IPFE Description
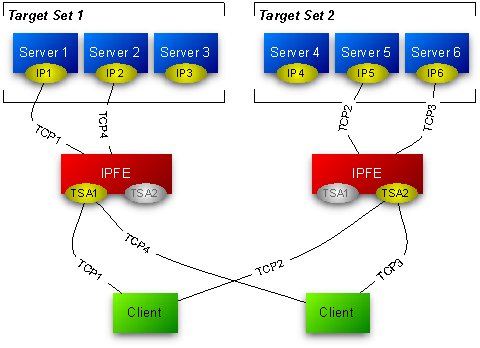
The IPFE acts as a specialized layer-3 router. The various servers to which the IPFE routes packets are divided into up to 16 groups, called Target Sets. Each of the target sets are assigned a shared Target Set Address, a publicly exposed service address.
Figure 2-1 shows either two connections are maintained at all times, in active/active or active/standby, or that a single connection is maintained, with a backup address for clients to establish a connection, if the first connection fails.
Figure 2-1 IPFE Architecture
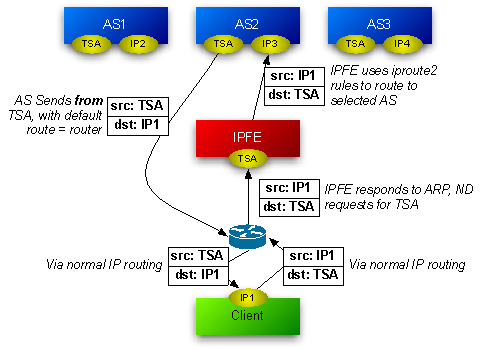
When the IPFE routes packets to application servers, it does not perform any rewriting of the packet. Figure 2-2 shows that neither the source IP address nor the destination IP address changes as it passes through the IPFE. The IPFE behaves as an IP router and does not act as a network address translator (NAT).
Figure 2-2 Packet Routing Through and Around the IPFE