5Web Services
Web Services
This chapter describes Web services, their uses, and how to create, implement, and publish Siebel Web services. This chapter also provides examples of how to invoke an external Web service and a Siebel Web service. The following topics are included:
About Web Services
Web services combine component-based development and Internet standards and protocols that include HTTP, XML, Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP), and Web Services Description Language (WSDL). You can reuse Web services regardless of how they are implemented. Web services can be developed on any platform and in any development environment as long as they can communicate with other Web services using these common protocols.
Business services or workflows in Siebel Business Applications can be exposed as Web services to be consumed by an application. Siebel Web Services framework has an ability to generate WSDL files to describe the Web services hosted by the Siebel application. Also, the Siebel Web Services framework can invoke external Web services. This is accomplished by importing a WSDL document, described as an external Web service, using the WSDL Import Wizard in Siebel Tools.
To specify the structure of XML used in the body of SOAP messages, Web services use an XML Schema Definition (XSD) standard. The XSD standard describes an XML document structure in terms of XML elements and attributes. It also specifies abstract data types, and defines and extends the value domains.
Users or programs interact with Web services by exchanging XML messages that conform to Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). For Web services support, SOAP provides a standard SOAP envelope, standard encoding rules that specify mapping of data based on an abstract data type into an XML instance and back, and conventions for how to make remote procedure calls (RPC) using SOAP messages.
Supported Web Services Standards
For information on the Web services standards supported with Siebel CRM, see the Certifications tab on My Oracle Support.
About RPC-Literal and DOC-Literal Bindings
In Siebel Business Applications, publishing a Siebel Web service as a Document-Literal (DOC-Literal) or RPC-Literal bound Web service partly conforms to the specification as defined by the Web Services Interoperability Organization’s (WS-I) Basic Profile specification. Adherence to this specification makes sure that Siebel Business Applications can interoperate with external Web service providers.
WS-I is a trademark of the Web Services Interoperability Organization in the United States and other countries.
RPC-Literal Support
RPC allows the use of transports other than HTTP (for example, MQ and MSMQ), because you do not have to use the SOAPAction header to specify the operation.
For information on the Web services standards supported with Siebel CRM, see the Certifications tab on My Oracle Support.
Making a Web Service an RPC-Literal Web Service
RPC literal processing is enabled by rendering a Web service as an RPC-literal Web service, and choosing the correct binding on the Inbound Web Services view.
To make a Web service an RPC-literal Web service
Navigate to the Administration - Web Services screen, Inbound Web Services view.
Select or add a new namespace from the Inbound Web Services list following the instructions in Invoking Siebel Web Services Using an External System.
Create a new inbound service port record in the Service Ports list, as indicated in Invoking Siebel Web Services Using an External System
In the Binding column, select SOAP_RPC_LITERAL from the drop-down list.
DOC-Literal Support
When a SOAP DOC-literal binding is used, the SOAP envelope (the Body element) will contain the document WSDL part without any wrapper elements. The SOAP operation is determined by way of a SOAPAction HTTP header.
For information on the Web services standards supported with Siebel CRM, see the Certifications tab on My Oracle Support.
About One-Way Operations and Web Services
One-Way operations provide a means of sending a request to a Web service with the expectation that a SOAP response will not be returned. The Siebel application provides the ability to publish and consume Web services that implement one-way operations.
One-way operations come into play in both inbound and outbound scenarios:
Inbound. If the Business Service Workflow method does not have any output arguments, then it is a one-way operation.
Outbound. If the service proxy method has no output arguments, then it is a one-way operation.
Consider using one-way operations when data loss is tolerable. In cases involving one-way operations, you send a SOAP request and do not receive a SOAP response. The provider receives the SOAP request and processes it.
Defining Support for One-Way Operations
For information on the Web services standards supported with Siebel CRM, see the Certifications tab on My Oracle Support.
Invoking Siebel Web Services Using an External System
The Siebel application allows enterprises to publish any business service or business process as a Web service. This process is also known as creating an inbound Web service. When the business service or business process is defined, a Siebel administrator navigates to the Administration - Web Services screen, Inbound Web Services view in the Siebel Web Client, and publishes it as a Web service. When the business service or business process is published as a Web service, the administrator generates the Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) document for the newly created Web service. The resulting WSDL document is consumed by an external application to invoke this Web service.
The following inbound Web services topics are covered:
Publishing Inbound Web Services
You can create and publish an inbound Web service using the Inbound Web Services view, as illustrated in the following procedure. You can then use the new inbound Web service when generating a WSDL document.
To create an inbound Web service
Navigate to the Administration - Web Services screen, Inbound Web Services view.
In the Inbound Web Services list, create a new record:
Enter the namespace for your organization’s Web services in the Namespace column.
Note: This step is required for generating various XML documents.Enter the name of the inbound Web service in the Name column.
Select Active in the Status field to enable external applications to invoke the Web service.
Note: If the Web service is inactive, then the external applications cannot invoke the Web service without clearing the cache.(Optional) Enter a description of the Web service in the Comment column.
Create an inbound service port record in the Service Ports list:
Click New and enter the name of the port in the Name column.
Pick the type of object published. If the required type is not available, then add a new type following Step c through Step f; otherwise, move to Step g.
Click New and select the implementation type (Business Service or Workflow Process).
Select the implementation name (the business service or workflow that implements the port type).
Enter a name for the new type in the Name field and click Save.
Click Pick in the Inbound Web Services Port Type Pick Applet to complete the process of adding a new Type.
Select the protocol or transport that will publish the Web service.
Enter the address appropriate for the transport chosen:
For the HTTP transport, enter an HTTP address of the Web service to be invoked, such as:
http://mycompany.com/webservice/orderservice
For the JMS transport, enter the following:
jms://YourQueueName@YourConnectionFactory
For the Local Web Service transport, enter the name of the inbound port.
For the EAI MSMQ Server transport, enter one of the following:
mq://YourQueueName@YourQueueManagerName msmq://YourQueueName@YourQueueMachineName
Note: With the EAI MQSeries, EAI MSMQ, and EAI JMS transports, the request and response must be in the same queue. When publishing using EAI MQSeries, EAI MSMQ, or EAI JMS, you cannot generate WSDL files.
Select the binding that will publish the Web service.
Note: RPC_Encoded, RPC_Literal, and DOC_Literal styles of binding are supported for publishing Web services.Enter a description of the Port in the Comment column.
In the Operations list, create a new operation record for the new service port:
Note: Only the operations created in this step will be published and usable by applications calling the Web service. Other business service methods will not be available to external applications and can only be used for internal business service calls.
Generating a WSDL File
The WSDL file specifies the interface to the inbound Web service. This file is used by Web service clients to support creation of code to call the Siebel Web service.
When you have created a new inbound Web service record you can generate a WSDL document, as described in the following procedure.
To generate a WSDL file
In the Inbound Web Services view, choose the inbound Web services you want to publish, and then click Generate WSDL.
A WSDL file is generated that describes the Web service.
Save the generated file.
Import the WSDL to the external system using one of the following utilities:
In Microsoft VisualStudio.Net, use the wsdl.exe utility, for example:
wsdl.exe /l:CS mywsdlfile.wsdl
In Apache AXIS, use the wsdl2java utility, for example:
java org.apache.axis.wsdl.WSDL2Java mywsdlfile.wsdl
In IBM WSADIE, depending on the version, add the WSDL file to the Services perspective and then run the Create Service Proxy wizard.
In Oracle JDeveloper, use the Java Web Service from WSDL wizard.
Note: These utilities only generate proxy classes. Developers are responsible for writing code that uses the proxy classes.
About the Relationship of Port Types and Operations
Port types are defined in the Inbound Web Services view, in the Service Ports applet. The Type and Business Service/Business Process Name fields are based on the same dynamic picklist. Opening it displays all the port types. Here you can create or delete port types.
After a port type has been created, you can create the operations that the port type will define. This is done in the Operations applet. Clicking the New button displays any operations that are currently defined for the specified port type. You can expose as many business service methods as you want, but once defined they cannot be deleted or modified through the picklist or through the Operations applet. You can only delete the link between the specified port and operation.
The business service methods are read from the runtime repository. When an operation is defined, a new record is added to the S_WS_OPERATION table, with the Method Display Name field set to the business service method.
Subsequent attempts to add new operations display the dynamic picklist of operations stored in the S_WS_OPERATION table. Any changes to the business service definition made after the Web service operation was created are not reflected, because operations are read from the database.
When generating a WSDL, the generator reads the port type definition from the database and retrieves all associated operations. It processes the operations and then checks them against the business service methods in the runtime repository. Any discrepancy causes an error to be thrown.
This design allows port types to be shared across Web services. Changes to a port type (including the associated operations) made in one Web service definition do not affect other Web services. You can only make changes to a port type (such as deletion) after no Web services are pointing to it.
Deleting Operations by Deleting the Port Type
Operations themselves cannot be deleted after being created. The only way to delete an operation is to delete the associated port type.
To delete a port type and its operations
Delete all Service Port records that use this port type.
Click New to display the picklist.
Delete the port type, which will trigger the deletion of all associated operations.
About Defining the Web Service Inbound Dispatcher
The Web Service Inbound Dispatcher is a business service that is called by an inbound transport server component (or an outbound Web service dispatcher locally). This business service analyzes input SOAP messages containing XML data, converts the XML data to an XML hierarchy, maps the XML hierarchy to business service method arguments, and calls the appropriate method for the appropriate service (business service or process). After the called method finishes its execution, the Web Service Inbound Dispatcher converts the output arguments to XML data, and returns the XML embedded in the SOAP envelope. During this process, any errors are returned as SOAP fault messages.
SOAP Fault Message Example
When the code within a Web service raises an exception anywhere in the Web services stack, the exception is caught and transformed into a SOAP fault message.
For instance, the following example illustrates a particular case where mustUnderstand has been set to 1; and therefore, the header is interpreted as being mandatory. However, the corresponding filter and handler to process the header was not defined. This causes a SOAP fault message to be returned.
The format of the Siebel SOAP fault message for this example follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
- <SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
- <SOAP-ENV:Body>
- <SOAP-ENV:Fault>
<faultcode>SOAP-ENV:MustUnderstand</faultcode>
<faultstring>Unable to process SOAP Header child element
'newns:AnotherUselessHeader' with 'mustUnderstand="1"'(SBL-EAI-08000)
</faultstring>
- <detail>
- <siebelf:errorstack xmlns:siebelf="http://www.siebel.com/ws/fault">
- <siebelf:error>
<siebelf:errorsymbol />
<siebelf:errormsg>Unable to process SOAP Header child element
'newns:AnotherUselessHeader' with 'mustUnderstand="1"'(SBL-EAI-08000)
</siebelf:errormsg>
</siebelf:error>
</siebelf:errorstack>
</detail>
</SOAP-ENV:Fault>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
For more information on SOAP fault handling, see About SOAP Fault Schema Support.
Invoking Web Services on the Siebel Mobile Web Client
The Siebel Mobile Web Client can serve the same Web services as those deployed on the Siebel Server, while protecting access through simple authentication. This feature allows developers to integrate external applications with Siebel Business Applications and test their integrations, without having to install an entire Siebel Enterprise.
The Web service functionality is an extension of the Siebel Mobile Web Client, and runs as a separate siebel.exe process. This second siebel.exe process is started by the Siebel Mobile Web Client as its child process. The child process listens on the specified port for all Web service requests. The Web service requests are processed and sent to the EAI Inbound Dispatch Service, and then the response is sent back to the Siebel Mobile Web Client. The child process exits when the Siebel Mobile Web Client exits.
Exceptions to Web Service Support
The Siebel Mobile Web Client provides the same Web service support as an EAI-enabled Siebel Server, with the following exceptions:
The Web service consumer, such as soapUI, must be on the same computer as the Siebel Mobile Web Client.
HTTPS is not supported.
The Stateless, Stateful, and ServerDetermine session types are not supported. Only the None session type is supported.
Concurrent requests are not serviced in parallel. There is only one siebel.exe process that serves Web services, so concurrent requests are queued.
Note: When multiple Siebel Mobile Web Client instances are running, there will not be multiple processes serving Web services. However, if the port number is modified in the application configuration file, then with the next Siebel Mobile Web Client instance a new siebel.exe process will start and listen to requests on the new port specified in the configuration file.Anonymous Web service requests are not supported.
Chunked HTTP requests and responses are not supported.
Supported Authentication Formats
User authentication is the same as for the Siebel Mobile Web Client. The following authentication formats are supported:
Username and password in the URL
Username and password inside the SOAP header
Username and password inside the Web Services-Security (WS-Security) header
Authentication Formats That Are Not Supported
The following authentication formats are not supported:
Single sign-on (SSO)
Stateful Web services using separate login and logout requests
Stateless Web services using a session token
Enabling Web Services on the Siebel Mobile Web Client
Two new parameters have been added to the application configuration file to enable the Web service functionality: EnableWebServices and WebServicesPort.
To enable Web services on the Siebel Mobile Web Client
Set the following parameters in the [Siebel] section of the application configuration file, such as uagent.cfg:
Parameter Value EnableWebServices
TRUE
WebServicesPort
Port number on which to listen. The default is 2330.
The next time the Siebel Mobile Web Client starts, it will start the siebel.exe child process. After the process has started, it can send requests and receive responses.
Starting the siebel.exe Process From the Command Line
When it is not required to start a Siebel Mobile Web Client instance, you can start the siebel.exe process independently using the command line.
To start the siebel.exe process from the command line
Enter the following command:
SIEBEL_CLIENT_ROOT\bin\siebel.exe /l <language_code> /c <configuration_file> /u <username> /p <password> /d <datasource_in_cfg> /webservice <port_number>
For example:
C:\Siebel\client\bin\siebel.exe /l enu /c enu\uagent.cfg /u SADMIN /p SADMIN /d Sample /webservice 2330
Confirming that the siebel.exe Process is Listening
You can use the netstat utility from the DOS prompt to determine whether the siebel.exe child process is listening for Web service calls.
To confirm that the siebel.exe process is listening
From the DOS prompt, type the following:
netstat -a -p TCP
Examine the output for the port number you set in the application configuration file, for example:
TCP mycomputer:2330 mycomputer.mycompany.com:0 LISTENING
LISTENINGindicates that the siebel.exe process is listening for Web service calls.
Invoking Web Services on the Siebel Mobile Web Client
You can invoke Web services on the Siebel Mobile Web Client by passing credentials in the URL, in the SOAP header, or in the WS-Security header.
Example of Passing User Credentials in the URL
The URL format is:
http://<host>:<port>?SWEExtSource=WebService&Username=<username> &Password=<password>
For example:
http://localhost:2330?SWEExtSource=WebService&Username=<username> &Password=<password>
The following is an example of a request:
soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:asi="http://siebel.com/asi/"> <soapenv:Header/> <soapenv:Body> <asi:SiebelAccountQueryById> <PrimaryRowId>99-28B0A</PrimaryRowId> </asi:SiebelAccountQueryById> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>
Example of Passing User Credentials in the SOAP Header
The URL format is:
http://<host>:<port>?SWEExtSource=WebService&WSSOAP=1
For example:
http://localhost:2330?SWEExtSource=WebService&WSSOAP=1
The following is an example of a request:
soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:asi="http://siebel.com/asi/"> <soapenv:Header> <UsernameToken xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">SADMIN</UsernameToken> <PasswordText xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">SADMIN</PasswordText> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">None</SessionType> </soapenv:Header> <soapenv:Body> <asi:SiebelAccountQueryById> <PrimaryRowId>99-28B0A</PrimaryRowId> </asi:SiebelAccountQueryById> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>
Example of Passing User Credentials in the WS-Security Header
The URL format is:
http://<host>:<port>?SWEExtSource=SecureWebService&WSSOAP=1
For example:
http://localhost:2330?SWEExtSource=SecureWebService&WSSOAP=1
The following is an example of a 2002 request:
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soapenv="http:// schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:asi="http://siebel.com/asi/"> <soapenv:Header> <wsse:Security xmlns:wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/secext"> http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/secext <wsse:UsernameToken xmlns:wsu="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/utility"> <wsse:Username>SADMIN</wsse:Username> <wsse:Password Type="wsse:PasswordText">SADMIN</wsse:Password> </wsse:UsernameToken> </wsse:Security> </soapenv:Header> <soapenv:Body> <asi:SiebelContactQueryById soapenv:encodingStyle="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ soap/encoding/"> <PrimaryRowId xsi:type="xsd:string">04-LLSQ5</PrimaryRowId> </asi:SiebelContactQueryById> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>
The following is an example of a 2004 request:
<wsse:Security mustUnderstand="1" xmlns:wsse="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/
01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecuritysecext-1.0.xsd">
<wsse:UsernameToken wsu:Id="UsernameToken-zsXRc97TujDINUug8ibD2Q22"
xmlns:wsu="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wsswssecurity-
utility-1.0.xsd">
<wsse:Username>SADMIN</wsse:Username>
<wsse:Password Type="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-
usernametoken-profile-1.0#PasswordText">SADMIN</wsse:Password>
<wsse:Nonce EncodingType="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-
200401-wss-soap-message-security-1.0#Base64Binary">f61vAYvDD0t2sUFEmXSVU+FlOvA=</
wsse:Nonce>
<wsu:Created>2014-05-13T17:27:33Z</wsu:Created>
</wsse:UsernameToken>
</wsse:Security>
Consuming External Web Services Using Siebel Web Services
An outbound Web service acts as a proxy to a Web service published by an external application. This process creates services that you can then use in a business process, virtual business component (VBC), run-time event, or any other mechanism within the Siebel application that can call a business service.
Consumption of external Web services is a two-step process:
A WSDL file is imported using Siebel Tools.
The consumed Web service is published for run-time clients to use.
Additional steps can involve defining VBCs based on the Web service.
The following outbound Web services topics are covered:
Creating an Outbound Web Service Based on a WSDL File
Consumption of external Web services is accomplished using the WSDL Import Wizard in Siebel Tools. The procedure in this topic describes how to use this wizard to read an external WSDL document.
As of Siebel Innovation Pack 2014, you can import the following kinds of cyclic WSDL:
Different namespace for same type and same element name
Different element name for same type and same namespace
Indirect cycle
Direct cycle with same element name, type, and namespace
Note the following restrictions on WSDL import:
The WSDL Import Wizard expects each schema to have a unique target namespace. Using the same namespace for more than one schema will generate an error.
Importing a WSDL with a mix of different SOAP operation styles (for example, RPC and Document) within one service port binding is not supported. Modify the WSDL to have a service port binding defined for each SOAP operation style.
To create an outbound Web service based on a WSDL file
In Siebel Tools, create a new project and lock the project, or lock an existing project.
From the File menu, choose New Object to display the New Object Wizards dialog box.
Click the EAI tab, and then double-click Web Service.
The WSDL Import Wizard appears.
Select the project where you want the objects to be held after they are created from the WSDL document.
Specify the WSDL document that contains the Web service or Web services definition that you want to import.
Specify the file where you want to store the run-time data extracted from the WSDL document or accept the default.
Specify the log file where you want errors, warnings, and other information related to the import process to be logged or accept the default.
(Optional) Select the Process Fault Schema checkbox, and specify an existing Fault Integration Object Name, to create and reuse SOAP fault integration objects.
Note: SOAP fault integration objects are prepended with Fault_.For more information on SOAP fault integration objects, see About SOAP Fault Schema Support.
Click Next.
A summary of your import information, as well as any errors, appears.
(Optional) Select the Deploy the Integration Object(s) and the Proxy Business Service(s) checkbox to deploy these objects to the Siebel run-time database.
Deployed integration objects are shown in the Administration - Web Services screen, Deployed Integration Objects view in the Siebel client. Deployed business services are shown in the Administration - Business Services screen in the Siebel client.
Note: If you deploy integration objects while the Siebel Server is running, then you must subsequently clear the Web services cache in the Administration - Web Services screen, Inbound (or Outbound) Web Services view.Click Finish to complete the process of importing the business service into the Siebel repository.
This procedure generates three objects in the Siebel repository:
An outbound proxy business service of CSSWSOutboundDispatcher class. This service acts as a client-side implementation of the Web service and includes the operations and the arguments to the operations defined in the WSDL document.
Note: For RPC services, the order of input arguments is important. You can set the order through the Preferred Sequence property of the business service method argument in Siebel Tools. By specifying this parameter, the outbound dispatcher makes sure that the sequence parameters for an operation are in the correct order. The Preferred Sequence property is only supported with outbound services.Integration objects, representing input and output parameters of the service methods, if any of the operations require a complex argument (XML Schema) to be passed. If the service does not use complex arguments, then no integration object definitions will be created.
A Web service administration document (XML file) containing the run-time Web service administration data to be imported into the Siebel Web Client, using the Outbound Web Services view of the Administration - Web Services screen.
Note: This is applicable only for the DR environment.The purpose of the document is to allow administrators to modify run-time parameters such as the URL and encoding rules. The data contained within the document is used by the Web Services Dispatcher to assemble the SOAP document, to set any HTTP headers required (for example, soapAction), and to route the request to the correct URL. For information on how to migrate to runtime environment, see Migrating Outbound Web Services.
Migrating Outbound Web Services
You can migrate outbound web services to a run-time environment.
To migrate outbound web services, perform the following tasks:
-
Create migration rules with the following tables:
S_WS_WEBSERVICE
S_WS_OPERATION
S_WS_BNDNG_DTL
S_WS_PORT
S_WS_PORT_TYPE
S_WS_PORT_OPER
Export the created rules to generate the datamig.inp and datamig.rul files.
Create a migration plan for export and import using Application Data Service. For more information, see “Creating a Migration Plan” in the Database Upgrade Guide.
Note: You must select the Migration Application Data Service as a resource while creating a Migration plan. To migrate the outbound web services, you must execute this Migration Plan. For more information, see “Executing a Siebel Migration Plan” in the Database Upgrade Guide.
Creating an Outbound Web Service Manually
WSDL does not provide native bindings for EAI MQSeries and EAI MSMQ transports. If your business requires you to pick up messages using these transports, then you can manually create an outbound Web service definition and update a corresponding business service in Siebel Tools to point to that Web service. The following procedure describes this process.
To manually create a new outbound Web service
Navigate to the Administration - Web Services screen, Outbound Web Services view.
In the Outbound Web Services list applet, create a new record:
Enter the namespace of the Web service in the Namespace column.
Enter the name of the Web service in the Name column.
Select Active or Inactive in the Status field.
Enter a description of the Web service in the Comment column.
Note: When importing an external Web service, you do not have to specify the proxy business service, integration objects, or the run-time parameters.
In the Service Ports list applet, create a new outbound service ports record:
Enter the name of the Web service port in the Name column.
Select a transport name for the protocol or queuing system for the Transport.
Enter the address for the transport chosen to publish the Web service:
The URL format to publish using HTTP is:
http://webserver/eai_anon_lang/ start.swe?SWEExtSource=SecureWebService&SWEExtCmd=Execute
where:
webserver is the name of computer where the Siebel Web Server is installed
lang is the default language of the Object Manager that handles the request
The format to publish using the EAI JMS Transport is:
jms://queue name@connection factory
where:
queue name is the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) name of the queue
connection factory is the JNDI name of the JMS connection factory
Note: The JNDI name varies depending upon the JMS provider and your implementation.The format to publish over the EAI MQSeries or EAI MSMQ transport is:
mq://queue name@queue manager name msmq://queue name@queue machine name
where:
queue name is the name of the queue that is specified by either the EAI MQ Series or the EAI MSMQ transport at the time of its design
queue manager name is the name of the EAI MQSeries Transport queue manager
queue machine name is the name of the computer that owns the queue specified by the physical queue name for the EAI MSMQ Transport
Note: When publishing using EAI MQSeries or EAI MSMQ, you cannot generate WSDL files.
For the Local Workflow Process or Local Business Service transport, enter the name of the workflow or business service to be called.
For the Local Web Service transport, enter the name of the inbound port.
Select the binding that will publish the Web service.
Note: RPC_Encoded, RPC_Literal, DOC_Literal, and Property Set styles of binding are supported for publishing Web services.Use the Property Set binding when the input property set to the proxy service is forwarded without changes to the destination address. This is intended primarily for use in combination with the Local Workflow Process or Local Business Service transport to avoid the overhead of processing XML.
Enter a description of the port in the Comment column.
In the Operations list applet, create a new operation record for the new service port you created in Step 3:
Select the name of the business service method in the Method Display Name column to complete the process.
Select the authentication type from the drop-down list.
Note: For more information on using the Username/Password Authentication Type, see About Web Services Security Support.
Generate the WSDL file. For information, see Generating a WSDL File.
Updating the Outbound Proxy Business Service
When you have created your outbound Web service, update a corresponding outbound proxy business service in Siebel Tools to point to that Web service. This associates the outbound proxy business service and the outbound Web service. The following procedure outlines the steps you take to accomplish this task.
To update an outbound Web service proxy business service to point to an outbound Web service
In Siebel Tools, select the outbound Web service proxy business service you want to use to call your outbound Web service.
Add the following user properties for this business service and set their values based on the outbound service port of your Web service:
siebel_port_name
siebel_web_service_name
siebel_web_service_namespace
Integration Objects as Input Arguments to Outbound Web Services
It is recommended that the property set used as an input argument to the outbound Web service have the same name as the input argument's outbound Web service proxy.
You can do this using one of the following options:
Change the output from all your business services that provide the input to the outbound Web service from SiebelMessage to the actual outbound Web service argument name specified in Siebel Tools.
Change the output from your business services in Siebel Tools, as well as the name of the property set child that contains the integration object instance.
Change the property set type name from SiebelMessage to the actual outbound Web service argument name by using Siebel eScript on a business service before calling the outbound Web service.
The following Siebel eScript example shows how to pass an integration object and a session token to a proxy business service using the integration object as an input argument. The script is written on the Service_PreInvokeMethod event of the proxy business service.
function Service_PreInvokeMethod (MethodName, Inputs, Outputs) {
var childPS;
var newInputPS;
var svc;
for (var i = 0; i < Inputs.GetChildCount(); i++) {
if(Inputs.GetChild(i).GetType() == "SiebelMessage") {
childPS = Inputs.GetChild(i);
}
}
childPS.SetType("myBusSvcMethod:myIntegrationObject");
newInputPS = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
newInputPS.SetProperty("myBusSvcMethod:sessionToken:string",
Inputs.GetProperty("token"));
newInputPS.AddChild(childPS);
svc = TheApplication().GetService("myBusSvc");
svc.InvokeMethod("myBusSvcMethod", newInputPS, Outputs);
return (CancelOperation); // must use CancelOperation with custom methods
}
Web Services Support for Transport Headers
The outbound Web service dispatcher supports input arguments for user-defined (or standard) transport headers.
The following is the format for the outbound Web service dispatcher input arguments:
Name: siebel_transport_header:headerName
Value: Header value
The following table shows examples of input arguments for transport headers.
Table Examples of Transport Headers as Input Arguments
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
siebel_transport_header:UserDefinedHeader |
myData |
siebel_transport_header:Authorization |
0135DFDJKLJ |
Web Services Support for Transport Parameters
The outbound Web service dispatcher supports input arguments for transport parameters defined in proxy business services such as EAI HTTP Transport.
The following is the format for the outbound Web service dispatcher input arguments:
Name: siebel_transport_param:parameterName
Value: Parameter value
The following table shows examples of input arguments for transport parameters.
Table Examples of Transport Parameters as Input Arguments
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
siebel_transport_param:HTTPRequestMethod |
HTTP method to use with the data request, such as Post or Get |
siebel_transport_param:HTTPRequestURLTemplate |
Template for the request URL, which is the address to which the data is sent or from which a response is requested, for example: http://mycompany.com/* |
For more information on transport parameters, see the topic on EAI HTTP Transport business service method arguments in Transports and Interfaces: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.
SHA2 Support for Outbound Web Service
Siebel supports SHA2 for outbound calls through the framework described here. This support for SHA2 is through the introduction of a Config Agent between the Siebel Server and the external Web Server. The Config Agent accepts local requests from mainwin within the Siebel server and transfers the same to the external Web Server in SHA2 as seen in the following figure. To configure certificates for the Config Agent, see the chapter on communications and data encryption in the Siebel Security Guide.
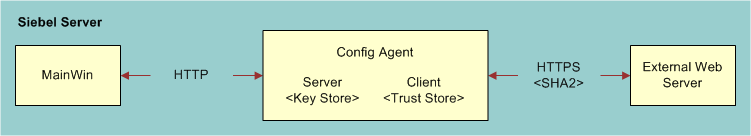
The transfer is made possible by a servlet named outboundeai that resides on the Config Agent. This servlet copies the outbound request body and Siebel server header information and transfers it to the external Web Server. The servlet also collects the response from the Web Server and transfers it back to the Siebel server as seen in the following figure.
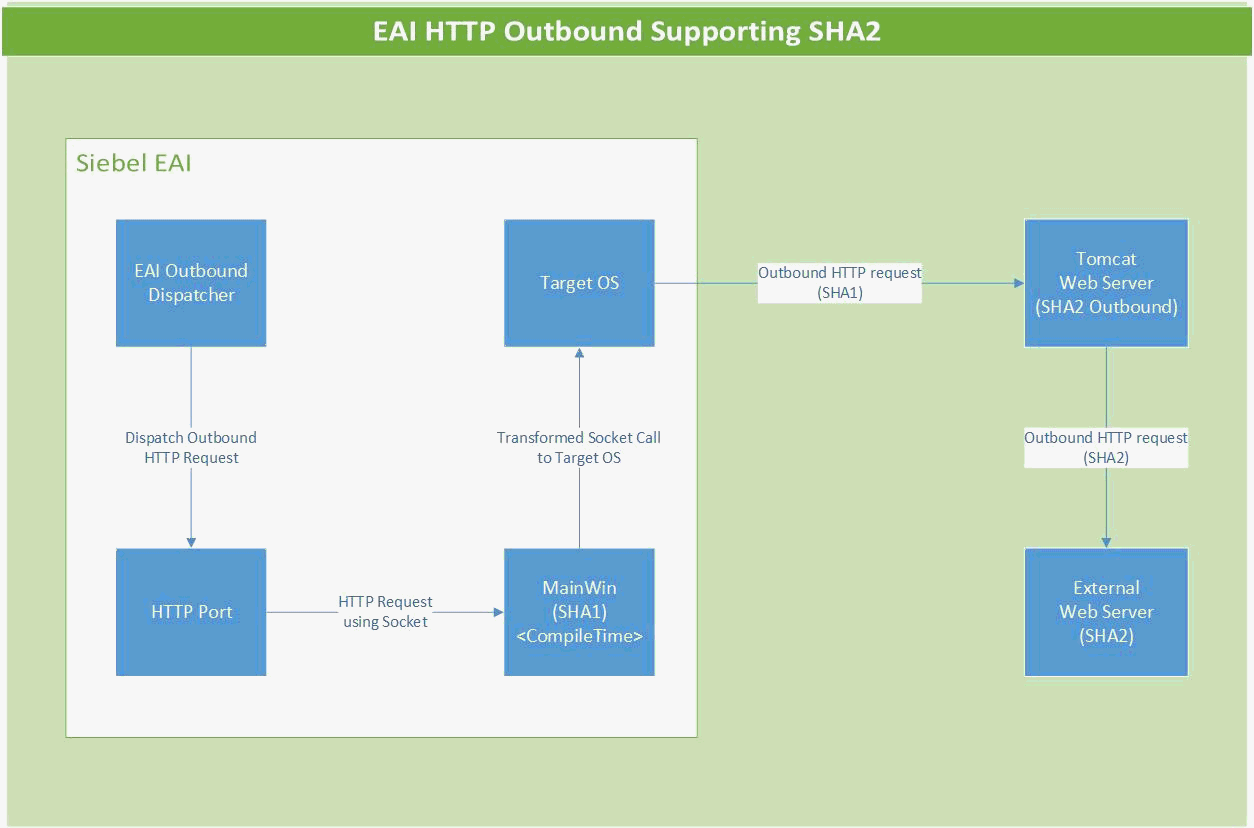
Configuring Siebel Server and Config Agent for SHA2 Outbound
The SHA2 support for HTTP outbound is achieved via configuring a named subsystem of type JavaContainerSubSys. The name of this named subsystem is then set to the value of the EAIOutboundSubSys component parameter as described in the following procedure.
To configure the named subsystem for SHA2 support in outbound
Go to the Siebel Server Manager and search on OUTBOUNDSHA2 as follows:
list param for named subsystem OUTBOUNDSHA2
where:
OUTBOUNDSHA2 is the name of the new named subsytem
Set the name of this named subsystem as value of the EAIOutboundSubSys component parameter:
change param EAIOutboundSubSys=OUTBOUNDSHA2 for comp SCCObjMgr_enu
where:
SCCObjMgr_enu is the Siebel Object Manager component
When the user makes an outbound call, the EAI Outbound Dispatcher checks for the value of the component parameter.
If the value is present, the dispatcher will make a http call to the servlet hosted in the Config Agent specified in CONTAINERURL and the Config Agent will make the https call to the external Web Server.
If the value is not present for the component parameter or the named subsystem parameter, the dispatcher makes a direct https call to the external Web Server.
Restart component.
stop comp sccobjmgr_enu start comp sccobjmgr_enu
Parameters for the named subsystem
The named subsystem has three parameters as seen in the following table.
Table Parameters for the named subsystem
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
CLASSPATH |
Not applicable. |
OPTIONS |
Not applicable. |
CONTAINERURL |
URL for siebel-eaioutbound.war hosted on the Config Agent. |
Using the Local Business Service
In many instances, Web services use specialized SOAP headers for common tasks such as authentication, authorization, and logging. To support this common Web service extensibility mechanism, the Local Business Service transport for outbound Web services can be used. When specified as a transport, the Web services infrastructure will route the message to the specified business service for additional processing and delivery to the Web service endpoint as shown in the first half of the following figure.
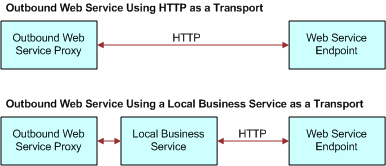
If the Web service to be invoked is within the sample application, then no need exists to call such a Web service by using HTTP (or anything else).
An example of using a local business service is a department store developing a workflow in Siebel Tools to perform credit card checks before purchases. The purchase is entered into the sales register along with the credit card information (the outbound Web service proxy). If the credit card is issued by the department store, then the information can be checked using the internal database (a local business service). The send request stays within the department store’s own computer network. An approval or denial is the output (the Web service endpoint). If the credit card is a MasterCard or a Visa card, then the card information is passed over the Internet for verification. No local business service would be involved.
The input to the local business service is a property set representation of the SOAP request. Once within the local business service, additional SOAP headers can be added to address infrastructure requirements by direct modification of the input property set by using Siebel eScript or Siebel VB.
The following local business service topics are also discussed:
Script Example for a Local Business Service
A portion of the sample script for a local business service used to add a custom SOAP header to an outbound Web service request is shown in the following example. Local variables, error handling, and object destruction are omitted for clarity.
// Create the SOAP header.
soapHdr.SetType("SOAP-ENV:header");
// Populate the SOAP header elements.
appId.SetType("ns1:ApplicationID");
appId.SetValue("Siebel");
pwd.SetType("ns1:PWS");
pwd.SetValue("123456789");
langCd.SetType("ns1:Lang");
langCd.SetValue("ENU");
uName.SetType("ns1:userID");
uName.SetValue("first.last@mycompany.com");
// Populate the profileHeader element.
profileHeader.SetType("authHeader");
profileHeader.SetProperty("xmlns:ns1", "http://siebel.com/authHeaders");
profileHeader.AddChild(appId);
profileHeader.AddChild(pwd);
profileHeader.AddChild(langCd);
profileHeader.AddChild(uName);
// SOAP header property set. Once this is complete, add the SOAP header as a child
of the Input property set (which contains the SOAP:body).
soapHdr.InsertChildAt(profileHeader, 0)
Inputs.InsertChildAt(soapHdr, 0);
// Convert the property set to a well-defined XML document.
// Using the XML Hierarchy Converter: must add a child element of type XMLHierarchy.
childPS.SetType("XMLHierarchy");
childPS.AddChild(Inputs);
inPs.AddChild(childPS);
inPs.SetProperty("EscapeNames", "FALSE");
inPs.SetProperty("GenerateProcessingInstructions", "FALSE");
xmlSvc.InvokeMethod("XMLHierToXMLDoc", inPs, outPs);
// Proxy the request through a trace utility to view the SOAP document.
// Set custom HTTP header - SOAPAction
outPs.SetProperty("HTTPRequestURLTemplate", "http://localhost:9000/search/beta2");
outPs.SetProperty("HTTPRequestMethod", "POST");
outPs.SetProperty("HTTPContentType", "text/xml; charset=UTF-8");
outPs.SetProperty("HDR.SOAPAction","customSOAPActionValue");
// Invoke the Web service using the standard HTTP protocol.
httpSvc.InvokeMethod("SendReceive", outPs, hpOut);
// Convert the SOAP document to a property set using the XML Converter, returning
the SOAP header and SOAP body.
xmlCtr.InvokeMethod("XMLToPropSet", hpOut, Outputs);
…
After you have created your business service, deliver its workspace.
SOAP Document Generated by the Local Business Service
The following example displays the resulting SOAP document generated by the Script Example for a Local Business Service. The addition of the authHeader element to the SOAP header corresponds to the structure defined in the sample code sections that populate the SOAP header and profileHeader elements.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV=http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/ xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <SOAP-ENV:header> <authHeader xmlns:ns1="http://siebel.com/authHeaders"> <ns1:ApplicationID>Siebel</ns1:ApplicationID> <ns1:PWS>123456789</ns1:PWS> <ns1:Lang>ENU</ns1:Lang> <ns1:userID>first.last@mycompany.com</ns1:userID> </authHeader> </SOAP-ENV:header> <SOAP-ENV:Body> … </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Using the Local Business Service in an Outbound Web Service
You use the Outbound Web Services view in the Administration - Web Services screen to configure an outbound Web service to use the local business service created by Script Example for a Local Business Service.
To use the local business service in an outbound Web service
In the Siebel client, navigate to the Administration - Web Services screen, Outbound Web Services view.
In the Outbound Web Services list, select the desired outbound Web service.
In the Service Ports list, set the following properties:
Name Value Transport
Local Business Service
Address
Name of the local business service
Restart the Siebel Server component to allow the changes to take effect.
About XML Schema Support for the xsd:any Tag
In the current framework, WSDL Import Wizard makes use of the XML Schema Import Wizard to create integration objects to represent hierarchical data. Integration objects are meant to be strongly typed in the Siebel application. You are now able to import a schema that uses the xsd:any tag, which indicates a weakly typed data representation, and to possibly create an integration object from it.
Mapping the xsd:any Tag in the WSDL Import Wizard
In the WSDL Import Wizard, two possible mappings exist for the xsd:any tag. The tag can be mapped as an integration component or as an XMLHierarchy on the business service method argument.
The xsd:any tag can contain a namespace attribute. If the value for that attribute is known, then one or more integration components or even an integration object can be created. If the value for that attribute is not known, then the business service method argument for that particular wsdl:part tag is changed to data type Hierarchy, consequently losing any type information.
The value for the attribute being known refers to the following situations:
A schema of targetNamespace value, being the same as that of the namespace attribute value, is imported by way of the xsd:import tag.
A schema of targetNamespace value, being the same as that of the namespace attribute value, is a child of the wsdl:types tag.
For the case of being known, all the global elements belonging to the particular schema of that targetNamespace will be added in place of the tag. One or more integration components can potentially be created.
Another tag similar to the xsd:any tag is the xsd:anyAttribute tag. The mapping is similar to that of the xsd:any tag. In this case, one or more integration component fields can be created.
The xsd:anyAttribute tag has a namespace attribute. If the namespace value is known (the conditions for being known were previously noted in this topic), then all the global attributes for that particular schema will be added in place of this tag. Therefore, one or more integration component fields can potentially be created.
In the case where the namespace value is not known, then the wsdl:part tag that is referring to the schema element and type will be created as data type Hierarchy.
Mapping the xsd:any Tag in the XML Schema Wizard
For the case of the XML Schema Wizard, there is only one possible mapping for the xsd:any tag, namely as an integration component.
The xsd:any tag can contain a namespace attribute. If the value for that attribute is known, then one or more integration components or even an integration object can be created. If the value for that attribute is not known, then an error will be returned to the user saying that the integration object cannot be created for a weakly typed schema.
The value for the attribute being known refers to the situation of the XML Schema Wizard where a schema of targetNamespace value, being the same as that of the namespace value, has been imported by way of the xsd:import tag.
For the case of being known, all the global elements belonging to the particular schema of that targetNamespace will be added in place of the tag. So, one or more integration components can potentially be created.
The mapping of the xsd:anyAttribute is similar to that of the xsd:any tag. In this case, one or more integration component fields can be created.
The xsd:anyAttribute tag has a namespace attribute. If the namespace value is known (the condition for being known was previously noted in this topic), then all the global attributes for that particular schema will be added in place of this tag. Therefore, one or more integration component fields can potentially be created.
In the case where the namespace value is not known, then an error is returned to the user stating that an integration object cannot be created for a weakly typed schema.
Examples of Invoking Web Services
The following two examples show sample flows of how to call an external Web service from a Siebel application, or how to call a Siebel Web service from an external application.
Invoking an External Web Service Using Workflow or Scripting
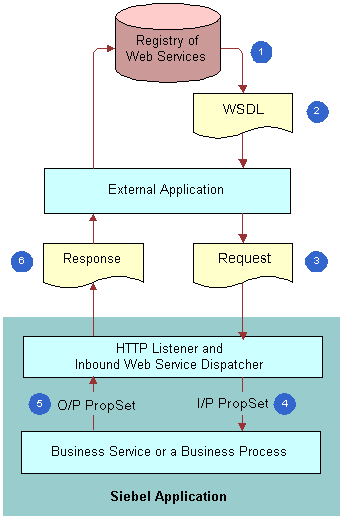
As illustrated in the following figure, the following steps are executed to call an external Web service:
The developer obtains the Web service description as a WSDL file.
The WSDL Import Wizard is called.
The WSDL Import Wizard generates definitions for outbound proxy, integration objects for complex parts, and administration entries.
The Outbound Web Service proxy is called with the request property set.
The request is converted to an outbound SOAP request and sent to the external application.
The external application returns a SOAP response.
The SOAP response is converted to a property set that can be processed by the caller, for example, Calling Function.
- The following example shows how to invoke Web services using Siebel eScript:
function Service_PreCanInvokeMethod (MethodName, &CanInvoke) {if (MethodName == "invoke") {CanInvoke = "TRUE";return (CancelOperation);}elsereturn (ContinueOperation);}function Service_PreInvokeMethod (MethodName, Inputs, Outputs) {if (MethodName == "invoke") {var svc = TheApplication().GetService("CustomerDBClientSimpleSoap");var wsInput = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();var wsOutput = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();var getCustInput = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();var listOfGetCustomerName = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();var getCustomerName = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();try {// obtain the customer ID to query on. This value will be provided in the input property setvar custId = Inputs.GetProperty("custId");// set property to query for a customer ID with a value of '1'getCustomerName.SetType("getCustomerName");getCustomerName.SetProperty("custid", custId);// set Type for listOfGetCustomerNamelistOfGetCustomerName.SetType("ListOfgetCustomerName");// set Type for getCustInputgetCustInput.SetType("getCustomerNameSoapIn:parameters");// assemble input property set for the service.listOfGetCustomerName.AddChild(getCustomerName);getCustInput.AddChild(listOfGetCustomerName);wsInput.AddChild(getCustInput);// invoke the getCustomerName operationsvc.InvokeMethod("getCustomerName", wsInput, wsOutput);// parse the output to obtain the customer full name check the type element on each PropertySet (parent/child) to make sure we are at the element to obtain the customer nameif (wsOutput.GetChildCount() > 0) {var getCustOutput = wsOutput.GetChild(0);if (getCustOutput.GetType() == "getCustomerNameSoapOut:parameters") {if (getCustOutput.GetChildCount() > 0) {var outputListOfNames = getCustOutput.GetChild(0);if (outputListOfNames.GetType() == "ListOfgetCustomerNameResponse") {if (outputListOfNames.GetChildCount() > 0) {var outputCustName = outputListOfNames.GetChild(0);if (outputCustName.GetType() == "getCustomerNameResponse") {var custName = outputCustName.GetProperty("getCustomerNameResult");Outputs.SetProperty("customerName", custName);}}}}}}return (CancelOperation);}catch (e) {TheApplication().RaiseErrorText(e);return (CancelOperation);}}elsereturn (ContinueOperation);}
Invoking a Siebel Web Service from an External Application
As illustrated in the following figure, the following steps are executed to invoke a Siebel Web service from an external application:
The WSDL document for an active Web service is published in the Siebel Inbound Web Services view. To allow processing of the Web service requests, the developer has to make sure:
The Web Server and the Siebel Server are up and running.
The appropriate setup is done in the Siebel Server.
In the external application, the WSDL document is imported to create a proxy that can be used to invoke the Siebel Web service from Step 1.
The external application sends the SOAP request into the Siebel application.
The Web Service Inbound Dispatcher converts the SOAP request to a property set. Depending on the inbound Web service configuration, the property set is passed to a business service or a business process.
The property set is returned from the business service or business process to the Web Service Inbound Dispatcher.
Response is converted to a SOAP message and sent back to the invoking external application.

The following is an example of invoking a Siebel-published Web service using .NET.
// Removed using declaration
namespace sieOppClnt {
public class sieOppClnt : System.Web.Services.WebService {
public siebOptyClnt() {
InitializeComponent();
}
// WEB SERVICE CLIENT EXAMPLE
/* The optyQBE returns a list of opty based upon the required input params. Because
the input to the Siebelopty.QueryByExample method uses an Input/Output param,
ListOfInterOptyIntfaceTopElmt will be passed by ref to Siebel. To add the Siebel
Opportunity Web Service definition to the project, the wsdl.exe utility was run
to generate the necessary helper C# class for the service definition. */
[WebMethod]
public ListOfInterOptyIntfaceTopElmt optyQBE(string acctName, string acctLoc,
string salesStage) {
Siebelopty svc = new Siebelopty();
ListOfInterOptyIntfaceTopElmt siebelMessage = new
ListOfInterOptyIntfaceTopElmt();
ListOfInteroptyInterface optyList = new ListOfInteroptyInterface();
opty[] opty = new opty[1];
opty[0] = new opty();
opty[0].Account = acctName;
opty[0].AccountLocation = acctLoc;
opty[0].SalesStage = salesStage;
/* Assemble input to be provided to the Siebel Web service. For the sake of
simplicity the client will query on the Account Name, Location, and Sales
Stage. Ideally, also check to make sure that correct data is entered. */
optyList.opty = opty;
siebelMessage.ListOfInteroptyInterface = optyList;
// Invoke the QBE method of the Siebel Opportunity business service
svc.SiebeloptyQBE(ref siebelMessage);
/* Return the raw XML of the result set returned by Siebel. Additional
processing could be done to parse the response. */
return siebelMessage;
}
}
}
About Web Services Security Support
Oracle endorses the industry standard known as the Web Services Security (WS-Security) specification. The WS-Security specification is a Web services standard that supports, integrates, and unifies multiple security models and technologies, allowing a variety of systems to interoperate in a platform- and language-independent environment.
By conforming to industry standard Web service and security specifications, secure cross-enterprise business processes is supported. You can deploy standards-based technology solutions to solve specific business integration problems.
For security support, you can also apply access control to business services and workflows. For more information on configuring access control, see Siebel Security Guide.
Configuring the Siebel Application to Use the WS-Security Specification
To use the WS-Security specification in the Siebel application, two parameters, UseAnonPool and Impersonate, must be set. An example of configuring WS-Security for Siebel inbound Web services follows.
To configure the Siebel application to use the WS-Security specification
Check Configure Anonymous Pool parameter in the basic information section of the eai_anon application in the AI profile.
Start the Siebel Server.
Navigate to the Administration - Server Configuration screen, Enterprises view, and then Profile Configuration.
In the Profile Configuration list, query the Alias field for SecureWebService.
Make sure that the SecureWebService profile (named subsystem) has parameters with the following values:
Parameter Alias Value Service Method to Execute
DispatchMethod
Dispatch
Service to Execute
DispatchService
Web Service Inbound Dispatcher
Impersonate
Impersonate
True
When the client makes a call to the Web service, make sure that SWEExtSource points to the correct application name and named subsystem, for example:
http://myserver/siebel/app/eai_anon/enu/?SWEExtCmd=Execute &SWEExtSource=SecureWebService
About WS-Security User Name Token Profile Support
Siebel Business Applications support the WS-Security UserName token mechanism, which allows for the sending and receiving of user credentials in a standards-compliant manner. The UserName token is a mechanism for providing credentials to a Web service where the credentials consist of the UserName and Password. The password must be passed in clear text. The UserName token mechanism provides a Web service with the ability to operate without having the username and password in its URL or having to pass a session cookie with the HTTP request.
The following is an example of a UserName token showing the username and password:
<wsse:Security xmlns:wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/secext"> <wsse:UsernameToken xmlns:wsu="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/utility"> <wsse:Username>WKANDINSKY</wsse:Username> <wsse:Password Type="wsse:PasswordText">AbstractArt123</wsse:Password> </wsse:UsernameToken> </wsse:Security>
About Support for the User Name Token Mechanism
Support for the UserName Token mechanism includes the following:
Allows an inbound SOAP request to contain user credentials that can be provided to the inbound SOAP dispatcher to perform the necessary authentication
Allows an inbound SOAP dispatcher to perform the necessary authentication on an inbound SOAP request that contains user credentials
Allows an outbound SOAP request to contain user credentials that can be utilized by the external application
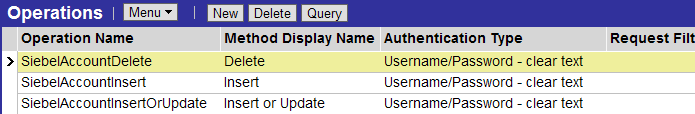
Using the User Name Token for Inbound Web Services
The Inbound Web Services view provides an interface for associating operations with authentication types. The names of the operations must be globally unique. The applet shown in the following figure can be defined as requiring a UserName Token with username and password provided in clear text.
Using the User Name Token for Outbound Web Services
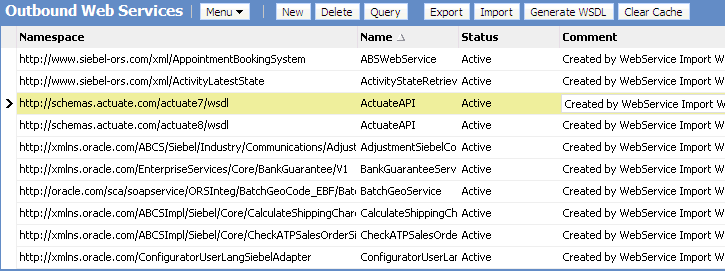
Each Web service operation in the Outbound Web Services list applet might be tied to an authentication type by selecting from the Authentication Type picklist (see the following figure) in the Operations picklist, in the following applet.
Proxy Configuration for Java Web Container
If your enterprise network is connected to the Internet through a proxy Internet server then configure the Java Web Container to route its traffic through the enterprise proxy server. To do so, apply the following proxy configuration:
HTTP proxy configuration
In the <installation_root>\ses\siebsrvr\javacontainer\javacontainer1\bin\setenv.bat file, add after line:
set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dhttp.proxyHost=<proxy_server_name> -Dhttp.proxyPort=<port_num>
HTTPS proxy configuration:
In the <installation_root>\ses\siebsrvr\javacontainer\javacontainer1\bin\setenv.bat file, add after line:
set CATALINA_OPTS=-Dhttps.proxyHost=<proxy_server_name> -Dhttps.proxyPort=<port_num>
To configure MainWin and import certificates in to it, see the chapter on communications and data encryption in the Siebel Security Guide.
About Siebel Authentication and Session Management SOAP Headers
You can use Siebel Authentication and Session Management SOAP headers to send and receive user credentials and session information. You can send a username and password for login that calls one of the following sessions:
One that closes after the outbound response is sent.
One that remains open after the response is sent.
For example, a custom Web application can send a request that includes a username and password, and calls a stateless session, one that remains open after the outbound response is sent. The Siebel Server generates an encrypted session token that contains user credentials and a session ID. The Siebel Server includes the session token in the SOAP header of the outbound response. The client application is responsible for capturing the returned session token and including it in the SOAP header of the next request.
The Session Manager on the Application Interface (AI) extracts the user credentials and session ID from the session token and reconnects to the session on the Siebel Server. If the original session has been closed, then a new session is created.
You can use the SOAP headers listed in the following table to call different types of sessions and pass authentication credentials:
Table Siebel Session Management and Authentication SOAP Headers
| SOAP Header Block | Description |
|---|---|
SessionType |
You use the SessionType SOAP header to define the type of session. Valid values are None, Stateless, Stateful, and ServerDetermine:
If the UsernameToken and PasswordText SOAP headers are excluded from the SOAP header, then anonymous login is assumed. The anonymous login requires additional configuration in the Siebel Application Interface profile and Named Subsystem configuration (AllowAnonymous equals (=) True, Impersonate equals (=) False). For more information about configuring anonymous login, see Siebel Security Guide.
Stateless session management is the best method to use for high-load Web service applications. Using Stateless mode, the application provides the username and password only once, that is for the initial request. A session is opened on the server and is dedicated for this user. In the response Siebel Business Applications return the SessionToken, which is an encrypted string containing the information about username, password, and timestamp. For subsequent requests the application must use the SessionToken to reuse the session. For security reasons, SessionTokens are regenerated for each response. The application must provide the last received SessionToken for the next request. The SessionToken-Siebel session map is maintained in the Siebel Application Interface (AI); based on the SessionToken value, AI sends the request to the correct Siebel session (task). Although the session is persistent, authentication happens for each request (AI decrypts the UserName and Password from the SessionToken). |
SessionType |
As with Stateless sessions, Siebel Business Applications return the SessionToken in the response. For subsequent requests the application must use the SessionToken to reuse the session. Unlike Stateless sessions, transparent failover (automatic relogin) is not supported. This is because Stateful sessions might have state information stored that makes it mandatory to connect to the same task for each request.
ServerDetermine provides the most flexibility: the session can be dedicated or not. If the number of users increases and resources must be recovered, then the session state is written to the database so that it can be restored. The session can then serve other users. If SessionType is absent, then the default value is None, and the session will be closed after the request is processed. |
UsernameToken |
You use the UsernameToken SOAP header to send the Login ID to the Siebel Server. |
PasswordText |
You use the PasswordText SOAP header to send the password used by the login ID to the Siebel server. If using Web single sign-on (SSO), then use the Siebel trust token value in PasswordText instead of the password. |
SessionToken |
Session tokens are used with stateless requests. They are sent and received using the SessionToken SOAP header. After receiving an initial request with valid authentication credentials and a session type set to Stateless, the Siebel Server generates a session token and includes it in the SOAP header of the outbound response. The session token is encrypted and consists of a session ID and user credentials. The custom Web application uses the session token for subsequent requests. The Session Manager on the AI extracts a session ID and user credentials from the session token, and then passes the information to the Siebel Server. The session ID is used to reconnect to an existing session or automatically log in again if the session has been terminated.
Note: Reconnecting or automatic logging in again will only happen if the token has not timed out. If it times out, then the user must manually log in again. Token timeout must be greater than or equal to session timeout. For more information on session token timeout, see
Session and Session Token Timeout-Related Parameters.
However, the session token must be changed to the new one sent on every response. The session token has a maximum time to live, which can invalidate it even if its timeout (for being inactive) has not been reached. Always get the newest session token returned by the response and use it on the next request. The same session token must not be used by concurrent requests, because having multiple requests point to the same session can cause errors. |
For examples of using SOAP headers for session management and authentication, see Examples of Using SOAP Headers for Authentication and Session Management.
The namespace used with Siebel Authentication and Session Management SOAP headers is:
xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices"
Combinations of Session Types and Authentication Types
The following table summarizes the combinations of authentication types and session types.
Table Summary of Authentication Types and Session Types
| Authentication Type | Session Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
None |
None |
A single request is sent with an anonymous user login, and the session is closed after the response is sent out. In order for the anonymous session to be identified by the AI Plug-in, UsernameToken and PasswordText must be excluded in the SOAP headers. |
Username and password |
None |
A single request is sent with the username and password used to log in, and the session is closed after the response is sent out. |
Username and password |
Stateless |
The initial request to log in establishes a session that is to remain open and available for subsequent requests. Username/password are used to log in and a session token is returned in a SOAP header included in the outbound response. The session remains open. |
Session token (stateless) |
Stateless |
Request to reconnect to an established session, using the information contained in the session token. If the session has been closed, then automatic relogin occurs. The Siebel servers include the session token in the SOAP header of the response. The session remains open. |
Session token (stateless) |
None |
When a SOAP header carries a session token and has the session type set to None, then the Session Manager on the AI closes (logs out) of this session, and invalidates the session token. The session token is not used after the session is invalidated. |
For examples that illustrate some of these combinations, see Examples of Using SOAP Headers for Authentication and Session Management.
Enabling Session Management on AI
To enable Session Management on the Application Interface (AI) for SOAP header handling, the Web service request must include the following URL parameter: WSSOAP=1. For example:
http://mywebserver/siebel/app/eai/enu/ swe?SWEExtSource=CustomUI&SWEExtCmd=Execute&WSSOAP=1
Session and Session Token Timeout-Related Parameters
You control the session timeout length and session token timeout length and maximum age by setting the parameters listed in the following table. These parameters are set in the eai application section of the AI profile.
Table Session and Session Token Timeout-Related Parameters
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
SessionTimeout |
Number in seconds |
The total number of seconds a session can remain inactive before the user is logged out and the session is closed. The default value is 900 seconds (15 minutes). |
GuestSessionTimeout |
Number in seconds |
The total number of seconds a guest session can remain inactive before the guest is logged out and the session is closed. The default value is 300 seconds (5 minutes). |
SessionTokenTimeout |
Number in minutes |
The Siebel Application Interface (AI) rejects the session token if the token is inactive for more than the SessionTokenTimeout value. Whenever the token is used, this value is refreshed. You typically set SessionTokenTimeout to the same length of time as the global parameter SessionTimeout, whose default is 900 seconds (15 minutes). The default value is 15 minutes. |
SessionTokenMaxAge |
Number in minutes |
The SessionTokenMaxAge parameter will make the AI reject the token if it has been used for more than the SessionTokenMaxAge value (for example, 240 minutes, or 4 hours). This is different from the SessionTokenTimeout because it does not refresh every time the token is used. The default value is 2880 minutes (two days). |
For information on SessionTimeout, see Siebel Security Guide. For information on application configuration parameters in general, see Siebel System Administration Guide.
Examples of Using SOAP Headers for Authentication and Session Management
The following examples illustrate using Siebel Authentication and Session Management SOAP headers. These examples use various authentication and session type combinations. For more information, see Combinations of Session Types and Authentication Types.
Anonymous Request No Session
This example illustrates an anonymous request and a session type of None, which closes the session after the response is sent out:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">None</SessionType> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Siebel Authorization No Session
This example illustrates a request that includes authentication credentials (username and password) and a session type of None, which closes the session after the response is sent out:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <UsernameToken xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">user</UsernameToken> <PasswordText xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">hello123</PasswordText> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">None</SessionType> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Siebel Authorization Stateless Session
The following examples illustrate a request, response, and subsequent request for a session type set to Stateless, which keeps the session open after the initial response is sent out.
Initial Request
This example illustrates the initial request that includes authentication credentials (username and password) needed to log in:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <UsernameToken xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">user</UsernameToken> <PasswordText xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">hello123</PasswordText> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">Stateless</SessionType> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Response
This example illustrates the session token (encrypted) generated by the Siebel Server and sent back in the SOAP header of the response:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <siebel-header:SessionToken xmlns:siebel-header="http://siebel.com/ webservices">2-r-JCunnMN9SxI9Any9zGQTOFIuJEJfCXjfI0G- 9ZOOH4lJjbSd2P.G7vySzo07sFeJxUA0WhdnK_ </siebel-header:SessionToken> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Subsequent Request Using Session Token
This example illustrates a subsequent request that includes the encrypted session token that was generated by the Siebel Server and passed in a previous response. The session token includes the user credentials and session information needed to reconnect to an existing session, or log in to a new one if the initial session has been closed:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">Stateless</SessionType> <SessionToken xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices"> 2-r-JCunnMN9SxI9Any9zGQTOFIuJEJfCXjfI0G-9ZOOH4lJjbSd2P.G7vySzo07sFeJxUA0WhdnK_ </SessionToken> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Siebel Authorization Stateful Session
The following examples illustrate a request, response, and subsequent request for a session type set to Stateful, which keeps the session open after the initial response is sent out.
Initial Request
This example illustrates the initial request that includes authentication credentials (username and password) needed to log in:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <UsernameToken xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">user</UsernameToken> <PasswordText xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">hello123</PasswordText> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">Stateful</SessionType> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Response
This example illustrates the session token (encrypted) generated by the Siebel Server and sent back in the SOAP header of the response:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <siebel-header:SessionToken xmlns:siebel-header="http://siebel.com/ webservices">Q7ABhvXBNUX5qTIoKJ9hZjhMzJ6lfTPa0oUDYxOBHkmOXB7j </siebel-header:SessionToken> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Subsequent Request Using Session Token
This example illustrates a subsequent request that includes the encrypted session token that was generated by the Siebel Server and passed in a previous response. The session token includes the user credentials and session information needed to reconnect to an existing session:
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soap:Header> <SessionType xmlns="http://siebel.com/webservices">Stateful</SessionType> <SessionToken xmlns="http://siebel.com/ webservices">Q7ABhvXBNUX5qTIoKJ9hZjhMzJ6lfTPa0oUDYxOBHkmOXB7j </SessionToken> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <!-- data goes here --> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
Simple Query Starting With <soap:body>
This example illustrates data for a simple query starting with the <soap:body> element:
<soap:body>
<Account_spcService_Account_spcServiceQueryPage_Input
xmlns="http://siebel.com/CustomUI">
<ListOfTestAccount
xmlns="http://www.siebel.com/xml/Test%20Account/Query">
<Account>
<Name>A*</Name>
</Account>
</ListOfTestAccount>
</Account_spcService_Account_spcServiceQueryPage_Input>
</soap:body>
About Web Services and Web Single Sign-On Authentication
Siebel Web services support Web single sign-on (SSO) deployment scenarios in which third-party applications handle authentication, and then pass authentication information to the Siebel application. When the third-party application authenticates it, users do not have to explicitly log in to the Siebel application. The following illustrates a Web single SSO deployment scenario using Siebel Web services. For more information about Web SSO, see Siebel Security Guide.
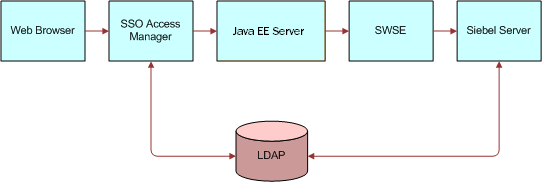
Each component in the SSO scenario shown in the previous figure is described in the following:
SSO Access Manager. SSO Access Manager, configured in front of the Java EE server, challenges user login, authenticates user credentials with LDAP, and sets a security token in the browser (http header), which is forwarded to the Java EE server.
Java EE Server. This server extracts user credentials from the security token in the request. The Session Manager Login method takes the request as an argument and forwards it to the AI. The request contains the security token in the header.
AI. AI extracts the user credentials from the security token and sends user credentials and the trust token to the Siebel Server.
Siebel Server. The Siebel Server validates user credentials with LDAP and validates the trust token with security settings.
About SOAP Fault Schema Support
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) applications typically use Web services to expose functionality. The application describes a Web service through a WSDL document that is published. This WSDL document carries information about the input and output schema for each operation.
A client that invokes the Web service can use this WSDL document to determine the format of the request and response messages. Request and response messages are in SOAP format.
Siebel Business Applications consume external Web services by processing the WSDL document and creating proxy business services. These proxy business services send requests to the external application and receive responses in a SOAP format. The responses are presented to the caller as Siebel property sets.
The WSDL document can optionally give a list of named faults (and their schema) that can occur for each operation. If an application error occurs, then the SOAP Fault element is used to capture it. The SOAP Fault element in the SOAP response body defines the following four subelements:
faultcode. Identifies the fault.
faultstring. Displays text that describes the fault.
faultactor. Indicates the source of the fault.
detail. Encodes application-specific errors.
The following WSDL example, which shows named faults, is from
http://www.gridlab.org:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <definitions name="MyService" targetNamespace="urn:myuri:1.0" xmlns:tns="urn:myuri:1.0" xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:SOAP-ENC="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:ns1="urn:myuri:1.0" xmlns:SOAP="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:MIME="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/mime/" xmlns:DIME="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/04/dime/wsdl/" xmlns:WSDL="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"> <types> <schema targetNamespace="urn:myuri:1.0" xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:SOAP-ENC="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:ns1="urn:myuri:1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="unqualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified"> <import namespace="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"/> <!-- fault element --> <element name="MyFirstException"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="text" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" nillable="false"/> </sequence> </complexType> </element> <!-- fault element --> <element name="MySecondException"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="number" type="xsd:int" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> </sequence> </complexType> </element> <!-- operation request element --> <element name="myOperation"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="myInput" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/> </sequence> </complexType> </element> <!-- operation response element --> <element name="myOperationResponse"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="myOutput" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> </types> <message name="myOperationRequest"> <part name="parameters" element="ns1:myOperation"/> </message> <message name="myOperationResponse"> <part name="parameters" element="ns1:myOperationResponse"/> </message> <message name="MyFirstExceptionFault"> <part name="fault" element="ns1:MyFirstException"/> </message> <message name="MySecondExceptionFault"> <part name="fault" element="ns1:MySecondException"/> </message> <portType name="MyType"> <operation name="myOperation"> <documentation>Service definition of function ns1__myOperation</documentation> <input message="tns:myOperationRequest"/> <output message="tns:myOperationResponse"/> <fault name="MyFirstException" message="tns:MyFirstExceptionFault"/> <fault name="MySecondException" message="tns:MySecondExceptionFault"/> </operation> </portType> <binding name="MyService" type="tns:MyType"> <SOAP:binding style="document" transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/> <operation name="myOperation"> <SOAP:operation soapAction=""/> <input> <SOAP:body use="literal"/> </input> <output> <SOAP:body use="literal"/> </output> <fault name="MyFirstException"> <SOAP:fault name="MyFirstException" use="literal"/> </fault> <fault name="MySecondException"> <SOAP:fault name="MySecondException" use="literal"/> </fault> </operation> </binding> <service name="MyService"> <documentation>gSOAP 2.7.1 generated service definition</documentation> <port name="MyService" binding="tns:MyService"> <SOAP:address location="http://localhost:10000"/> </port> </service> </definitions>
The following SOAP message shows the first named fault from the example WSDL:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:ns1="urn:myuri:1.0"> <SOAP-ENV:Body> <SOAP-ENV:Fault> <faultcode>SOAP-ENV:Client</faultcode> <faultstring>Deliberately thrown exception.</faultstring> <detail> <ns1:MyFirstException> <text>Input values are wrong.</text> </ns1:MyFirstException> </detail> </SOAP-ENV:Fault> </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
For more information on fault handling in Web services, see the SOAP and WSDL standards listed in Supported Web Services Standards.
Handling SOAP Faults in Siebel Business Applications
The fault schemas described in the WSDL are accepted and modeled in Siebel Business Applications as integration objects. This is similar to how other input and output messages are modeled as strings (simple type) or integration objects (complex type). These named faults are available as output parameters.
Having named faults available as output parameters is useful in SOA environments. For example, Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) can only send named faults.
Handling SOAP Messages
SOAP messages are handled as follows:
An end user calls a proxy business service, for example, by clicking a button.
The proxy business service reads the input parameters and invokes the external Web service.
The proxy business service reads the SOAP response and checks for a SOAP Fault element.
If no SOAP fault is found, then the message is handled as normal.
If a SOAP fault is found, then the proxy business service tries to match the fault with a SOAP fault integration object.
If a match is found, then Siebel converts the fault into a fault integration object instance and sets it in the output parameter.
Whether or not a match is found, Siebel puts the fault into the XML Hierarchy (for backward compatibility).
Handling WSDL Imports
The handling of SOAP faults while importing WSDL files into Siebel Business Applications is as follows:
A developer uses the WSDL Import Wizard in Siebel Tools to import a WSDL document for creating proxy business services.
If the operation has a named fault that is not defined in the WSDL, then it is put into the XML Hierarchy.
If the operation has a named fault defined in the WSDL:
If the Process Fault Schema check box is not selected, the named fault is ignored.
If the Process Fault Schema check box is selected and an existing fault integration object is specified, then that fault integration object is added as an output parameter.
If the Process Fault Schema check box is selected and an existing fault integration object is not specified, then a new fault integration object is added as an output parameter. The integration object name is prepended with Fault_.
For information on using the WSDL Import Wizard, see Creating an Outbound Web Service Based on a WSDL File.
About Custom SOAP Filters
Headers represent SOAP's extensibility mechanism and provide a flexible and standards-based mechanism of adding additional context to a request or response. Custom SOAP header support provides a flexible extensibility mechanism when integrating with external Web services, and a means of providing additional context as required by the Web service implementation.
Handling Custom Headers Using Filters
SOAP headers provide the option of providing optional or mandatory processing information. To process optional custom headers that are provided by external applications, a special business service known as a filter might be defined. Filters can process both request and response headers. A special attribute, mustUnderstand, is used to indicate whether or not the custom header is to be processed:
If 'mustUnderstand' equals 1, then the custom header is interpreted as being mandatory and the custom header is processed by the filter defined for this purpose.
If 'mustUnderstand' equals 1 and a filter is not specified, then the custom header is not read and a SOAP:MustUnderstand fault is generated.
If 'mustUnderstand' equals 0, then no processing of the custom header is attempted.
You must keep SOAP body and header processing isolated. The inbound dispatcher and outbound proxy can process the SOAP body, but cannot set or consume headers. Headers are application-specific. Some customization is needed to set and consume custom headers. To process optional custom headers that are provided by external applications, a special business service, a filter, is defined. You can configure the Web service outbound proxy and the Web service inbound dispatcher to call specific filters for the processing of individual (custom) headers.
Enabling SOAP Header Processing Through Filters
For each operation, you can set the inbound and outbound filters to be run. You can also define the methods you want to call on the filter.
The following code sample illustrates a filter that has been written for the handling of custom SOAP headers. The interface provided by this code sample lets you define the method on the filter that you want to call, as well as the corresponding input and output parameters.
function Service_PreInvokeMethod (MethodName, Inputs, Outputs) {
if(MethodName == "StripHeader") {
if(Inputs.GetChildCount() > 0) {
// Set the input SOAP message property set as the output.
Outputs.InsertChildAt(Inputs.GetChild(0), 0);
var soapEnv = Outputs.GetChild(0);
if(soapEnv.GetChildCount() == 2) // headers and body {
// Here is where the header is found and processed.
var count = soapEnv.GetChildCount();
var i = 0;
var headerParam1;
var headerParam2;
var headerParam3;
// Use a loop just in case the header is not the first hierarchy.
for (; i < count; i++) {
// For simplicity, the string comparison must be done using the exact same value
// as the SOAP message tag name.
if (soapEnv.GetChild(i).GetType() == "soapenv:Header") {
// Found the header. Now it is processed.
var soapHeader = soapEnv.GetChild(i);
// This example assumes that the following header hierarchy is received:
// <soapEnv:Header>
// <headerParam1>Value1</headerParam1>
// <headerParam2>Value2</headerParam2>
// <headerParam3>Value3</headerParam3>
// </soapEnv:Header>
// The parameters headerParam1, headerParam2, and headerParam3
// are saved into variables. Nothing further done with them.
headerParam1 = soapHeader.GetChild(0);
headerParam2 = soapHeader.GetChild(1);
headerParam3 = soapHeader.GetChild(2);
break; // Stop the loop after the header is found.
}
}
// Must remove the header from the SOAP property set.
soapEnv.RemoveChild(i);
}
}
}
else if(MethodName == "AddHeader") {
if(Inputs.GetChildCount() > 0) {
// Create the SOAP header hierarchy with the desired data.
var soapHeader = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
soapHeader.SetType("soapEnv:Header");
soapHeader.SetProperty("xmlns:soapEnv",
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/");
// These will be created as property sets because we want the following header:
// <soapEnv:Header>
// <headerParam1>Value1</headerParam1>
// <headerParam2>Value2</headerParam2>
// <headerParam3>Value3</headerParam3>
// </soapEnv:Header>
var param1PS = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var param2PS = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
var param3PS = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
param1PS.SetType("headerParam1");
param1PS.SetValue("Value1");
param2PS.SetType("headerParam2");
param2PS.SetValue("Value2");
param3PS.SetType("headerParam3");
param3PS.SetValue("Value3");
// Add the data to the SOAP header.
soapHeader.AddChild(param1PS);
soapHeader.AddChild(param2PS);
soapHeader.AddChild(param3PS);
// Get the SOAP envelope from the SOAP hierarchy.
var soapEnv = Inputs.GetChild(0);
// Add the header to the SOAP envelope.
soapEnv.InsertChildAt(soapHeader, 0);
Outputs.InsertChildAt(soapEnv, 0);
}
}
return(CancelOperation);
}
Inputting a SOAP Envelope to a Filter Service
Using a SOAP envelope as the input to a filter service is the property set representation of an XML document. For example, each tag in the XML document is a property set. Each attribute on the tag is a property in the property set.
To pass the information in the headers further down the stack to the actual business service method or workflow being called, the HeaderContext property set is passed to the business service or workflow that is called. For example, on a call to an inbound Web service, if there are a couple of headers in the SOAP message, the filter service extracts the header information. To use this information in the business service or workflow execution call, it has to be contained in the HeaderContext. Internally, the Siebel Web services infrastructure passes HeaderContext to the eventual business service or workflow that is called.
About EAI File Streaming
Siebel Business Applications support streaming of EAI requests and responses encountered. This feature allows the Siebel Web Engine (SWE) and the EAI Object Manager (OM) to process Web service calls that involve large requests or responses. Large requests and responses can occur when inserting or querying file attachments by way of a Web service. By transferring data internally in 100-KB chunks, the memory footprints of the Siebel Web Engine and EAI Object Manager processes are reduced and system scalability is improved.
This topic describes the streaming process for inbound EAI requests and outbound responses.
About Inbound EAI Streaming Requests
The following figure provides an overview of the components and process flow used for streaming an inbound request.
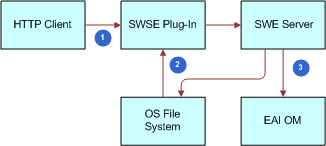
About Inbound EAI Streaming Requests illustrates the following process:
When the Application Interface (AI) Plug-in receives the request from the HTTP client by way of the Web Server, it determines that this request must be chunked based on the HTTP request body size, embeds streaming information in the request, and then sends the first chunk of the request body to the SWE Server.
The SWE Server extracts the streaming information from the request, determines it is a streaming request, and then writes the first chunk to the file system and sends a response to the plug-in indicating that the request has been processed. The AI sends the next chunk and the cycle continues until the last chunk has been written to the file system.
After the entire body of the HTTP request has been written to a file on the disk, the SWE Server calls the Web service method on EAI Object Manager, passing the name of the file as an input argument.
About Outbound EAI Streaming Responses
The following figure provides an overview of the components and process flow used for streaming an outbound response.
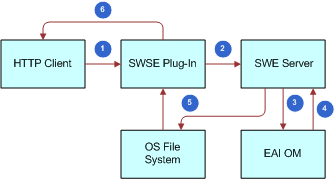
The previous figure illustrates the following process:
An EAI request from the HTTP client is received by the AI.
The AI forwards the request to the SWE Server.
The SWE Server then performs one of the following actions:
If the request is not a streaming request, the SWE Server calls the EAI Object Manager method.
If the request is a streaming request, then the file is first written to disk before the SWE Server calls the EAI Object Manager method.
The EAI Object Manager forwards the response to the SWE Server, and SWE queries the output arguments.
If a file reference is found, then the SWE Server transmits the file to the client.
Whether multiple chunks will be sent or not depends upon the size of the file. If chunking is needed, then the SWE Server sends the first chunk to the plug-in, also embedding the streaming information in the response.
The Plug-in sends the chunk to the client including the HTTP headers in the response, and then it requeries the SWE Server to get the next chunk.
Note: The plug-in sends the HTTP response headers only for the first chunk.The cycle continues until the entire file has been transmitted to the HTTP client.
About EAI Streaming Criteria
The following criteria are used internally to decide whether a particular request or response is streamed:
The Application Interface initiates chunking of an inbound EAI request only if the following conditions are met:
The Configure EAI HTTP Inbound Transport parameter is selected in the basic information section of the AI profile of the eai application.
The size of the body of the inbound HTTP request is greater than 100 KB.
If these conditions are not met, then the plug-in does not stream the contents of the EAI request, and the request is processed as one chunk.
The SWE server initiates outbound chunking only if the following conditions are met:
The SWE finds a property named ExtSvcFileName in the output arguments after calling the EAI Object Manager method.
The value of this property must be a fully qualified path, and the name of the response file is written to disk by EAI.
The file size is greater than 100 KB.
If these conditions are not met, then the plug-in does not stream the contents of the EAI response, and the request is processed as one chunk.
About Web Services Cache Refresh
Both Siebel inbound and outbound Web services are typically cached into memory on the Siebel Server. At times, administrators must update the definitions of these services to provide more current or correct functionality. Administrators have the ability to directly refresh the memory cache in real time, without stopping and restarting the Siebel server.
The Web services cache is used to store all the global administration information that can be manipulated in the Inbound and Outbound Web Service administration views.
The Clear Cache feature is a button on the Administration - Web Services screen. This feature is available for inbound and outbound Web services. When the administrator decides when the Web service configuration must be refreshed, he or she clicks Clear Cache.
When Clear Cache is clicked, the integration object and Web services definitions in the run-time database are invalidated. Object definitions are reloaded when requested in the client.
Enabling Web Services Tracing
You can enable Web services tracing on the Siebel Server to write all inbound and outbound SOAP documents to a log file.
To enable Web services tracing
Navigate to the Administration - Server Configuration screen, Servers view.
The view that appears displays three different list applets. The first applet lists the Siebel Servers for the enterprise. The middle applet has three tabs: Components, Parameters and Events. The last applet has two tabs: Events and Parameters.
In the first list applet, select the Siebel Server that you want to configure.
In the middle applet, click the Components tab.
This list applet contains the components for the Siebel Server selected in the first applet.
Choose the relevant application object manager.
In the last applet, click the Parameters tab.
This list applet contains the parameters for the Component selected in the middle applet.
Set the Log Level to 4 for any or all of the following Event Types.
Event Type Alias Description Comment Web Service Performance
WebSvcPerfWeb Service Performance Event Type
Used for performance logging
Web Service Outbound Argument Tracing
WebSvcOutboundArgTrcWeb Service Outbound Run-time Argument Tracing
Used for logging arguments to the outbound dispatcher
Web Service Outbound
WebSvcOutboundWeb Service Outbound Run-time Event Type
Used for run-time logging of outbound Web services
Web Service Loading
WebSvcLoadWeb Service Configuration Loading Event Type
Used for logging of the loading of Web services
Web Service Inbound Argument Tracing
WebSvcInboundArgTrcWeb Service Inbound Run-time Argument Tracing
Used for logging arguments to the inbound dispatcher
Web Service Inbound
WebSvcInboundWeb Service Inbound Run-time Event Type
Used for logging at Web service inbound run time. Information is logged to the inbound dispatcher
Web Service Design
WebSvcDesignWeb Service Design-time Event Type
Used for logging at Web service design time. For example, at the time of WSDL import and generation
In the middle applet, click the Components tab.
Select the EAI Object Manager component, and then click the Parameters tab.
The Component Parameters list appears.
Click Advanced to see the advanced parameters. (Click Reset to hide them again.)
Query for Enable Business Service Argument Tracing.
Set its Value and Value on Restart fields to True.
Restart or reconfigure the server component.
For information on restarting server components and on advanced and hidden parameters, see Siebel System Administration Guide.
Previewing the Repository Changes Before Delivery
You can preview changes to a developer or integration workspace even before you deliver them. This is due to the Workspace&Version parameter, which helps preview changes specific to an object in a developer branch and/or its version. To learn more about using this parameter, see Siebel REST API Guide.
This topic gives an example of a SOAP request and response before and after changes to the Related Contact integration component (IC) in a developer workspace.
SOAP URI: https://<host_name>:<port_number>/siebel/app/eai/enu?SWEExtSource=WebService&SWEExtCmd=Execute&WSSOAP=1
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:asi="http://siebel.com/asi/"> <soapenv:Header> <ns1:SessionType xmlns:ns1="http://siebel.com/webservices">Nonens1:SessionType xmlns:ns1="http://siebel.com/webservices">None</ns1:SessionType> <ns2:UsernameToken xmlns:ns2="http://siebel.com/webservices"><username>:UsernameToken xmlns:ns2="http://siebel.com/webservices"><username></ns2:UsernameToken> <ns3:PasswordText xmlns:ns3="http://siebel.com/webservices"><password>:PasswordText xmlns:ns3="http://siebel.com/webservices"><password></ns3:PasswordText> </soapenv:Header> <soapenv:Body> <asi:SiebelAccountQueryById_Input> <asi:PrimaryRowId><Primary Row Id></asi:PrimaryRowId> </asi:SiebelAccountQueryById_Input> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>
When you request details, the Related Contacts IC displays along with other objects in the workspace:
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <SOAP-ENV:Body> <ns:SiebelAccountQueryById_Output xmlns:ns="http://siebel.com/asi/"> <ListOfAccountInterface xmlns="http://www.siebel.com/xml/Account%20Interface"> <Account> . . . <ListOfRelatedSalesRep> . . . </ListOfRelatedSalesRep> <ListOfRelatedContact> <RelatedContact> <ContactId><Contact IdContact Id>ContactId> <FirstName>JohnFirstName>John> <ContactIntegrationId/> <LastName>Smith FINSLastName>Smith FINS> <MiddleName/> <PersonUId>Contact IdPersonUId>Contact Id> <PrimaryOrganization>ABC Insurance IN ENUPrimaryOrganization>ABC Insurance IN ENU> </RelatedContact> <RelatedContact> . . . </RelatedContact> </ListOfRelatedContact> <ListOfRelatedOrganization> . . . </ListOfRelatedOrganization> . . </Account> </ListOfAccountInterface> </ns:SiebelAccountQueryById_Output> </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
You can modify the object definition and then preview the changes before delivery of workspace. In the following example, Related Contact is no longer a child component of the base List of Related Contact integration object (IO). This change to the structure of the IO is seen by passing the workspace name and its version as query parameters in the request. The response fetches other objects but not the Related Contacts IC and its IO due to inactivation of the IC.
For more information about how to inactivate an object in Web Tools, see Using Siebel Tools. For more information on how to activate a web service, see Invoking Siebel Web Services Using an External System.
SOAP URI: https://<host_name>:<port_number>/siebel/app/eai/enu?SWEExtSource=WebService&SWEExtCmd=Execute&WSSOAP=1&Workspace=<Workspace_<workspace_name>&Version=<ver_num>>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> </soapenv:Body> <ns:SiebelAccountQueryById_Output xmlns:ns="http://siebel.com/asi/"> <ListOfAccountInterface xmlns="http://www.siebel.com/xml/Account%20Interface"> <Account> . . . <ListOfRelatedSalesRep> . . . </ListOfRelatedSalesRep> <ListOfRelatedOrganization> . . . </ListOfRelatedOrganization> </Account> </ListOfAccountInterface> </ns:SiebelAccountQueryById_Output> </SOAP-ENV:Body> </SOAP-ENV:Envelope>