10About Siebel Replication Manager
About Siebel Replication Manager
This chapter describes Oracle’s Siebel Replication Manager. It includes the following topics:
Overview of Siebel Replication Manager
This topic describes Replication Manager. It includes the following information:
For more information, see About the Siebel Enterprise and the Siebel Enterprise Server.
Hierarchy of a Siebel Replication Manager Implementation
Replication Manager is a data replication technology that copies data throughout a network of Siebel nodes. It copies data that originates in the headquarters node (HQ) to multiple regional nodes. These regional nodes are subordinate to the headquarters node. It uses a hierarchical model.
A Replication Manager implementation includes a single headquarters node and one or more regional nodes. The headquarters node contains the master set of data that the regional nodes use. A regional node can possess one of the following types of relationships:
Subordinate to the headquarters node. The regional node synchronizes directly with the headquarters node.
Subordinate to a regional node. The regional node synchronizes directly with this regional node. A hierarchy of regional nodes is a hierarchy that includes a regional node that is a child node of another regional node.
Each subordinate node is a Siebel Enterprise Server that contains a subset of users from the Siebel Enterprise Server that resides on the parent node.
The following diagram illustrates an example configuration for Siebel Replication Manager. It includes the following items:
Two regional nodes that are children of the headquarters node.
One regional node that is a child node of a regional node.
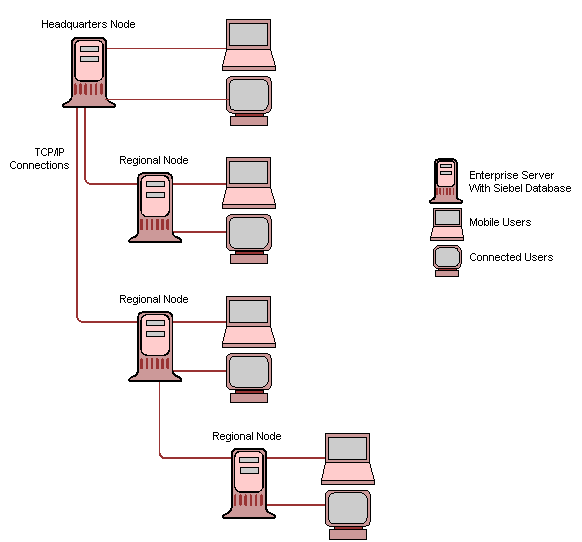
Headquarters Node
A headquarters node is a separate Siebel Enterprise Server that includes the Siebel database, the Siebel File System, and one or more Siebel Servers. The Siebel database and file system contain the entire set of database records and file attachments that the nodes use. Siebel Servers that reside in the headquarters node manage replication to the following items:
Regional nodes that are children of the headquarters node
Remote clients that synchronize with the headquarters node
A regional node can support connected users and remote clients that synchronize with the Siebel Server of a regional node.
For more information, see About the Siebel Enterprise and the Siebel Enterprise Server.
Regional Node
A regional node is a separate Siebel Enterprise Server that includes a Siebel database, Siebel Servers, and Siebel File System that support a set of connected users. The set of registered users at the regional node determines the set of connected users.
Each regional node is a child of a parent node. A parent node is another Siebel Enterprise Server that is the headquarters node or another regional node. A regional node contains a full copy of data or a subset of data from the parent node. This copy includes database records and file attachments. A regional node is typically geographically separated from the headquarters node, but this configuration is not required.
Replication Agent
The Replication Agent server component runs on the Siebel Server on the regional node. To keep data current at these locations, it periodically synchronizes the regional database with the parent database. Replication Agent runs as a service mode task, which is a type of task that runs continuously after it starts.
Benefits of Siebel Replication Manager
Replication Manager can help solve the performance degradation that occurs if bandwidth is limited or if network latency is a problem. Placing data closer to a cluster of connected users instead of requiring data transfer from a single headquarters node can improve response time. This configuration also provides the user with continuous access to the Siebel application even if the network link to the headquarters node is not reliable or is only available intermittently. The user can synchronize with a local regional node to decrease network costs and to improve the performance and reliability of the synchronization process.
Comparison Between Siebel Remote and Siebel Replication Manager
The following table provides a comparison between Siebel Remote and Siebel Replication Manager.
Table Comparison of Siebel Remote to Siebel Replication Manager
| Siebel Remote | Siebel Replication Manager |
|---|---|
Siebel Remote provides the following:
|
Siebel Replication Manager provides the following:
|
How Siebel Replication Manager Uses Routing Groups
A routing group is associated with each Siebel Server of a regional node. It does the following:
Determines the data that Replication Manager extracts and the transactions that it synchronizes with the Siebel Server of a regional node.
Determines how much of the data from the parent node Replication Manager copies to the regional database.
You cannot modify a routing group.
Each regional node contains a full copy of the Siebel database in the parent node and file system, or a subset of that data. To specify the routing group that the Replication Manager uses, you can associate one of the following routing groups with the regional database:
To specify a routing group, you use the Administration - Siebel Remote screen when you register the regional node.
For more information about the following items:
Registering a regional node, see Defining the Regional Node.
Routing, see Controlling the Data That Siebel Remote Routes to Clients.
Predefined user routing rules, see Transaction Router Server Component.
About the Regional Server - Full Copy Routing Group
The Regional Server - Full Copy routing group copies all nonsystem data, including all user data, from the parent database to the regional database. Full Copy disregards routing rules. It considers the regional database as a full copy of the parent database. You must not use Full Copy as a backup system for the headquarters node for the following reasons:
The Full Copy routing group might note copy some data that is related to Siebel CRM data.
If you cannot restore the parent node properly, then it might be necessary to reextract a regional node.
The Full Copy routing group does not copy every user.
You cannot convert a regional node to a headquarters node.
About the Regional Server - Standard Routing Group
The Regional Server - Standard routing group uses routing rules to identity the data to copy to the regional database. The data that it copies to the regional database is the data that is visible to connected users who you assign to the regional node. It applies predefined routing rules to determine the data that the Replication Manager parent node copies to the regional node.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Full Copy and Standard Routing Groups
The following table describes advantages and disadvantages of the Regional Server - Full Copy routing group and the Regional Server - Standard routing group. Note the following:
If Replication Manager routes more than half of the data on the parent node to the regional node, then it might be more beneficial to use Full Copy rather than Standard for optimal performance.
Replication Manager supports All views, such as All Opportunities Across Organizations, only on a regional node that is assigned the Regional Server - Full Copy routing group.
Table Advantages and Disadvantages of Full Copy and Standard Routing Groups
| Routing Group | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Regional Server - Full Copy |
Quick data routing because Replication Manager does not use a routing rule. |
Replication Manager stores more data at the regional node. |
Full access to data for every user. |
More network traffic. |
|
Not applicable. |
Requires more powerful hardware. |
|
Regional Server - Standard |
Replication Manager routes only necessary data. |
The Transaction Router must determine the data that the Replication Manager must route, which increases processing time. |
Replication Manager stores less data at the regional node, which requires fewer resources. |
Not applicable. |
|
Less network traffic. |
Not applicable. |
Assignment to Multiple Databases
If you assign a user to multiple databases, then Replication Manager synchronizes the data that user can view to each of these databases. If you assign a user to only one database, then this database is a headquarters database or a regional database. An example of a user whom you assign to multiple databases might include assignment to one headquarters database or regional database and one Siebel Remote database.
Server Components That Siebel Replication Manager Uses
This topic describes the server components that Replication Manager uses. For more information, see the following topics:
Server Component Usage on Headquarters and Regional Nodes
The server components that Replication Manager uses on the headquarters node include the components listed in the table in the topic Server Components That Siebel Remote Uses, except for the Replication Agent server component.
The table in the topic Server Components That Siebel Remote Uses lists the server components that Replication Manager uses on the Siebel Server in the regional node if that regional node includes remote clients or child regional nodes. In this situation, Replication Manager also uses the Regional Database Initialization (srvrinit) server component.
If a regional node does not contain remote clients or child regional nodes, then Replication Manager uses the following server components on the Siebel Server in the regional node:
Regional Database Initialization (srvrinit). A server component that loads Database Extract onto the Siebel Server of a regional node.
Replication Agent. A server component that copies the Siebel database to a regional node, according to the assigned routing group.
Support for Siebel Server Features on a Regional Node
Most Siebel Server processes run only on the Siebel Server of the headquarters node. Some Siebel Server features and server components do run on the regional node. For more information, see Siebel Server Features on a Regional Node.
How Siebel Replication Manager Filters a Regional Workflow
Workflow administration allows for filtering out a workflow process that only applies at the regional level. Replication Manager routes to the regional node only the records that are associated with workflows that the remote client requires. This configuration decreases the amount of data and helps optimize the local database. For more information, see Siebel Business Process Framework: Workflow Guide.