example, you can connect directly to the database from a JDBC client such as JSP or Servlet. For information about programming when a JDBC client uses the WebLogic Server jDriver for Oracle, see the "Connecting to an Oracle DBMS" section in the chapter "Using WebLogic jDriver for Oracle" of the Installing and Using WebLogic jDriver for Oracle.
If you use connection pools, you need to do the following settings in the Administration Console. For more information on how to set up connection pools, see the "Setting Up a Connection Pool" section in the chapter "Installing WebLogic jDriver for Oracle" of the Installing and Using WebLogic jDriver for Oracle.
URL:
jdbc:weblogic:oracle
Driver Class Name:
weblogic.jdbc.oci.Driver
Properties:
user=scott
password=tiger
server=ora81
weblogic.codeset=MS932
Now, you can use the WebLogic Server jDriver for Oracle.
Notes: When using CLOB, please note the following settings
weblogic.oci.codeset_width
This property tells the WebLogic Server which type you are using. Note the following restrictions on codeset use:
Possible Values:
weblogic.oci.use_clob_unicode_io
When using CLOB in conjunction with a character set on the Oracle server (this applies to Client version 8.1.5 only), WebLogic Server converts the characters from Unicode to the character set in use by the database. The Oracle server then converts this data back into Unicode. This obvious inefficiency can be avoided by setting this property to true, in which case all communication will be made in Unicode, preventing unnecessary and expensive character set conversions from occurring. The default value for this property is false.
Setting Up the Environment for Using Oracle Oci Driver
d:_oracle_ora81_jdbc_lib_classes12.zip;d:_oracle_ora81_jdbc_lib
c:_oracle_ora81_bin
NLS_LANG = japanese_japan.ja16euc (for Japanese)
Now, you can use the Oracle Oci driver without using connection pools from WebLogic Server. For example, you can connect directly to the database from a JDBC client such as JSP or Servlet. For information about programming when a JDBC client uses the Oracle Oci driver, see the Oracle documentation.
If you use connection pools, you need to do the following settings in the Administration Console. For more information on how to set up connection pools, see the "Connection Pools" section in the chapter "Managing JDBC Connectivity" of the WebLogic Server Administration Guide.
URL:
jdbc:oracle:oci8:@ora81
Driver Class Name:
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
Properties:
user=scott
password=tiger
Now, you can use the Oracle Oci driver.
Setting Up the Environment for Using Oracle Thin Driver
For the Thin driver, you need not to specify the NLS_LANG environment variable.
d:_oracle_ora81_jdbc_lib_classes12.zip; d:\oracle\ora81\jdbc\lib\nls_charset12.zip
c:_oracle_ora81_bin
Now, you can use the Oracle Thin driver without using connection pools from WebLogic Server. For example, you can connect directly to the database from a JDBC client such as JSP or Servlet. For information about programming when a JDBC client uses the Oracle Thin driver, see the Oracle documentation.
If you use connection pools, you need to do the following settings in the Administration Console. For more information on how to set up connection pools, see the "Connection Pools" section in the chapter "Managing JDBC Connectivity" of the WebLogic Server Administration Guide.
URL:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@jpsol1:1521:ora81
Driver Class Name:
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
Properties:
user=scott
password=tiger
Now, you can use the Oracle Thin driver.
Limitations when Connecting Simultaneously to the Databases whose Encodings are Different
When using the OCI driver, you must specify the same encoding for the NLS_LANG and the weblogic.codeset. If these parameters are set to the same value, the encoding conversion will be performed on the Oracle side because you are connected to the Oracle side as a client which has a particular NLS_LANG. For example, if both the encodings for the NLS_LANG and the weblogic.codeset are SJIS, the appropriate encoding conversion will be performed on the Oracle side, even though the encoding for the Oracle DB is EUC-JP. If the two parameters are same, the connection will be made successfuly regardless of the DB's encoding.
Notes about the Encoding Conversion on Using DB
If you don't use the same converter on the conversion between the platform native encoding to the Java encoding, the characters may be handled incorrectly. This problem is caused by the definition of Unicode and JIS.
For example, if you use the following converters on the encoding conversion between the platform native and Java...
DB -------------> WLS -------------> Web Browser
SJIS ------------- MS932
...Then the following codes cannot be handled correctly.
-------------------
"`" (0x8160)
"a" (0x8161)
"" (0x8191)
"|" (0x817C)
"" (0x8192)
"Ê" (0x81CA)
In this case, you must use SJIS explicitly for the output from WLS to the Web browser. For example, if the following encoding is specified in the page tag in JSP,
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=Shift_JIS" %>
this Shift_JIS setting must be converted from Unicode to the platform native using the SJIS converter not the MS932 converter.
Therefore, in this case, you must write the definition like the following in the deployment descriptor (weblogic.xml) for the Web application to change the default encoding mapping table WLS has internally.
<charset-params>
<charset-mapping>
<iana-charset-name>
Shift_JIS
</iana-charset-name>
<java-charset-name>
SJIS
</java-charset-name>
</charset-mapping>
</charset-params>
Miscellaneous
Notes on Using Examples
In the Japanese version of the examples, only the strings for comments for producing the javadocs have been translated. The strings of the programming part are not translated.
Shift-JIS is explicitly specified where the codeset needs to be specified.
When you make changes to an example in order to use Japanese, the specification of the codeset and the contentType must be modified to specify the desired encoding.
Known Problems
About the Administration Console Online Help (Japanese Version)
On the "search" tab, you can do a search operation only using single-byte characters. You can't search using double-byte characters.
You Can't Use Multi-byte Characters for a Server Name of a Managed Server
If you use multi-byte characters for a server name of a Managed Server, the server will not start. You can create such a server in the Administration Console, but you cant use it.
ExampleFStartup commands for a Managed Server
java -ms64m -mx64m -Dweblogic.Domain=mydomain -Dweblogic.Name=managedserver -Dweblogic.management.server=http://127.0.0.1:8801 -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy=weblogic.policy -Dweblogic.management.mbean.propInit=true weblogic.Server
Essentially, you can't use multi-byte characters for "-Dweblogic.Name" which specifies a server name of a Managed Server.
About Using Multi-byte Characters in a Cookie
Currently, you can't use multi-byte characters in a cookie.
When Using MS SQL Server
You cannot use kannji characters for the username.
Resolved Issue
Problem related to the getCharacterEncoding()
The problem with "ISO-8859-1" being always returned when running the getCharacterEncoding() in JSP has been fixed. Now you can retrieve the current encoding specification.
Appendix A: WebLogic Specific Default IANA-Java charset Mapping
WebLogic Server is maintaining a mapping table for the MIME charset and the Java charset. See the following table. Note that it is including charset which is not defined to IANA charset.