3Siebel Connector For IFX XML
Siebel Connector for IFX XML
This chapter describes the methods, input arguments, and output arguments for configuring the components of Siebel Connector for IFX XML. It includes the following topics:
The Siebel Connector for IFX XML consists of the following components:
Transaction Manager
Transformation Engine
Converter
Dispatcher
Transport Adapter
The following images shows the connector components.
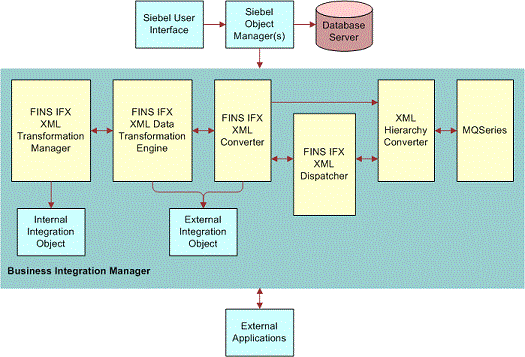
The Connector components are Siebel business services, which are configured in the Workflow view. The integration objects are created using the FINS IFX XML wizard, and they are configured using the Data Map editor.
IFX XML Syntax and Rules
IFX is a financial-industry version of XML. It contains messages that are appropriate for the financial and banking industries.
The IFX standard defines the required structure and format of an XML message for use with a Siebel connector. The definition is in the IFX DTD, and the IFX DTD is incorporated by the Siebel connector to construct messages.
This section provides a summary of the IFX XML syntax and rules, and provides the appropriate vocabulary for discussing IFX XML messages. This section supplies knowledge that is basic for any troubleshooting you may need to do.
IFX XML Documents
Each IFX XML document has three distinct parts:
Envelope
Header
Body
The parts are presented as a hierarchy: the envelope is the root, which contains the header and the body. Elements of an IFX XML document that contain other elements are called aggregates.
The envelope and header provide information required by the XML converter and by other components in the connector. The services identify the kind of business service affected by the information, and the messages provide the data that is being exchanged. There are elements that precede the message proper, which specify the versions of XML and IFX.
The following example shows a sample IFX XML document:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <?ifx version="1.0.1" oldfileuid="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" newfileuid="11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111" ?> <IFX> <SignonRq> <SessKey>ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZYXWVUTSRQPONML</SessKey> <ClientDt>2001-10-10T17:04:33.0-07:00</ClientDt> <CustLangPref>ENU</CustLangPref> <ClientApp> <Org>Customer Organization</Org> <Name>Siebel FINS</Name> <Version>7.0</Version> </ClientApp> </SignonRq> <PaySvcRq> <SPName>IFX Service Provider</SPName> <RqUID>7796AAAA-685E-47b0-9C2F-27FB475B05FA</RqUID> <PmtAddRq> <RqUID>83DA5F9C-7781-4ebb-BB62-311B8B9C6AD7</RqUID> <PmtInfo> <RemitInfo> <CustPayeeId>SibelCustomerBank</CustPayeeId> <CurAmt> <Amt>500</Amt> <CurCode>US</CurCode> </CurAmt> </RemitInfo> <DepAcctIdFrom> <AcctId>2547-86392</AcctId> <AcctType>CDA</AcctType> <BankInfo> <Name>SiebelCustomerBank</Name> </BankInfo> </DepAcctIdFrom> <DueDt>2001-12-24</DueDt> </PmtInfo> <DupChkOverride>1</DupChkOverride> </PmtAddRq> </PaySvcRq> </IFX>
Envelope
The envelope is the root element of an XML document. For an IFX XML document, it begins with <IFX> and ends with </IFX>.
The indicator <IFX> is the only item in the envelope.
Header
Every message header has a sign-on element that authenticates the message, and it may have a sign-off element that ends a particular session.
The header has four elements:
SignonRq
SignonRs
SignoffRq
SignoffRs
The header for a request has the header element <SignonRq>. The header for the response has the header element <SignonRs>. Similarly, the sign-off elements are specifically for requests and responses.
Signon Information
The <SignonRq> or <SignonRs> header element provides a location for status information, authentication information, date and time stamps, language preferences, and identification of the application that will use the data. You can find complete information in the IFX specification.
Authentication Information
The initial <SignonRq> for any session must provide authentication information, typically the user name and password, or a certificate ID. When the server authenticates the user, using the information in the header, the server issues a session key in the <SignonRs>. Subsequent messages use the session key as a token. After a session has finished, any subsequent session must start with the authentication information again.
Following is an example of an initial SignonRs authentication element.
<SignonRq> <SignonPswd> <CustId> <SPName>com.siebel</SPName> <CustLoginId>RLIU</CustLoginId> </CustId> <CustPswd> <CryptType>NONE</CryptType> <Pswd>DROWSSAP</Pswd> </CustPswd> <GenSessKey>1</GenSessKey> </SignonPswd> <ClientDt>2001-11-16T16:56:39.0-08:00</ClientDt> <CustLangPref>ENU</CustLangPref> <ClientApp> <Org>Siebel FINS</Org> <Name>Siebel FINS Application</Name> <Version>7.0</Version> </ClientApp> </SignonRq>
Additional elements may be included in a Signon element. You can find complete information in the IFX specification.
Status information, which includes error codes, may also appear in the Signon element. Status information is discussed in IFX XML Status Information and Error Codes.
Signoff Information
The Signoff header element is used to end a session. A typical time to end a session is at the close of business for the day.
The Signoff element, <SignoffRq> or <SignoffRs>, appears at the end of the message, just before the end of the envelope </IFX>. The Signoff element may optionally contain a <custID> element.
Body
The body of an IFX XML document provides the content of the information request or response. The body serves as an aggregate containing services and messages. Services and messages, in turn, are aggregates that contain smaller elements.
Service.A service identifies the kind of service being requested or delivered, identifying the business function that will be affected. For example, <PaySvcRq> is a request for a payment service, and <BankSvcRq> is a request for a bank service.
Message. A message identifies the business object affected by the message and the operation that is to be performed on the data. For example, <PmtAddRq> is a request to add a payment.
Data Element. A data element identifies the business component or fields affected by an operation defined in the message. For example, <FirstName> is a data element that contains information about a person’s first name.
Services
The basic body element is a service, for example <PaySvcRq>, <BaseSvcRq>, or <BankSvcRq>. <BaseSvcRq> is a request for the base service, which all service providers can provide.
An IFX body can include multiple services. A body almost always contains at least one service. A body with no service would provide only authentication.
The same service may be included in a body more than once, but each service must be for a different service provider.
Following is an example of a message with a single payment service request.
<PaySvcRq> <SPName>Partner IFX Middleware</SPName> <RqUID>50DBF4F7-7888-480b-927E-333652FEBF87</RqUID> <PmtAddRq> <RqUID>BD620AC4-53E7-4UIL-588C-YOR8D6224FE9</RqUID> <PmtInfo> <RemitInfo> <CustPayeeId>0VF-VEBQ</CustPayeeId> <CurAmt> <Amt>2500</Amt> <CurCode>USD</CurCode> </CurAmt> </RemitInfo> <CardAcctIdFrom> <AcctId>2574-86392</AcctId> <AcctType>Savings/MMA</AcctType> </CardAcctIdFrom> <DueDt>2001-11-13</DueDt> </PmtInfo> <DupChkOverride>1</DupChkOverride> </PmtAddRq> </PaySvcRq>
The service aggregate includes a universally unique identifier (UUID) to match responses to requests. The UUID is generated using an algorithm that makes it unique. It appears in the <RqUID> element. It is generated by the client (which sends out the request). It is stored at the client site, which then matches it to the UUID in the response message. The UUID generator can be a Siebel business service or an extension provided by a third party. In any case, the UUID generator is identified by a parameter to the IFX Converter.
Messages
Messages (sometimes called business messages) are contained in Service aggregates. Each service can contain one or more business messages. Each service can contain any number of messages.
The message tag identifies the business object that is affected by the message and a command operator. A business object can be a payment or a cash drawer—anything on which an operation can be performed.
A message uses one of the following operations:
Add
Delete
Cancel
Inquiry
Modify
Audit
Synchronize
The business message name tag contains the object and the operation. For example, a business message called <PmtAddRq> identifies “payment" as the business object, and “add" as the operation. The details of the added payment are provided within the message.
A complete list of business messages for IFX XML is provided in the IFX XML implementation specification.
Data Elements
Within the business message are additional elements that identify the record that will be affected by the request or response and provide any other specifications, such as <CustName>, <PostAddr>, <FirstName>, and <LastName>.
The additional elements include field labels, field information, and tags that provide program access to the data.
Following is an example of data elements for the add payment request.
<PmtAddRq> <RqUID>BD620AC4-53E7-4UIL-588C-YOR8D6224FE9</RqUID> <PmtInfo> <RemitInfo> <CustPayeeId>0VF-VEBQ</CustPayeeId> <CurAmt> <Amt>2500</Amt> <CurCode>USD</CurCode> </CurAmt> </RemitInfo> <CardAcctIdFrom> <AcctId>2574-86392</AcctId> <AcctType>Savings/MMA</AcctType> </CardAcctIdFrom> <DueDt>2001-11-13</DueDt> </PmtInfo> <DupChkOverride>1</DupChkOverride> </PmtAddRq>
The information in this request is sent to the external application, which performs the request and returns a response.
IFX XML Status Information and Error Codes
Status information is information about the current status of a message. It appears only in response documents. It can appear in a response header or in any element of a response body.
The external server inserts status information after processing the document. If the processing is satisfactory, status information may or may not be inserted. If there is a problem in the processing, the status information identifies the problem.
A status code of zero means the status is satisfactory. If any other number appears, it is an error code or warning, and the message is flagged. The error code can be used in troubleshooting.
Status information in the header applies to the entire IFX XML document. Status information in a service applies to that service. Status information in a message applies to that message. The following example shows status information in a header.
<Status> <StatusCode>100</StatusCode> <Severity>Error</Severity> <StatusDesc>General Error</StatusDesc> </Status>
For details of status codes, see the IFX XML specification, which provides a description of all error codes.
FINS IFX XML Wizard Business Service
Siebel applications provide wizards to guide you through the process of building integration objects and updating dispatcher maps.
You can use the FINS IFX XML Wizard to build integration objects for the Siebel Connector for IFX XML. The wizard guides you through the process of selecting objects (from the Siebel repository or from an external system) on which you can base your new Siebel integration object. The wizard builds a list of valid components from which you choose the specific components to be included in your Siebel integration object.
You access Siebel wizards within the Siebel Integration Object Builder in Siebel Tools. Use the IFX XML wizard to create an appropriate elements hierarchy that reflects the IFX XML DTD. The wizard:
Creates a set of integration objects to handle outbound and inbound messages and to handle internal and external integration.
Updates the dispatcher map, which is later used by the dispatcher.
FINS IFX XML Integration Objects
Siebel integration objects allow you to represent integration metadata between a Siebel business object and an external XML standard, using the IFX XML DTD. The integration object represents a common structure that the EAI infrastructure can understand.
Because these integration objects adhere to a set of structural conventions, they can be traversed and transformed programmatically, using Siebel eScript objects, methods, and functions, or transformed declaratively using Siebel data mapper.
To use Siebel Connector for IFX XML to integrate data you need to build three different integration objects:
IFX XML Envelope Integration Object. An envelope integration object provides envelope and header information for an IFX XML document.
User properties in an IFX XML envelope provide flexibility to the connector. For example, when a user sends an initial IFX XML request, the IFX XML document uses a <SignonRq> header that is different from subsequent <SignonRq> headers.
IFX XML Internal Integration Object. An internal integration object represents the Siebel business object hierarchy for a particular Siebel business object. See Creating an Internal Integration Object, for an example of creating an internal integration object.
IFX XML External Integration Object. An external integration object represents the IFX XML hierarchy for a particular IFX XML message. See Configuring FINS IFX XML, for an example of creating an external integration object.
FINS IFX XML Dispatcher Map
The dispatcher map is used by FINS IFX XML Dispatcher. The dispatcher map is another integration object that provides a rule set for handling incoming IFX XML messages. The dispatcher map is created and updated by the FINS IFX XML Wizard during the process of creating an external integration object.
The map contains information that associates message instances with the appropriate internal and external integration objects for incoming and outgoing messages. It associates each incoming or outgoing message with all the Siebel Connector for IFX XML elements that are necessary to translate it into Siebel data.
The map contains DTE map names, the internal integration object name, the external integration object name, and Siebel adaptor operations. These elements make up the translation scheme for the message instance. The dispatcher map allows the dispatcher to associate the proper translation scheme with each message instance.
All the mapping information is stored in the user property part of the dispatcher map integration object.
IFX XML Transaction Manager Business Service
The FINS IFX XML Transaction Manager is responsible for retrieving data from a Siebel application. It may invoke the Siebel adapter or another business service configured in its user properties. It is an adapter that resides logically between the Siebel object manager and the rest of the connector. It executes operations specified in an XML message instance as Siebel database transactions.
The transaction manager translates XML command elements into Siebel EAI Adapter actions. The transaction manager either carries out the action or finds another business service to carry out the action.
The transaction manager combines return results into a single property set. A property set is an intermediate data store that can be used in subsequent operations within the connector.
For inbound processing, the transaction manager accepts an IFX XML property set, which may contain multiple integration object instances for multiple transactions. It pairs each individual transaction request with an integration object instance and invokes methods in the Siebel EAI Adapter.
For outbound processing, the transaction manager pairs a transaction request with an integration object instance and sends an IFX XML property set to the DTE.
FINS IFX XML Transaction Manager User Properties
The following table describes the FINS IFX XML Transaction Manager user properties.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
<Integration object name> |
The dispatch map name. Transaction manager will use this map to tag the Body information for other components. This value can be set as runtime input argument, which will overwrite this value. |
<Operation Name> |
<Service name>/<Method name>/ <Argument List> |
<OperationName> can be any literal value you want to use to name the operation. The operation can be invoked from the MethodName method in ServiceName business service passing Argument arguments. <OperationName> is an alias for the method specified by ServiceName/MethodName. <OperationName> is referenced in dispatcher map entries. For information about configuring the <Operation Name>, see the following section. |
Configuring the <Operation Name> Property
Use a meaningful name for the operation name, such as “IXMLOperation_Query."
The value must follow this format:
"Service/Method/Argument;Argument;"
"/Method/Argument;Argument;"
Note that the service, method, and argument are separated by a slash (/)
Each argument ends with semi-colon (;)
The default service name is "EAI Siebel Adapter"
The default argument name is "SiebelMessage"
Uses of the Siebel operation include the following:
"EAI Siebel Adapter/Query/PrimaryRowId;!SiebelMessage;SearchSpec;"
"EAI Siebel Adapter/Query/#XMLHierarchy;"
"EAI Siebel Adapter/Delete/RollbackOnSame;"
The following table shows examples of the Siebel operation.
| Example | Meaning |
|---|---|
!SiebelMessage |
The default value is to use SiebelMessage as the type of integration object instance. !SiebelMessage means to not use the default value. |
#XMLHierarchy |
Replace SiebelMessage with XMLHierarchy |
FINS IFX XML Transaction Manager Methods and Arguments
The FINS IFX XML Transaction Manager methods and arguments are described in the following tables. The following table describes the FINS IFX XML Transaction Manager methods.
| Method | Display Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
Execute |
Execute Transaction |
Can be used for inbound or outbound messages when the integration object instance is provided. When only Row_Id is available, use the Execute Outbound method. |
Execute Outbound |
Execute Outbound |
Use only for executing an outbound message. |
The following table describes the arguments for the Execute Outbound method.
| Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
<Integration object name> |
Required input string. The name of the dispatcher map that contains the target IFX message. |
IsVBC |
true, false |
Optional input string. Value is TRUE if the source Business Component is a VBC. |
IXMLMapPath |
<IFX absolute path> |
Stores the key for looking up a dispatcher map entry. Transaction Manager uses it to look up the entry value for the integration object instance. Absolute path of the target IFX message. |
PrimaryRowId |
<row_id> |
The primary row ID of the integration object. |
SearchSpec |
<Search spec> |
The search specification of a query for the operation business service to retrieve an integration object instance from the Siebel database. |
SiebelFINSOperationOut |
<Operation name> |
The operation to be used by the transaction manager, which is predefined in the user properties of the transaction manager. |
VBCFieldMap |
<Property Set> |
Optional input hierarchy. A hierarchy contains the field values for the target VBC. |
XMLHierarchy |
<XML property set> |
A property set that contains an IFX message instance in Siebel internal integration object format. |
The following table provides specifications for the Execute Outbound method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IXMLMapPath |
IXML Map Path |
String |
Input |
No |
PrimaryRowId |
Primary Row Id |
String |
Input |
No |
SiebelFINSOperationOut |
Outbound operation |
String |
Input |
No |
SearchSpec |
Search Spec |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Output |
No |
The following table describes the arguments for the Execute method.
| Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
OnlyIOI |
true, false |
For an inbound message, the integration object instance for request may contain header, body, and envelope portions. When the transaction manager takes the proper operation against the Siebel application, the integration object instance for response is generated as well. If this value is set to TRUE, all information from the request message is dropped; in this case, the converter and DTE do not need to deal with the information overhead. If this value is set to FALSE, request information is carried over. |
XMLHierarchy |
<XML property set> |
A property set that contains an IFX document instance in Siebel internal integration object format. |
The following table provides specifications for the Execute method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Only IOI |
Produce only an integration object instance |
String |
Input |
No |
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input or Output |
No |
FINS IFX XML Data Transformation Engine (DTE) Business Service
The FINS IFX XML DTE transforms property sets in a Siebel internal integration hierarchy to an external integration object hierarchy, and vice versa. This function allows the FINS IFX XML Converter to exchange data between two systems with different data models. The transformation map is defined at run time from Siebel Administration views.
For inbound processing, the DTE accepts a property set from the FINS IFX XML Converter and transforms it into a property set to be used by the FINS IFX Transaction Manager. The incoming property set is made up of one or more external integration object instances. If there are multiple instances, the DTE parses them into individual instances and transforms them. The DTE then packages the returned transformed instances as an output property set as internal integration object instances.
For outbound processing, the DTE accepts a property set from the transaction manager and transforms it into a property set to be used by the converter. The outgoing property set is made up of one or more internal integration object instances. The DTE then packages the returned transformed instances as an output property set as external integration object instances.
FINS IFX XML DTE Methods and Arguments
The FINS IFX XML DTE methods and arguments are described in the following tables. The following table describes the methods for the FINS IFX XML DTE.
| Method | Display Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
ToExternal |
Transform to External Hierarchy |
Transforms a Siebel hierarchy into an external hierarchy. |
ToInternal |
Transform to Siebel Hierarchy |
Transforms an external hierarchy into a Siebel hierarchy. |
The following table describes the arguments for the ToExternal method.
| Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
<XML property set> |
Takes as input the output of the Execute outbound method of the IFX XML transaction manager. Output hierarchy that contains the IFX Document in Siebel external integration object format. |
<MapArgs> |
Runtime input arguments that can be used by DTE maps. See explanation in the following section. |
|
DTE Argument 1 |
<Any literal value> |
|
DTE Argument 2 |
<Any literal value> |
|
DTE Argument 3 |
<Any literal value> |
The following table provides specifications for the ToExternal method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input Output |
No |
<MapArgs> |
String |
Input |
Yes |
|
DTE Argument n |
Yes |
The following table describes the arguments for the ToInternal method.
| Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
<XML property set> |
Takes as input the output of the XMLPropetySetToPropertySet method of the IFX Converter. Output hierarchy that contains the IFX Document in Siebel internal integration object format. |
<MapArgs> |
Runtime input arguments that can be used by DTE maps. See explanation in the following section. |
|
DTE Argument 1 |
<Any literal value> |
|
DTE Argument 2 |
<Any literal value> |
|
DTE Argument 3 |
<Any literal value> |
The following table provides specifications for the ToInternal method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input Output |
No |
<MapArgs> |
String |
Input |
Yes |
|
DTE Argument n |
Using <MapArgs>
<MapArgs> is a runtime input argument used by the DTE map to match an integration map argument of an integration object map. The FINS IFX XML DTE can take as many <MapArgs> as needed as long as each name is unique among all the <MapArgs> that are passed to the FINS IFX XML DTE at the same time.
For example, suppose that the output integration object instance has some fields mapping to a workflow process property, such as an ID field.
Using the Data Map view, select the integration map to edit in the Integration Object Map applet.
In the Integration Map Argument applet, create the map and set the following values:
Name = CompId
Data Type = “DTYPE_TEXT"
Display Name = Component ID
In the Integration Field Map applet, set the following values:
Target Field Name = [Id]
Source Expression = [&CompId]
In the workflow, set the data transformation engine input argument as follows:
Input Argument = CompId
Type = Process Property
Property Name = Object Id
At runtime, the DTE replaces [&CompId] with the value of the Object ID.
For some mappings, if the DTE cannot find the source field value, the DTE creates empty tags by default. To remove the empty tags, add IgnoreEmptyTag as the map argument.
For complete information, see Business Processes and Rules: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.
FINS IFX XML Converter Business Service
The purpose of the FINS IFX XML Converter is to generate and process IFX XML-specific elements, such as the <SignonRq> aggregate and the <SignonRs> aggregate.
The FINS IFX XML Converter receives hierarchy output and converts it into a property set or an XML string.
FINS IFX XML Converter User Properties
The following table describes the FINS IFX XML Converter user properties.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
PI_Parameter:<PI_Name> |
<PI_Value> |
PI_Parameter: is a constant prefix. PI_Name is provided by the configurator. “PI_Name=PI_Value" would be a PI name-value pair included in IFX PI. Zero or more pairs can be defined. Examples:
|
PI_Type |
ifx |
Process Instruction Type |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
<Integration object name> |
Integration object name that defines the IFX envelope. |
ExceptionForIFXErr |
true, false |
If true, IFX converter generates an exception when any <StatusCode> in the incoming response message contains a non-zero value. This behavior can be overridden by providing a ProcessStatus outcall function. If a ProcessStatus outcall is provided, this flag does not take effect whether its value is true or false. |
FINS IFX XML Converter Methods and Arguments
The FINS IFX XML Converter methods and arguments are described in the following tables. The following table describes the FINS IFX XML Converter methods.
| Method | Display Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
PropSetToXML |
PropSetToXML |
Generate the XML message to be sent. |
PropSetToXMLPropSet |
PropSetToXMLPropSet |
Prepare the DOM structure of the XML message to be sent. |
XMLPropSetToPropSet |
XMLPropSetToPropSet |
Convert the XML message received into hierarchical property sets. |
XMLToPropSet |
XMLToPropSet |
Prepare the hierarchical property sets from DOM structure of the XML message received. |
Generate Envelope Only |
Generate Envelope Only |
Generate an IFX document that contains only an IFX envelope and header. No body portion. |
The following table describes the arguments common to FINS IFX XML Converter methods.
| Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
Client Application Name |
<Client application name> |
Required input string. Value of <Name> of <ClientApp> aggregate. |
Client Application Organization |
<Client organization name> |
Required input string. Value of <Org> of <ClientApp> aggregate. |
Client Application Version |
<Client application version> |
Required input string. Value of <Version> of <ClientApp> aggregate. |
Date Input Format |
<Date format> |
Optional input string. Default value: YYYY-MM-DD |
Date Output Format |
<Date format> |
Optional input string. Default value: YYYY-MM-DD |
DateTime Input Format |
<Date, time format> |
Optional input string. Default value: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.0Z |
DateTime Output Format |
<Date, time format> |
Optional input string. Default value: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.0Z |
Time Input Format |
<Time format> |
Optional input string. Default value: HH:mm:ss.0Z |
Time Output Format |
<Time format> |
Optional input string. Default value: HH:mm:ss.0Z |
YrMon Input Format |
<Year, month format> |
Optional input string. Default value: YYYY-MM |
YrMon Output Format |
<Year, month format> |
Optional input string. Default value: YYYY-MM |
Enable Data Formatting |
true, false |
Optional input string. Default value: false. See additional explanation in Siebel Versus IFX Data Formats. |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
<Business service name> |
Optional input string. Business service name that contains out-called functionality. If no value is entered, the connector uses default functionality. See the next section for further information about outcalls. |
Is Log Out |
true, false |
Optional input string. Set to “true" for signing off IFX session. |
Is Client |
true, false |
Optional input string. Set to “true" if connector is used at client side. Default value: “True". |
Service Provider Name |
<IFX service provider name> |
Optional input string. Value of <SPName> of <xxxSvcRq> aggregate. |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
<Integration object name> |
Required input string. Name of the integration object that defines IFX envelope. |
XML Property Set |
<XML hierarchy> |
Required input hierarchy. |
The following table provides specifications for the PropSetToXML method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Date Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Client Application Name |
Client Application Name |
String |
Input |
No |
Client Application Organization |
Client Application Organization |
String |
Input |
No |
Client Application Version |
Client Application Version |
String |
Input |
No |
Date Output Format |
Date Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
DateTime Output Format |
DateTime Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Time Output Format |
Time Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
YrMon Output Format |
YrMon Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Enable Data Formatting |
Enable Data Formatting |
String |
Input |
Yes |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Is Log Out |
Is Log Out |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Is Client |
Is Client |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Service Provider Name |
Service Provider Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Output |
No |
The following table provides specifications for the PropSetToXMLPropSet method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Date Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Client Application Name |
Client Application Name |
String |
Input |
No |
Client Application Organization |
Client Application Organization |
String |
Input |
No |
Client Application Version |
Client Application Version |
String |
Input |
No |
Date Output Format |
Date Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
DateTime Output Format |
DateTime Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Time Output Format |
Time Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
YrMon Output Format |
YrMon Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Enable Data Formatting |
Enable Data Formatting |
String |
Input |
Yes |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Is Log Out |
Is Log Out |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Is Client |
Is Client |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Service Provider Name |
Service Provider Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Output |
No |
The following table provides specifications for the XMLPropSetToPropSet method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Date Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Date Input Format |
Date Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
DateTime Input Format |
DateTime Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Time Input Format |
Time Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
YrMon Input Format |
YrMon Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Enable Data Formatting |
Enable Data Formatting |
String |
Input |
Yes |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Input |
No |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Output |
No |
The following table provides specifications for the XMLToPropSet method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Date Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Date Input Format |
Date Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
DateTime Input Format |
DateTime Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Time Input Format |
Time Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
YrMon Input Format |
YrMon Input Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Enable Data Formatting |
Enable Data Formatting |
String |
Input |
Yes |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Output |
No |
The following table provides specifications for the Generate Envelope Only method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Date Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Client Application Name |
Client Application Name |
String |
Input |
No |
Client Application Organization |
Client Application Organization |
String |
Input |
No |
Client Application Version |
Client Application Version |
String |
Input |
No |
Date Output Format |
Date Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
DateTime Output Format |
DateTime Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Time Output Format |
Time Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
YrMon Output Format |
YrMon Output Format |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Enable Data Formatting |
Enable Data Formatting |
String |
Input |
Yes |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
IFX Application Business Service Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Is Log Out |
Is Log Out |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Is Client |
Is Client |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Service Provider Name |
Service Provider Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XML Property Set |
XML Property Set |
String |
Output |
No |
FINS IFX XML Outcalls
The Siebel Connector for IFX XML provides default behaviors for a variety of methods shown in the Connector Outcall Methods table. If the default behaviors do not suit your needs, the Siebel Connector for IFX XML allows outcalls to override the defaults.
For example, the Siebel default for the <SignonRq> method is user name and password. The configurator can provide an outcall function for a certificate instead.
The outcall function is activated by the IFX Application Business Service Name parameter. If you want to use an outcall, you define a business service that encloses the outcall functionality, and then enter the business service name in the IFX Application Business Service Name parameter.
If the connector cannot find the business service identified in the IFX Application Business Service Name parameter, default functionality is used instead.
Siebel Connector for IFX XML Outcall Methods
This section lists all methods that the Siebel Connector for IFX XML can use for outcalls. You can implement them using either eScript or VB. For more details, see Siebel eScript Language Reference and Siebel VB Language Reference.
In the following table the input argument values are provided by the Siebel Connector for IFX XML, and the output argument values are returned to the Siebel Connector for IFX XML.
| Method | Input Argument | Output Argument | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
GenerateSignonRq |
An empty property set |
Property set contains <SignonRq> aggregate in property set format |
Generate a customized <SignonRq> aggregate instead of having the IFX connector generate a default <SignonRq> aggregate. |
GenerateSignonRs |
Complete IFX request document in property set format |
Property set contains <SignonRs> aggregate |
Generate a customized <SignonRs> aggregate instead of having the IFX connector generate a default <SignonRs> aggregate. |
GenerateSignoffRq |
An empty property set |
Property set contains <SignoffRq> aggregate in property set format |
Generate a customized <SignoffRq> aggregate instead of having the IFX connector generate a default <SignoffRq> aggregate. |
GenerateSignoffRs |
Complete IFX request document in property set format. |
Property set contains <SignoffRs> aggregate. |
Generate a customized <SignoffRs> aggregate instead of having the IFX connector generate a default <SignoffRs> aggregate. |
GenerateUUID |
A property set with Type = GUID |
A property set with generated GUID stored as its <Value> |
Generate a valid GUID to be <RqUID>. |
ProcessSignonRq |
Complete IFX request document in property set format |
Not required |
Process <SignonRq>. |
ProcessSignonRs |
Complete IFX request document in property set format |
Not required |
Process <SignonRs>. |
ProcessSignoffRq |
Complete IFX request document in property set format |
Not required |
Process <SignoffRq>. |
ProcessSignoffRs |
Complete IFX response document in property set format |
Not required |
Process <SignoffRs>. |
ProcessStatus |
An IFX response message |
Not required |
Process <Status>. This method is called once for every response message. |
FormatFieldFromXML |
A property set with Type: IFX data type for this element Value: Element value in IFX data format |
A property set with Value: Element value in Siebel data format |
Convert element value from IFX data format to Siebel data format. This method is called for every element when data formatting is enabled. |
FormatFieldToXML |
A property set with Type: IFX data type for this element Value: Element value in Siebel data format |
A property set with Value: Element value in IFX data format |
Convert element value from Siebel data format to IFX data format. This method is called for every element when data formatting is enabled. |
FINS IFX XML Dispatcher Business Service
The FINS IFX XML dispatcher handles inbound XML hierarchy instances. It provides the necessary information for subsequent modules to perform their operations, such as the integration objects to be used.
The dispatcher identifies incoming messages and parses them into header and envelope sections. It also analyzes incoming message body sections, walking through each command. Using the dispatcher map, the dispatcher associates the message with the appropriate external integration object so that the FINS IFX XML Converter can use it. It also associates the message with the DTE map so that the FINS IFX XML DTE can use it.
FINS IFX XML Dispatcher User Properties
The following table shows the user properties for the dispatcher.
| Name | Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
<Integration object name> |
Name of an integration object that details the dispatching rules and syntax for the IFX XML standard. This map is usually created along with all the other integration objects needed by the wizard. |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
<Integration object name> |
Name of an integration object that defines the content and hierarchy for the envelope and header sections of IFX XML. |
FINS IFX XML Dispatcher Methods and Arguments
The FINS IFX XML Converter methods and arguments are described in the following tables. The following table describes the FINS IFX XML Dispatcher method.
| Method | Display Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
Dispatch Message |
Dispatch Method |
Validates the incoming XML message. If the message conforms to the dispatching rules, the integration object names and other necessary information will be attached to the message. |
The following table describes the arguments for the Dispatch Message method.
| Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
<Integration object name> |
Required input string |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
<Integration object name> |
Required input string |
XML Hierarchy |
<XML property set> |
Required input hierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
<XML property set> |
Required output hierarchy |
The following table provides specifications for the Dispatch Message method arguments.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
DispatcherMapName |
String |
Input |
No |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
String |
Input |
|
XML Hierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input |
|
XML Hierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Output |
Transport Adapter for FINS IFX XML
The transport adapter is a Siebel business service that provides the interface between the outside data source and the Siebel connector. The connector can use any of the following standard transport mechanisms.
MQSeries
MQSeries AMI
HTTP
MSMQ
For details about the transport adapter, see Transports and Interfaces: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.