3Siebel Financial Services EAI Architecture
Siebel Financial Services EAI Architecture
This chapter describes Siebel Financial Services Enterprise Application Integration architecture.
Layered Architecture
The Siebel Financial Services Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) is an extension of the standard Siebel EAI designed to address integration approaches adopted by the vertical industry. It provides a platform for the development of specific connectors for different industry XML standards.
The following image illustrates the high-level architecture of Siebel Financial Services EAI and various industry XML connectors.
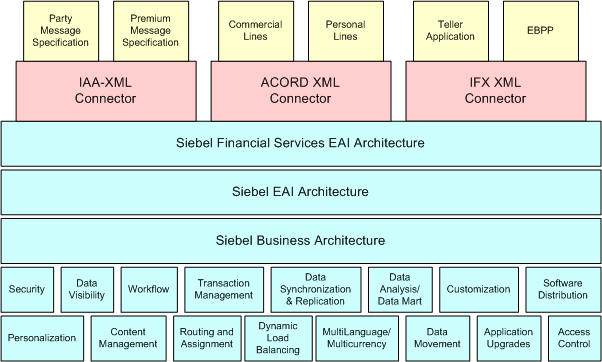
Integration Requirements and Siebel Financial Services EAI
The following table maps real-world data and application integration requirements with their corresponding Siebel Financial Services EAI features.
| Integration Requirements | Siebel Financial Services EAI Features and Components | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Metadata Definition XML Metadata External application metadata |
|
In any integration project, you need a way to supply data about data, called metadata. Siebel Financial Services applications provides XML as the common format for representing external application data. In addition, Siebel Financial Services applications provides an object type in Siebel Tools called the Integration Object, as well as an Integration Object Wizard, which automates the task of creating integration objects. |
Data Transformation Declarative data transformation mapping High-performance transformation engine |
|
Siebel Financial Services EAI allows you define what type of data is to be exchanged, and allows you to export a DTD for a Siebel integration object. |
Industry standards-based Integration Mechanism |
|
See Siebel Financial Services Connector for IFX XML Guide, and Siebel Financial Services Connector for ACORD P&C and Surety Guide. Also see Industry XML Connector Factory APIsand Industry XML Connector. |
Business Process Coordination |
|
|
Transport Mechanisms (for interfacing with other technologies) |
Transport Adapters:
|
See Transport Mechanisms. |
High Volume Data Exchange |
|
See Overview: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration. |
Business Process Coordination Using Workflows
Connectors are composed of multiple components. These components are tied together using workflows. With different sets of configuration, you can alter generated messages and behavior. You can use the Workflow Process Designer and the Workflow Process Manager to configure your data integration business process flow. The Siebel Financial Services application provides sample workflows which you can use as a reference implementation for your data integration business processes. The following image shows one of these sample workflows from the sample database.
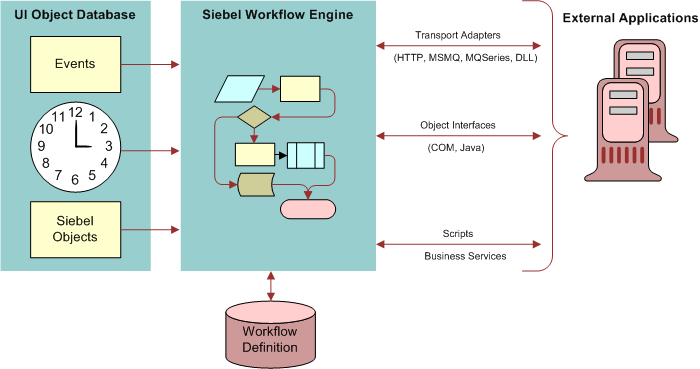
Transport Mechanisms
Many companies have standardized transport solutions such as MQSeries from IBM or MSMQ from Microsoft. These transports allow the transportation of messages between one system and another. Oracle conforms to this standard by allowing you to “plug" Siebel Financial Services applications into these environments through Siebel Financial Services EAI’s comprehensive set of adapters, that include the MQSeries adapter, the MSMQ adapter, and the HTTP adapter.
Transport adapters developed by Oracle and Oracle-certified partners allow diverse applications to communicate with Siebel Financial Services applications across virtually any operating system, network, and database. The Architecture for Siebel Financial Services EAI image in Business Process Coordination Using Workflows shows the various available transports to and from Siebel Financial Services applications as a new customer’s information is processed. Any one or any combination of these transports could be used in an integration solution, depending upon existing applications and other factors.
Industry XML Connector
The Industry XML Connector is a configured set of components that allows Siebel applications to exchange data with external systems using XML messages. These components are called business services and can be extended to support multiple connectors. You can use the overwrite methods to extend the functionality of both industry XML connectors as well as Siebel Financial Service EAI infrastructure for enterprise data sharing and data synchronization for your integration implementation. By using the overwrite methods to extend the functionality, you obey the rules of data exchange set forth by the legacy or back-end systems, such as specific XML structure and envelope details, while using the common requirements for business processes and transactions. The following image on High-level architecture of Industry XML Converter illustrates architecture of the Industry XML Connector.
The Industry XML connector has four key components: Industry XML Transaction Manager, Industry XML Data Transformation Engine, Industry XML Converter, and Industry XML Dispatcher.
For more information about each of these components, see the following:
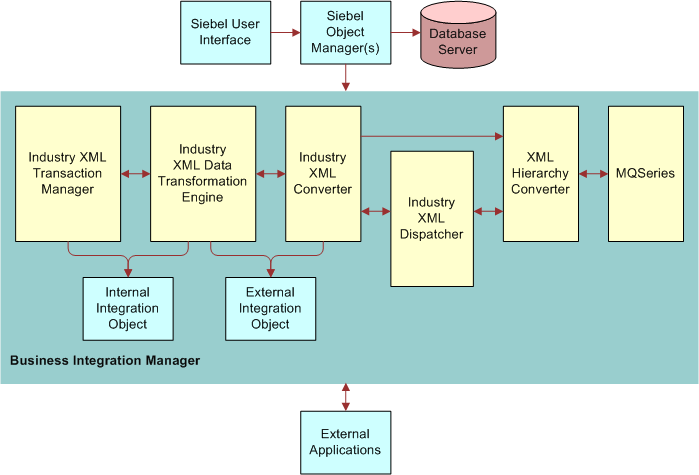
Industry XML Transaction Manager
The Industry XML Transaction Manager is responsible for interfacing with the Siebel database. It retrieves data and executes database operations for financial services industry integration architecture. The Industry XML Transaction Manager can also extract query specifications entered by users in the memory cache, and run them through the connector modules to send a query message to external systems. Furthermore, it can undo operations if it receives an error in the fault section of the response message indicating that the external systems failed to execute the specified operations.
The following table lists all the user properties for Industry XML Transaction Manager.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
IXMLDispMap |
Transaction Manager uses this map to tag the Body information for other components. This value can also be set as a runtime input argument. |
IgnoreSvcMethodArgs |
true or false |
This parameter allows runtime input arguments. |
SaveInFileForRollback |
<filename> |
The filename to save current record for future rollback when rollback operation is desired. |
SaveInMemForRollback |
<filename> |
The session key to set or look up the record cached in memory if rollback operation is desired. |
XXX (Operation) |
ServiceName/MethodName/Argument |
Type of operation to use. For example, Name = IXMLOperation_QUERY, Value= EAI Siebel Adapter/Query/PrimaryRowId;!SiebelMessage. |
The Industry XML Transaction Manager uses the prebuilt methods described in the following table to process inbound or outbound integration.
| Method | Default Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Execute |
Execute Transaction |
This method can be used for inbound or outbound purpose, as long as the integration object instance is provided. You should use the Execute Outbound method when Row Id is the only available input. |
ExecuteOutbound |
Execute Outbound |
This method can only be used for outbound purpose to execute operation specified in input arguments. See the Method Arguments for ExecuteOutbound Method table. |
ExecuteSave |
Execute and Save |
This method executes outbound operation specified in input arguments and also saves the transaction into memory or file. See the Method Arguments for ExecuteSave Method table. |
The Industry XML Transaction Manager business service uses combinations of user property, method, and method arguments to achieve different tasks. The following table lists all the method arguments available to use with The Industry XML Transaction Manager business service.
| Argument | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
OnlyIOI |
false |
This is only used for Inbound integration. The inbound message may contain header, body, and envelope portion. When Transaction Manager takes the proper operation against the Siebel application, the integration object instances for response is generated as well. All information from the request message is dropped if this value is set to true. Therefore, the Industry XML Converter and Industry XML Data Transformation Engine do not need to deal with the overheads. If this is not set to true, then request information will still be carried over. |
XMLHierarchy |
N/A |
Property set in internal integration object hierarchy. |
IXMLMapPath |
N/A |
Store the key value for the dispatch map. Industry XML Transaction Manager will use it to look up the value, and attach necessary value into integration object instance. |
PrimaryRowId |
N/A |
The PrimaryRowId of the integration object. |
SiebelFINSOperationOut |
N/A |
The outbound operation Industry XML Transaction Manager takes through its user property. |
SearchSpec |
N/A |
The Search Specification for query. |
PlaceToSave |
mem |
PlaceToSave indicates whether the rollback instance is getting from “file" or “mem." Valid values are “file" or “mem." |
RollbackInError |
false |
Indicates whether the transaction should be rolled back. Valid values are “true" or “false." |
Although these arguments are available to use with the Industry XML Transaction Manager, not all can be used with each method. The following tables list all the method arguments for each method.
| Argument | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
OnlyIOI |
Only produce Integration Object Instance |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
No |
RollbackInError |
Is Rollback in Error |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| Argument | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IXMLMapPath |
IXML Map Path |
String |
Input |
No |
PrimaryRowId |
Primary Row Id |
String |
Input |
Yes |
SiebelFINSOperationOut |
Outbound Operation |
String |
Input |
No |
SearchSpec |
Search Specification |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
No |
| Argument | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IXMLMapPath |
IXML Map Path |
String |
Input |
No |
PrimaryRowId |
Primary Row Id |
String |
Input |
Yes |
SiebelFINSOperationOut |
Outbound Operation |
String |
Input |
No |
SearchSpec |
Search Specification |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLHierarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Output |
No |
PlaceToSave |
Place To Save |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Industry XML Data Transformation Engine
The Industry XML Data Transformation Engine transforms the hierarchy between external and internal data models that are represented by integration object instances. The Industry XML Data Transformation Engine is designed to handle heterogeneous messages to allow more than one business object scenario. It also takes extra input arguments specified in the data transformation map to indicate the possibility of removing empty value tags from the instances transformed.
The following table lists the specific methods for the industry XML Data Transformation Engine.
| Methods | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
ToExternal |
Transform To External Hierarchy |
Transforms Siebel internal integration object hierarchy into the industry XML external hierarchy. |
ToInternal |
Transform To Siebel Hierarchy |
Transform industry XML external hierarchy into the Siebel internal integration object hierarchy. |
Industry XML Data Transformation Engine business service uses combinations of method, and method arguments to achieve different tasks. The following table lists all the method arguments available to use with Industry XML Data Transformation Engine business service.
| Argument | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
N/A |
Property set in internal or external integration object hierarchy. |
<MapArgs> |
N/A |
See Business Processes and Rules: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration. |
Each method defined for the Industry XML Data Transformation Engine business service takes some input arguments and produces some output arguments as listed in the following tables.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierrarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
No |
<MapArgs> |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierrarchy |
XML Property Set |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
No |
<MapArgs> |
String |
Input |
Yes |
Industry XML Converter
The Industry XML Converter supports the generic syntax and rules requirements of the general industry XML standard. It converts the data from Siebel external integration object hierarchy to XML hierarchy that conforms to DTD specifications. For example, it generates certain authentication parameters for the XML message, and also generates and detects the fault sections in an XML message for extended converters to manipulate. The following table lists all the user properties for this converter.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
EscapeNames |
true or false |
If set to true, the converter replaces illegal XML name characters with escape characters. Otherwise, it will ignore illegal XML name characters. The default value is true. |
HierarchyFormat |
XML Hierarchy |
Format of the property set input or output. Internal use only. |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
<integration object name> |
Name of an integration object that defines the content and hierarchy for the envelope and header section of any industry XML standards. |
This service provides several ready-to-use-methods as described in the following table.
| Methods | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
PropSetToXML |
PropSetToXML |
Converts an integration object hierarchy to XML string. |
PropSetToXMLPropSet |
PropSetToXMLPropSet |
Converts an integration object hierarchy to XML hierarchy. |
XMLToPropSet |
XMLToPropSet |
Converts an XML string to an integration object hierarchy. |
XMLPropSetToPropSet |
XMLPropSetToPropSet |
Converts an XML hierarchy to an integration object hierarchy. |
For each method defined the Industry XML Converter business service takes input arguments and produces output arguments. These arguments are described in the following table.
| Method Argument | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
XML Document |
N/A |
XML document streams. |
Escape Names |
true |
Escape characters, invalid XML characters, to be removed or not. |
Ignore Character Set Conversion Errors |
false |
If some characters cannot be represented in the destination character set, for example, local codepage, the errors can be ignored. |
XML Character Encoding |
N/A |
XML character encoding to use in the output XML document. If encoding is blank or not supported, errors will be produced. |
XML Header Text |
N/A |
Text to preappend to the XML document. |
XML Hierarchy |
N/A |
Property Set in external integration object or XML hierarchy. |
External Entity Directory |
N/A |
Location of an external entity file, such as a DTD file. |
Validate External Entity |
false |
If true, the XML parser will validate the document according to the DTD specified in the <DocType> element. |
Truncate Field Values |
true |
truncate field values. |
Contains Inline Attachments |
true |
Indicates the message contains attachment documents. |
Each Industry XML Converter method uses groups of these method arguments to convert the data for the next service in the integration process. The following tables display the method arguments for each method.
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
<Value> |
XML Document |
String |
Output |
Yes |
EscapeName |
Escape Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
IgnoreCharSetConvErrors |
Ignore Character String Set Conversion Errors |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLCharEncoding |
XML Character Encoding |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLHeaderText |
XML Header Text |
String |
Input |
Yes |
XMLHierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input |
No |
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
No |
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <Value> |
XML Document |
String |
Input |
No |
| EscapeName |
Escape Name |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| ExternalEntityDirectory |
External Entity Directory |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| IgnoreCharSetConvErrors |
Ignore Character String Set Conversion Errors |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| ValidateExternalEntity |
Validate External Entity |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| XMLCharEncoding |
XML Character Encoding |
String |
Output |
Yes |
| XMLHierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Output |
Yes |
| Name | Default Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ContainsInlineAttachments |
Contains Inline Attachments |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| TruncateFieldValues |
Truncate Field Values |
String |
Input |
Yes |
| XMLHierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input/Ouput |
No |
Industry XML Dispatcher
The Industry XML Dispatcher is responsible for receiving and dispatching inbound messages. It receives the message and determines the specific XML standards associated with the message. It also scans the message for commands that are supported and specified in its rule sets dispatcher map and associates each command with the corresponding integration objects and so on. The following table lists all the user properties for the Industry XML Dispatcher.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
DispatcherMapName |
<integration object name> |
Name of an integration object that details the dispatching rules and syntax for the XML standard. This map is usually created along with all the other integration objects by the wizard. The default map name is “IXMLDispMap". |
XMLEnvIntObjectName |
<integration object name> |
Name of an integration object that defines the content and hierarchy for the envelope and header section of any industry XML standards. |
XMLFaultObject_O |
<path to fault section or element> |
This allows the dispatcher to identify a fault section with the first token and further confirm it with the value of the second token if applicable. Extra fault objects can be added by incrementing the name with _1,_2, and so on. An example for the value for this user property name is XMLFaultObject_1 and value is //IOI/@cmdstatus;fail. |
The Industry XML Dispatcher business service provides ready-to-use methods described in the following table.
| Methods | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
DispatchMessage |
Dispatch Message |
Validates the incoming XML message. If the message conforms to the dispatching rules, integration object names and other necessary information will be attached. It also checks for the respective envelope, header, and fault section of the message and identifies them. |
DispatchStdMessage |
Dispatch Standard Message |
Identifies the industry XML standard of the incoming XML message. It recognizes all XML standards configured in its input arguments. Value “Unknown" will be the output argument, if it does not recognize the XML standard. |
For each method defined the Industry XML Dispatcher business service takes input arguments and produces output arguments. These arguments are described in the following tables.
| Argument | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
XML Hierarchy |
N/A |
Property Set in XML hierarchy. |
<XML Standard> |
N/A |
An XML standard. For example, when configuring this input argument, the Input Argument is the XML standard and the Value is its envelope XML tag. |
XML Standard |
N/A |
The XML standard that matches the incoming XML message’s envelope tag. |
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
No |
| Name | Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XMLHierarchy |
XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input |
No |
<XML Standard> |
String |
Input |
Yes |
|
XMLStandard |
XML Standard |
String |
Output |
No |