2Overview of Web Services On Demand
Overview of Web Services On Demand
This chapter provides an overview of support for Web services in Oracle CRM On Demand. It contains the following topics:
About Web Services
The term Web services describes a standardized way of integrating Web-based applications over the Web. Web services allow businesses to communicate with each other and with other clients, without intimate knowledge of each other's IT systems. Web services share business logic, data, and processes through a Web services application programming interface (API). Application developers can then add the Web services to a software application (such as a Web page or executable program) to offer specific functionality to users.
Web Services Core Technologies
The Web services core technologies are a set of standards-based technologies that include:
Extensible Markup Language (XML). The standard markup language that allows the definition of message structures and facilitates the passing of data between software applications.
Web Services Description Language (WSDL). The XML-formatted language that is used to describe a Web service. A WSDL file defines the available methods, message structures, and network addresses required for using a specific Web service.
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). The XML-based protocol that is used to send Web services request and response messages. Web services messages are sent between the customer implementation of Web services and the SOAP handler on the Oracle Web Server.
For more information on Web services technologies, see:http://www.w3.org/2002/ws
Oracle CRM On Demand Web Services Toolkit
The Web Services Toolkit provides access to an application programming interface (API) that companies can use to build programs to integrate with Oracle CRM On Demand. The Toolkit includes a set of WSDL files that describes the interface to the Oracle CRM On Demand objects. This provides a programmatic interface for accessing your company's Oracle CRM On Demand information. A customer application can use the WSDL files through standard Web services development tools, such as those provided by the Oracle SOA Suite.The API for this release of Oracle CRM On Demand is backward-compatible with previous releases.
The following figure shows how the Web Services Toolkit interacts with the Oracle CRM On Demand database. The customer uses the Web Services Toolkit (WSDL files) to define the objects and methods that are contained in the Oracle CRM On Demand Hosted Service. The customer application communicates with Oracle CRM On Demand over the Internet using the secure HTTPS protocol. It invokes the Web services implementation contained in the Oracle CRM On Demand Hosted Service.
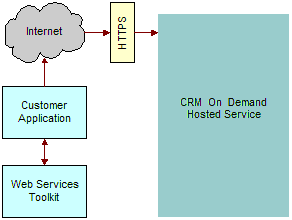
Oracle CRM On Demand is designed to be backward-compatible with previous releases. WSDL files from previous releases will continue to work with newer releases of Oracle CRM On Demand, and there is no need for customers to modify their code when upgrading to a new release of Oracle CRM On Demand.
Oracle CRM On Demand Web Services and Integration with Oracle CRM On Demand
The Web Services On Demand API allows companies to build programs to integrate with Oracle CRM On Demand. Some common examples of client integrations include the following:
Integrations of CRM and back-office applications. You can retrieve real-time sales, marketing, and service information from Oracle CRM On Demand and use it in financial and other back-office applications. For example, you can retrieve information about recently closed opportunities through the Web services interface and insert this information into an order entry system that has a Web services user interface. In addition, you can store information from back-office applications in Oracle CRM On Demand for instant access by users, visible in custom fields on any Oracle CRM On Demand page.
Web-based portal applications. You can create customized Web-based applications using Active Server Pages (ASPs), Java Server Pages (JSPs), or similar Web technology that accesses Oracle CRM On Demand through the Web services interface. For example, an Oracle CRM On Demand customer can deploy a customized Web form on its corporate Web site, allowing visitors to enter requests for more information. The application creates new lead records in Oracle CRM On Demand for these requests through the Web services interface. Another Web page can allow visitors to browse through solutions to common problems stored in Oracle CRM On Demand and retrieved in real time through the Web services interface.
Custom add-on modules. Customers can also extend Oracle CRM On Demand functionality. For example, a company can create a custom add-on module to streamline its unique quote creation process, or a company can create additional utilities to perform mass data cleanup operations. These modules access data in Oracle CRM On Demand directly through the Web services interface. Oracle CRM On Demand administrators and users can run these modules while concurrently accessing the Oracle CRM On Demand user interface.
Web Services Security
The Oracle CRM On Demand Web Services Integration framework includes the following security features:
The mustUnderstand attribute of Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) 1.1 is supported. This allows a client to specify that the target server must be capable of processing all parameters in the SOAP request header, otherwise the requests must be rejected.
SOAP message validation is performed, for example, to check for badly formed SOAP requests or for SOAP header elements that are not namespace-qualified.
Support is provided for the WS-I Basic Security Profile Version 1.0. For more information, see the following section.
All communications are encrypted with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for security (minimum 128-bit).
Access is session-based, requiring authorization with a valid Oracle CRM On Demand user name and password.
Inactive sessions are reused or closed automatically after a period of inactivity.
The same data visibility and access capabilities that apply to users in the Oracle CRM On Demand hosted service are applied to users connected through the Web services interface. Data visibility and access are restricted by the role that your company assigns. Permissions are checked for every data access.
A full audit trail of Web services activity is available through Oracle CRM On Demand's Administration pages. These pages display both current and historical usage statistics.
A number of other proprietary solutions protect Oracle CRM On Demand against malicious use of the Web services interface. These solutions are constantly reviewed and improved as new technologies and techniques become available.
A session with a standard HTTPS request is created to establish a connection with Oracle CRM On Demand through the Web services interface. A client can create a new session with the login operation and close it with the logoff operation. When a session is created, an encrypted session identifier is provided to the client, which for stateful Web services requests, must be included in all subsequent requests during that session. For more information, see About Establishing and Managing the Web Services Session.
Support for the WS-I Basic Security Profile Version 1.0
Support is provided for the WS-I Basic Security Profile Version 1.0, which describes the set of parameters used to authenticate a Web services transaction.
Oracle CRM On Demand has implemented support for the Username and PasswordType parameters, which are part of the UserNameToken standards. This allows a username and password to be passed with a SOAP request, which removes the necessity for a separate login operation. For more information, see Using Stateless Web Service Requests.
Passwords can be specified as type PasswordText only, which mean that the password is in clear text format.
WSSE Namespace Support
The SOAP header of messages received by Oracle CRM On Demand are validated to ensure they are namespace-qualified. Oracle CRM On Demand supports the following namespace values when specifying the WSSE namespace in a SOAP request:
Draft Namespaces:
wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/04/secext"
wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/secext"
Version 1.0 Namespace: wsse="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-secext-1.0.xsd"
The WSSE Version 1.0 namespace must be specified to perform a stateless transaction. (In addition, the Web Services R16 Compatibility Mode check box must be cleared in the Company Profile page and the Username and PasswordText tokens must be provided in the request.)
For more information about stateless transactions and the use of the WSSE namespace, see Establishing and Managing the Web Services Session
Web Services Reliability
All server components of Oracle CRM On Demand, including those responsible for the Web services interface, incorporate load balancing and other high-availability mechanisms. These mechanisms prevent the service from being interrupted by server or network infrastructure failure.
Web Services and the Oracle CRM On Demand Objects
Oracle CRM On Demand Web services allow applications to integrate with Oracle CRM On Demand. They provide the ability to find and invoke the core Oracle On Demand Web Services across the Web from any client application language. This ability makes the process of using Oracle CRM On Demand Web Services easy for those who want to use them.
The Oracle CRM On Demand services provide a basis for customers to perform integration with Oracle CRM On Demand based on SOAP technology.
All major Oracle CRM On Demand business objects are accessible in the Web services, with the names of the Web services matching the default names of the business objects. Oracle CRM On Demand Objects Accessible Through Web Services details the Oracle CRM On Demand parent and child objects that are accessible through Oracle CRM On Demand Web Services.
Web Service APIs
Starting with Web Services On Demand Version 4.0 (CRM On Demand Release 16), objects are accessible through two APIs:
Web Services v1.0. Used to interact with Custom Objects 01-03, as well as preconfigured objects.
Web Services v2.0. Used to interact with all Oracle CRM On Demand Custom Objects, as well as preconfigured objects. Also used to access custom Web applets.
Before Web Services On Demand Version 4.0, only the Web Services v1.0 was available. In addition, the following APIs are provided:
Service APIs. Used to perform management tasks and retrieve integration events through Web services.
Administrative Services APIs. Used to access company metadata through Web services.
For the Web Services v1.0 API, operations work on the parent objects and all child components are synchronized with the parent. The Web Services v2.0 API, however, works on a node basis, where parent and child components are treated as separate nodes.
The Web Services v2.0 API provides an Execute method for performing multiple operations on separate nodes, and the Web Services v2.0 QueryPage method offers additional options (through the searchspec, namedsearchspec, sortorder, and sortsequence arguments) for issuing queries compared to the Web Services v1.0 QueryPage method.
The following table shows the methods available through the Web Services v1.0 and Web Services v2.0 APIs for access to objects.
Table Web Services v1.0 and Web Services v2.0 Methods
| Web Services v1.0 | Web Services v2.0 | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Finds records in the Oracle CRM On Demand database that match specified field values, and then deletes them. Deleted records are visible in the Deleted Items area of the Oracle CRM On Demand UI and can be queried using the DeletedItemQueryPage method. |
||
Not applicable |
Deletes child records from the Oracle CRM On Demand database, or removes the association between the child and the parent object. |
|
Not applicable |
Executes multiple update, insert, and delete operations on separate records in the Oracle CRM On Demand database within the same Web services request. |
|
Inserts new records into the Oracle CRM On Demand database. |
||
Not applicable |
Inserts new child records into the Oracle CRM On Demand database. |
|
Not applicable |
Updates existing records or inserts a new record if one did not exist. |
|
Executes a query against a specified list of records, and returns a subset of the records that match the search criteria set by the method arguments. |
||
Updates records with a new value. |
||
Not applicable |
Updates child records with a new value. |
The following table shows differences between Web Services v1.0 and Web Services v2.0.
Table Web Services v1.0 and Web Services v2.0 Differences
| Web Services v1.0 | Web Services v2.0 |
|---|---|
Supports an upsert operation through InsertOrUpdate call |
Does not support an upsert operation |
Pagination parameters are supported only at the parent level |
Pagination parameters are supported at both the parent and child level |
Returns all child records even if the condition is true for one child. For example, the QueryPage call returns all partner children from an account even if the condition is true for only one partner child |
Outputs only the specific child whose condition was met. For example, QueryPage returns only the specific partner child from the account for which the condition was true. |
UseChildAnd argument of QueryPage call is available for using OR/AND logic between parent and child |
The UseChildAnd argument is not available. Instead, by default, all parent records matching the parent criteria and only children matching the child criteria are returned. |
Operators cannot be used to construct complex queries across multiple fields |
The SearchSpec argument of QueryPage can be used to construct complex queries across multiple fields in a request. For example, the OR operator can be used to find all records that match the specified condition for [Field A] OR the specified condition for [Field B]. |
Sort order is not customizable |
Sortorder and sortsequence arguments are available to customize the sorting order of the records |
Update call removes child objects not specified in the request |
An Execute call with "operation=update" at the parent level removes the unspecified children in the request |
InsertChild call is used to insert the children for existing parent objects |
For Web Services v2.0:
|
UpdateChild call is used to update child records |
For Web Services v2.0:
|
DeleteChild call is used to delete the child records |
For Web Services v2.0:
|
InsertChild, UpdateChild, and DeleteChild methods are used to perform operations on child records |
In an Execute request, a specific node within the request can be skipped using the "operation=skipnode" attribute. This can be used to simulate InsertChild, UpdateChild or DeleteChild by skipping the parent node and only performing the specified actions on the child records. |
LOVLanguageMode argument is not available |
The LOVLanguageMode argument is an input argument for all of the Web Services v2.0 calls. It determines whether the processing for picklist fields occurs using language independent codes (LIC) or language dependent codes (LDC). |
ViewMode argument is not available |
The ViewMode argument, which specifies the level of access to records specified in the method call, is available for all of the Web Services v2.0 calls. |
Does not support access to custom Web applets. |
Supports access to custom Web applets as read-only child objects of a parent object. |
There are some differences between the format of the WSDL files for Web Services v1.0 and Web Services v2.0:
In the Web Services v2.0 API, strong data typing is supported. Therefore, in the Web Services v2.0 WSDL files, fields are represented by a range of xsd: data types, while in Web Services v1.0 WSDL files, all fields have the xsd:string data type. For more information, see Field Types Supported by Oracle CRM On Demand.
In Web Services v2.0, messages do not include the business service name, and have the format:
[Objectname][Method]_[Input/Output]
For example:
AccountInsert_Input, ContactQueryPage_Output
as opposed to the following for Web Services v1.0:
AccountWS_AccountInsert_Input, ContactWS_ContactQueryPage_Output
The target namespace of the WSDL for Web Services v2.0 is:
urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/objectname/compared to the following for Web Services v1.0:
urn:crmondemand/ws/objectname/
About Parent-Child Relationships
Many of the Oracle CRM On Demand objects interact with each other through parent-child relationships. A parent object refers to the main or base object of interest and the child object refers to objects that are related to the parent in some way-for example, if the child is contained in the parent, or if the child has records that refer to the parent.
These parent-child relationships can be one-to-many or many-to-many. For example, a lead can be associated with a particular account, but an account can have many leads associated with it. In this case, you can think of the relationship between the account and its leads as a one-to-many parent-child relationship.
Other relationships can be many-to-many, meaning that many children are associated with many parents. For example, a contact can be associated with several opportunities, or an opportunity can have several contacts associated with it. In this case, you can think of the relationship between contacts and their opportunities as a many-to-many parent-child relationship. The parent-child relationship between contacts and opportunities can be treated with either the opportunity as the parent with contacts as children, or with the contact as the parent and the opportunities as children.
Web Services On Demand and Custom Fields
Oracle CRM On Demand allows company administrators to create custom fields that capture information specific to the company’s needs. Web Services On Demand allows customers to interact with the data stored in these custom fields. Each custom field has an associated integration tag that is used by Web services and Web links to reference data in custom fields. This feature allows administrators to change the display name of a field without making modifications to the existing Web services integration.
Custom Fields can be referenced using two different integration tags:
The Custom WSDL file uses the format:
fieldtypeDisplay_Name
For example, a custom Boolean field with the display name
Account Selectedwould have the default custom integration tagbAccount_Selected.The Generic WSDL file uses the format:
fieldtype##
For example, a custom Boolean field would have the generic integration tag
CustomBoolean0.
The following procedure describes how to view or modify the integration tag information:
To view or modify integration tag information for a record type
Navigate to the Field Setup Administration page for the required record type.
For example: Admin, Application Customization, Account, Account Field Setup, Rename Fields.
Click Advanced.
The integration tag information is displayed for you to view or modify.
You can download custom WSDL files in which the XML tags for the custom fields are based on the integration tags using the following procedure:
To download a WSDL file that is specific to your company’s customization
Navigate to the Web Services Administration page.
From the Select Service drop-down list, select Web Services v1.0, or Web Services v2.0 as required.
From the Document list, select WSDL.
From the Type list, select Custom.
From the WSDL Object list, select the required record type.
From the Select Related Information list, select the child record types that you wish to include in the WSDL.
Click Download.
Save the WSDL file to your computer.
For more information about downloading WSDL files, see Downloading WSDL Files.
Field Types Supported by Oracle CRM On Demand
The field types supported depend on whether the Web Services v1.0 or Web Services v2.0 API is used, as described in the following topics.
Web Services v1.0
For the Web Services v1.0 API, all fields in Web services On Demand are transmitted and received as strings. It is the client’s responsibility to cast these to and from the required data type in any application. The proper type can usually be determined from the name, purpose, or application of the field. There is no dynamic method for determining field types. You can derive clues about a field’s type from its name as follows:
A name ending in the suffix Id is usually a key field, such as a primary key, foreign key, or user key Id. It can usually be treated as a unique text string.
Fields with names containing Date or Time, such as LastUpdated, DueDate, StartTime, or EndTime might be date fields.
Telephone number fields can be treated as numeric phone numbers or as plain text. When performing queries on phone number type fields the following formats must be used in Query operations:
U.S. Format: +1 872 5550199
France: +33 01 40359564
Japan: +81 3 54579623
Other numeric fields, such as currency, size, revenue, or probability can be treated as integer, floating point, or text fields depending on the client application.
Boolean fields have the value Y for true or N for false.
Most other fields can be treated as ordinary text.
Web Services v2.0
The Web Services v2.0 API supports strong data types for fields, so fields are represented by appropriate XSD data types. The following table shows the list of supported XSD data types.
Table Data Type Mapping in the Web Services v2.0 API
| Data Type | Mapped XSD Data Type |
|---|---|
BOOL |
xsd:boolean |
CURRENCY |
xsd:decimal |
NUMBER |
xsd:decimal |
DATE |
xsd:date |
DATETIME |
xsd:dateTime |
UTCDATETIME |
xsd:dateTime |
ID |
xsd:string |
NOTE |
xsd:string |
PHONE |
xsd:string |
TEXT |
xsd:string |
INTEGER |
xsd:int |
TIME |
xsd:time |
Others |
xsd:string |
If an incorrect data type is provided in a Web services request, the field is updated to NULL or a default value for that specific data type, as shown in the following table.
Table Updating of Fields When Incorrect Data Types are Provided in the Web Services v2.0 API
| XSD Data Type | Default Value or Null |
|---|---|
xsd:boolean |
N |
xsd:decimal |
NULL |
xsd:date |
NULL |
xsd:dateTime |
NULL |
xsd:string |
NULL |
xsd:int |
0 |
xsd:time |
NULL |
For example, Activity has a field named Cost, which takes integer values. If you provide a text value for the field in an update request, the previous value is replaced with a 0.
You can find further details about the definition of XSD data types here:
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#built-in-datatypes
Special Search Fields
Some field names are prefixed with CI_ to denote that they are special fields that provide better search functionality. These fields do not exist for all objects but are easily identified in the WSDL files as shown in the following excerpt from the Account WSDL file:
<xsd:element name="CI_AccountName" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" type="xsd:string"></xsd:element> <xsd:element name="CI_Location" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" type="xsd:string"></xsd:element>
Support for Multi-Select Picklists
A multi-select picklist is a picklist from which the user can select multiple values. In Web Services On Demand, multi-select picklists are only accessible for the following record types:
Account
Activity
Contact
Custom Object 01
Custom Object 02
Custom Object 03
Lead
Opportunity
Service Request
For these record types, all standard and custom multi-select picklist fields are accessible. You can add, remove, replace or query selections in parent-level multi-select picklist fields, however child-level multi-select picklist fields are not supported.
Input and output values are language-independent code (LIC) delimited, but the multi-select picklist delimiter is always a semicolon regardless of locale for input and output: <LIC1>;<LIC2>.
Locale-Dependent Access to Oracle CRM On Demand
Oracle CRM On Demand Web Services does not provide any specialized localization interfaces. Oracle CRM On Demand supports full localization, so that the data created through Web services is localized for users. The localized fields in the Web services interfaces follow the formats outlined in the following topics.
Date and Time Fields
Date and time fields for Web services v1.0 are in the following format:
MM/DD/YYYY hh:mm:ss
For Web services v1.0, the time zone is assumed to be the logged in user’s time zone, which is determined from the user’s locale.
For Web services v2.0, the data in SOAP requests conforms to XSD data formats.
The XSD dateTime datatype has the format:
yyyy '-' mm '-' dd 'T' hh ':' mm ':' ss ('.' s+)? (zzzzzz)?
An example of a date and time in this format is:
2002-10-10T12:00:00-05:00
This example represents noon on 10th October 2002, Central Daylight Savings Time, which is equivalent to Eastern Standard Time in the US.
The same date and time for UCT, which is equivalent to the GMT time zone is as follows:
2002-10-10T17:00:00Z
For the QueryPage method of Web Services v2.0, either the XSD formats (recommended) or the locale-specific formats can be used.
Number and Currency Fields
Number and currency fields in Oracle CRM On Demand are in raw number format. In other words, number and currency fields hold only digits with no currency symbols, decimal separators, or other numeric separators.
When the company profile setting: Prevent Web Service Updates of Inactive Currencies is selected, currency field values cannot be updated to an inactive currency.
Validation of Email Fields
When Oracle CRM On Demand validates fields containing email addresses, it identifies the following as invalid:
Empty string
String too long
No characters before the at sign (@) character, for example: @riqhtequip.com
No at sign (@) character, for example:isampleriqhtequip.com
No period (.) character, for example: isample@riqhtequipcom
No domain, for example: isample@
No domain suffix such as com, for example: isample@riqhtequip
Multiple at signs (@), for example: isample@@riqhtequip.com
Consecutive period (.) characters, for example: isample@riqhtequip..com
Spaces in the string, for example: isa mple@riqhtequip
Characters other than the following in the local part of an email address:
Uppercase and lowercase letters (case insensitive)
The digits 0 through 9
The characters:
Exclamation point (!)
Hash symbol (#)
Dollar sign ($)
Percent (%)
Ampersand (&)
Single quotation sign (')
Asterisk (*)
Plus sign (+)
Minus sign (-)
Slash (/)
Equal sign (=)
Question mark (?)
Caret (^)
Underscore (_)
Back single quotation mark (`)
Left curly brace ({)
Vertical bar (|)
Right curly brace (})
Tilde (~)
Any special characters in the domain name of an email address. These special characters are the same as those allowed in the local part of the email address, and also the left and right parentheses ().
Unicode Characters in Email Addresses
For some fields in Oracle CRM On Demand, email addresses can include most Unicode (UTF-8) characters, if the Allow Unicode Characters in Email Fields company profile setting is selected. This allows, for example, email addresses to contain accented characters.
Oracle servers do not support Unicode characters in email addresses, therefore such addresses are not allowed in User email fields. However, Oracle Eloqua Marketing Cloud Service does support Unicode characters, therefore you can save email addresses containing Unicode characters in Contact and Lead email fields and use the Send Email via Engage button on Contact Detail, Contact List, Lead Detail, or Lead List pages to send the emails. For more information about the use of Unicode characters in email addresses, see Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help.
Mapping Primary Address Fields Using Web Services
In Web services requests, a PrimaryAddressLine1 field is used to dynamically map the primary address field from an external application to the primary address field in Oracle CRM On Demand. The primary address field in Oracle CRM On Demand can vary depending on the Country value for each address; thus the PrimaryAddressLine1 field will map to a different field in the address object based on the Country value. The following tables show the mapping for the PrimaryAddressLine1 field depending on the selected Country value.
Table Primary Address Line1 To Address Field Mapping by Country
| Address | Lead | Account (Billing Address) | Account (Shipping Address) | Contact (Account Address) | Contact (Contact Address) | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Street Address |
Street Address |
Bill To Street Address |
Ship To Street Address |
Personal Street Address |
Primary Street Address |
Group A See the following table |
Street Address 3 |
Street Address 3 |
Bill To Street Address 3 |
Ship To Street Address 3 |
Personal Street Address 3 |
Primary Street Address 3 |
Nauru |
Postal Code |
Postal Code |
Bill To Postal Code |
Ship To Postal Code |
Personal Postal Code |
Primary Postal Code |
Group B See the following table |
County |
County |
Bill To County |
Ship To County |
Personal County |
Primary County |
Group C See the following table |
Province |
Province |
Bill To Province |
Ship To Province |
Personal Province |
Primary Province |
Qatar |
City |
City |
Bill To City |
Ship To City |
Personal City |
Primary City |
Papua New Guinea |
Table Groups of Countries with Different Address Field Mappings
| Group | Countries |
|---|---|
A |
United States and all other countries apart from those in groups B and C, and those mentioned in the previous table. |
B |
Hungary, Belarus, Burkina Faso, Congo, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russian Federation, Congo Sudan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine |
C |
Antigua and Barbuda, Benin, Burundi, Botswana, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mauritania, Namibia, Niger, Niue, Oman, Puerto Rico, Rwanda, Seychelles, Solomon Islands, Tanzania, Togo, Tonga, Tuvalu, Uganda, United Arab Emirates, Vanuatu |
Querying for an Address Record using PrimaryAddressLine1
When using the PrimaryAddressLine1 field to query for an address record, the value returned is the value contained in the mapped field for the specified country. For example, when querying for an address with <Country>Canada</Country>, the PrimaryAddressLine1 field is mapped to the Address field:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/
2001/XMLSchema">
<SOAP-ENV:Body><ns:AccountQueryPage_Output xmlns:ns="urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/account/">
<ListOfAccount xmlns="urn:/crmondemand/xml/Account/Data" lastpage="true">
<Account>
<Location>Toronto</Location>
<AccountName>ACCOUNTTEST1</AccountName>
<ListOfAddress lastpage="true">
<Address>
<Id>1QA2-R7C3O</Id>
<StreetAddress3></StreetAddress3>
<Country>Canada</Country>
<County></County>
<Description></Description>
<Province>ON</Province>
<ZipCode>M2H 3G5</ZipCode>
<City>Toronto</City>
<IntegrationId>1QA2-R7C3O</IntegrationId>
<Address>100 Main Street</Address>
<StreetAddress2></StreetAddress2>
<PrimaryAddressLine1>100 Main Street</PrimaryAddressLine1>
</Address>
...
</ListOfAddress>
</Account>
</ListOfAccount>
</ns:AccountQueryPage_Output>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
whereas, when the <Country> value is Togo, the PrimaryAddressLine1 field maps to the County field:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/
2001/XMLSchema">
<SOAP-ENV:Body><ns:AccountQueryPage_Output xmlns:ns="urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/account/">
<ListOfAccount xmlns="urn:/crmondemand/xml/Account/Data" lastpage="true">
<Account>
<Location>Togo</Location>
<AccountName>ACCOUNTTEST2</AccountName>
<ListOfAddress lastpage="true">
<Address>
<Id>1QA2-R7IMS</Id>
<StreetAddress3></StreetAddress3>
<Country>Togo</Country>
<County>10222</County>
<Description></Description>
<Province></Province>
<ZipCode></ZipCode>
<City>Lomé</City>
<IntegrationId>1QA2-R7IMS</IntegrationId>
<Address></Address>
<StreetAddress2></StreetAddress2>
<PrimaryAddressLine1>10222</PrimaryAddressLine1>
</Address>
...
</ListOfAddress>
</Account>
</ListOfAccount>
</ns:AccountQueryPage_Output>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Inserting or Updating an Address Record using PrimaryAddressLine1
When inserting or updating an address record using the PrimaryAddressLine1 field, the value provided in the PrimaryAddressLine1 field is written to the primary address field based on the Country value provided in the request. If a value is provided for both the PrimaryAddressLine1 field and the primary address field (for example, County) for the specified country, the value in the PrimaryAddressLine1 field is respected and the value in the primary address field is ignored. This is shown in the following table.
Table Value specified for PrimaryAddressLine1 and Primary Address Field
| Field Name | SOAP Request | Value Written to DB |
|---|---|---|
Country |
Togo |
Togo |
County |
BP 128 |
1 Main Street |
Street Address 1 |
Not applicable |
None |
PrimaryStreetAddress1 |
1 Main Street |
None |
In the case where only a PrimaryAddressLine1 value is submitted, this value is written to the mapped field in the DB as shown in the following table.
Table Value specified for PrimaryAddressLine1 only
| Field Name | SOAP Request | Value Written to DB |
|---|---|---|
Country |
Togo |
Togo |
County |
Not applicable |
1 Main Street |
Street Address 1 |
Not applicable |
None |
PrimaryStreetAddress1 |
1 Main Street |
None |
Objects Supporting the PrimaryAddressLine1 Field
The PrimaryAddressLine1 field is available on a number of objects accessible through the Web Services v2.0 interface as shown in the following tables.
Table Parent Objects on Which the PrimaryAddressLine1 field is available
| Object Name | Fields |
|---|---|
Account |
BillingPrimaryAddressLine1, ShippingPrimaryAddressLine1 |
Contact |
PrimaryAddressLine1, AlternateAddressLine1 |
Lead |
BillingPrimaryAddressLine1 |
Table Child Objects on Which the PrimaryAddressLine1 field is available
| Parent Object Name | Child Object Name | Fields |
|---|---|---|
Account |
Address |
Not applicable |
Account |
Contact |
Not applicable |
Contact |
Address |
PrimaryAddressLine1 |
Contact |
Lead |
BillingPrimaryAddressLine1 |
Support for Web Link Fields
A Web link field is a custom field that allows you to place a hyperlink to an external Web site or Web-based application in a record in Oracle CRM On Demand. You can access Web link fields through Web Services v2.0 calls to retrieve the URL and the display text for the Web link field. You cannot create, update, or delete Web links through Web Services v2.0 calls.
Web services calls retrieve custom Web link field values in anchor tags with the following format:
<a href="www.link.com">Web Link Display Text</a>
However, in responses the URL and display text are encoded as shown in the following example:
<CustomWebLink0><a href="https&#x3a;&#x2f;&#x2f;www.google.com&#x2f;&#x3f;gws_rd& #x3d;ssl&#x23;q&#x3d;Oracle&#x25;20Corporation">Find Oracle Corporation</a></CustomWebLink0>
In the href attribute value, the URL is HTML attribute value encoded. The anchor tag content corresponds to the Web link display text. The URL and display text must be extracted from the encoded values, as described in the following section.
Example of Retrieving and Extracting Web Link Values
As an example, a contact can have a Web link field, CustomWebLink0, with the following configuration:
Display Text. Find %%%First_Name%%% %%%Last_Name%%%
URL. https://www.google.com/?gws_rd=ssl#q=%%%First_Name%%% %%%Last_Name%%%
For information about how to set up Web links in the UI, see Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help.
For a Web service QueryPage call for a Contact having Id = 1QA2-230MBG, First Name = Oracle, and Last Name = Corporation, the request and response are shown in the sample SOAP request and response in this topic..
The CustomWebLink0 field value is retrieved as:
<CustomWebLink0><a href="https&#x3a;&#x2f;&#x2f;www.google.com&#x2f;&#x3f;gws_rd& #x3d;ssl&#x23;q&#x3d;Oracle&#x25;20Corporation">Find Oracle Corporation</a></CustomWebLink0>
The display text and URL must then be extracted from the encoded values in the Web service response.
To extract Web link display text
From the field value, extract the Web link display text using the regular expression pattern "<a.*?>(.*?)</a>".
For the CustomWebLink0 example, the Web link display text is extracted as:
Find Oracle Corporation
To extract a Web link URL
From the field value, extract the Web link URL using the regular expression pattern "href=\"(.*?)\"".
For the CustomWebLink0 example, the following is extracted:
https://www.google.com/?gws_rd=ssl#q=Oracl e%20Corporation
The URL is HTML attribute value encoded, so to extract the actual URL, perform an unescape HTML operation.
For the CustomWebLink0 example, the following URL is extracted:
https://www.google.com/?gws_rd=ssl#q=Oracle%20Corporation
Sample SOAP Request for a Custom Web Link Field
The following is an example of a query request for the Web link field, CustomWebLink0:
<S:Envelope xmlns:S="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http:/
/schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<S:Body>
<ns2:ContactQueryPage_Input xmlns="urn:/crmondemand/xml/Contact/Data"xmlns:ns2="urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/contact/"
xmlns:ns3="urn:/crmondemand/xml/Contact/Query">
<ns3:ListOfContact pagesize="1">
<ns3:Contact>
<ns3:CustomWebLink0/>
<ns3:Id>='1QA2-230MBG'</ns3:Id>
</ns3:Contact>
</ns3:ListOfContact>
</ns2:ContactQueryPage_Input>
</S:Body>
</S:Envelope>
Sample SOAP Response for a Custom Web Link Field
The following response contains the encoded URL and display text for the Web link field, CustomWebLink0:
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/
XMLSchema-instance">
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<ns:ContactQueryPage_Output xmlns:ns="urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/contact/">
<ListOfContact xmlns="urn:/crmondemand/xml/Contact/Data" lastpage="true">
<Contact>
<Id>1QA2-230MBG</Id>
<CustomWebLink0><a
href="https&#x3a;&#x2f;&#x2f;www.google.com&#x2f;&#x3f;g
ws_rd&#x3d;ssl&#x23;q&#x3d;Oracle&#x25;20Corporation">Find
Oracle Corporation</a></CustomWebLink0>
</Contact>
</ListOfContact>
</ns:ContactQueryPage_Output>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Support for Concatenated Fields
A concatenated field is a field that can display the values from multiple fields and can also display additional text.
You cannot use Web services calls to update or query values within a concatenated field directly. To update or query the values of a concatenated field through Web service calls, you must update or query each of the individual fields separately. When you perform a QueryPage call on a concatenated field, the display text for the concatenated field is returned in the response.
For more information about concatenated fields, see Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help.
The Concatenated Field Administrative Service allows you to query, insert, and update concatenated field configuration data. For more information, see ConcatenatedFieldRead, ConcatenatedFieldReadAll, and ConcatenatedFieldUpsert.
Support for Maskable Fields
A maskable field is a field in which some of the data can be hidden from view from some users. The administrator can set up some custom fields as maskable fields for certain record types.
Users whose role includes the View Masked Data privilege, can view all of the data in a maskable field. However, users whose role does not include the View Masked Data privilege can see only the last four characters of the value in maskable fields. All of the other characters in the field are represented by the characters XXXX.
For example, if a maskable field contains the value 102030456789, then you see the following:
XXXX6789
If your user role includes the View Masked Data privilege, then the following applies to Web services requests:
You can insert data into maskable fields and update maskable fields.
The full (unmasked) field value is returned in query results.
If your user role does not include the View Masked Data privilege, then the following applies to Web services requests:
You can insert data into maskable fields and update maskable fields.
The masked field value is returned in query results.
You cannot use maskable fields in the search specification or sort specification in queries. Such queries return an error message.
For more information about maskable fields, see Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help.
Web Services Utilization
In the Oracle CRM On Demand application, the Web Services Utilization page provides detailed information on your company's Web services usage, both current and historical.
For each Web services request, Oracle CRM On Demand logs the following information:
Session Id. An identifier representing the session used to process a Web services request.
Web Service Name. The name of the Web service that was executed.
Operation. The operation that was performed.
Start Time. The date and time the request began processing.
End Time. The date and time the request completed processing.
Web Service Space. The namespace for the request that was executed.
User Alias. The alias of the user whose credentials were used to authenticate with.
Output Message Size (Bytes). The size of the response message in bytes.
Entry Type. Either Login, Logout, or Dispatch.
Input Message Size (Bytes). The size of the input message in bytes.
Web Service Client Name. The value provided in the <ClientName> parameter in the SOAP request. For more information about the Web Service Client Name parameter, see Web Service Client Name Identification.
# of Operations. The number of operations performed by Oracle CRM On Demand for the request.
Error Message. If the request resulted in an error, it is displayed, otherwise this field remains empty.
Type.. The user agent value for the request. For client integrations other than Oracle client integrations, this value defaults to
Web Services.For Web services requests, language-independent codes are used instead of the display values used in the Oracle CRM On Demand UI, as shown in the following table:
| Display Value for Type | Language-independent Code |
|---|---|
Interactive |
UI |
Unknown |
UNK |
Web Services |
WS |
The Web Services Utilization page supports Oracle CRM On Demand list management capabilities, allowing administrators to filter the list of entries and to export the data for further analysis in other applications.
You can also use the UserUsageQueryPage method to retrieve information about Web services utilization. For more information about this method, see UserUsageQueryPage.
See Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help for more information on using the Web Services Utilization page.
Web Service Client Name Identification
To allow accurate tracking of requests in the Web Services Utilization page, client applications require a mechanism to identify themselves in each Web service request that is sent to Oracle CRM On Demand. The SOAP header parameter, <ClientName> provides such a mechanism.
The <ClientName> parameter is optional, and is supported for both stateful and stateless web services operations.
Supported Client Name Characters and Usage
The <ClientName> value passed in the SOAP header is validated by Oracle CRM On Demand. The following characters are supported in the <ClientName> value:
UnicodeLetterOrDigit characters, that is, the set of Unicode characters identified as either a letter or a digit
Spaces
Commas
Any value passed in through the <ClientName> parameter that contains characters other than those specified above is not accepted by Oracle CRM On Demand. The request is still processed however, and the value Invalid Client Name is displayed in the Web Services Utilization page. The <ClientName> value is restricted to 100 characters; for any value longer than 100 characters, Invalid Client Name is displayed in the Web Services Utilization page.
It is also recommended that the following convention be used when specifying the <ClientName> value:
[Developer], [Client Name]
For example, an application developed by XYZ Consulting called Account Synchronization Utility can use the following:
XYZ Consulting, Account Synchronization Utility
This allows the customer to track not only which application has sent a request but also who to contact if an issue is discovered.
Sending the Client Name in Stateless Web Services Requests
Every stateless Web service request that requires tracking of the client name must include the <ClientName> element in the SOAP header, with the namespace "urn:crmondemand/ws" (or the namespace might be defined at the root level). This is shown in the following example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:wsse="http://docs.oasis-
open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-secext-1.0.xsd" xmlns:xsd="http://
www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<soap:Header>
<wsse:Security>
<wsse:UsernameToken>
<wsse:Username>USERNAME</wsse:Username>
<wsse:Password Type="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-
wss-username-token-profile-1.0#PasswordText">password</wsse:Password>
</wsse:UsernameToken>
</wsse:Security>
<ClientName xmlns="urn:crmondemand/ws">Oracle Corporation, Web Services On Demand Guide</ClientName>
</soap:Header>
<soap:Body>
<AccountQueryPage_Input xmlns="urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/account/10/2004">
<ListOfAccount xmlns="urn:/crmondemand/xml/account/">
<Account>
<AccountName>LIKE 'a1'</AccountName>
<Location/>
</Account>
</ListOfAccount>
</AccountQueryPage_Input>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
A stateless request execution might or might not result in an explicit login operation in Oracle CRM On Demand, as follows:
If a stateless request execution results in explicit login, then two entries are created in the Web Services Utilization page. Both the entries for this request, that is, the login and operation execution, show the client name specified in the SOAP request.
If a stateless request execution does not result in explicit login, then a single entry is created in the Web Services Utilization page, and it has the client name specified in the SOAP request.
Sending the Client Name in Stateful Web Services
A stateful Web service request execution involves:
Stateful login. A one time operation, which covers both login with username and password as well as SSO login.
Stateful request execution. Multiple request operations using the session ID returned by the login operation.
For a stateful request, the following considerations apply:
If the stateful request requires tracking of the client name, then it must be specified in the stateful login operation.
If a client name is specified in a stateful request execution, then it is ignored.
All the stateful requests executed with the session ID returned by the stateful login request are displayed in the Web Services Utilization page with the client name specified in the login operation.
Stateful Login
The login operation can be a HTTP request or a SOAP over HTTP request (R16 compatibility mode).
When the stateful login is a HTTP request, the client name is sent as the HTTP header parameter X-ClientName.
For a login with username and password:
GET http://<servername>:<portno>/Services/Integration?command=login
Http Header:
username: <username>
password: <password>
X-ClientName: Oracle Corporation, Web Services On Demand Guide
For an SSO login:
GET http://<servername>:<portno>/Services/
Integration?command=ssologin&odSsoToken=[Token Value]
X-ClientName: Oracle Corporation, Web Services On Demand Guide
Web Services R16 Compatibility Mode
If Web Services R16 Compatibility Mode is enabled, a stateless request is treated as stateful and returns a session ID. For SOAP requests when R16 Compatibility Mode is enabled:
The client name specified in the SOAP Header is used for the login operation and stateful operation execution
With the returned session ID, for subsequent requests, if the client name is specified in the SOAP header, it is ignored.
As for stateful requests, the client name with which login occurs (that is, the first SOAP request in this case) is displayed in the Web Services Utilization page with all requests for the stateful cycle.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:wsse="http://docs.oasis-
open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-secext-1.0.xsd" xmlns:xsd="http://
www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<soap:Header>
<wsse:Security>
<wsse:UsernameToken>
<wsse:Username>USERNAME</wsse:Username>
<wsse:Password Type="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-username-token-profile-1.0#PasswordText">password</wsse:Password>
</wsse:UsernameToken>
</wsse:Security>
<ClientName xmlns="urn:crmondemand/ws">Oracle Corporation, Web Services On Demand Guide</ClientName>
</soap:Header>
<soap:Body>
<AccountQueryPage_Input xmlns="urn:crmondemand/ws/ecbs/account/10/2004">
<ListOfAccount xmlns="urn:/crmondemand/xml/account/">
<Account>
<AccountName>LIKE 'a1'</AccountName>
<Location/>
</Account>
</ListOfAccount>
</AccountQueryPage_Input>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
About Service Allotments
Service allotments provide insight to customers regarding their usage of Oracle CRM On Demand and also promote equitable use of resources among all customers. Customers who understand their usage of Oracle CRM On Demand can improve user adoption of the application and can also optimize their usage both in the UI and their integrations.
The service allotments for Web service usage include the following:
Web Services Operations Allotment. The number of distinct operations performed by a company over a 24 hour window.
Web Services Concurrent Request Allotment. The maximum number of stateful and stateless Web service requests that can be processed at any point in time.
For service allotments, usage from all Web service clients, including those developed by Oracle, as well as those developed by customers and third parties is measured.
In the Oracle CRM On Demand UI, company administrators can view service allotment usage through the links under the Admin, Company Administration, Service Allotment Administration section. By selecting the Service Allotment Administration link, administrators can view details of their allotments, and current and remaining usage. By selecting the Service Allotment Usage History link, administrators can view historical usage for all of their service allotments.
The Web Service Utilization page provides additional details regarding Web service usage. This page can be accessed either from the Admin homepage or the Company Administration page through a link under the Service Allotment Administration section. Administrators can use this page to see the operations used for each Web service request issued.
Determining Current Usage
The Web Services Operations allotment is measured using a 24-hour rolling window. Current usage is displayed in the Oracle CRM On Demand UI or can be retrieved using the Service Allotment Web service (see Service Allotment). Current usage reflects the usage for the current hour plus the previous 23 hours.
For example, at 9:30 A.M., the current usage window extends from 10 A.M on the previous day, until the end of the current hour (10 A.M. today). All operations usage during this period is added together to calculate a company's current usage.
When the current hour elapses, the 24-hour window shifts, releasing any usage from the first hour of the previous window. For example, if a company has used 1000 operations in the current 24-hour window, 100 of which were used during the first hour, when the current hour elapses, the current usage is reduced to 900 operations.
Determining Historical Allotment Usage
Historical allotment usage is displayed in the Oracle CRM On Demand UI in a Related Information applet on the Service Allotment Detail page. You can retrieve this information for analysis or archiving using the following methods:
The Allotment Usage Web service (see Allotment Usage)
The Export Assistant
The List Management Export feature in the Service Allotment Usage History page under Company Administration.
For information about the Export Assistant and the List Management Export feature, see Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help.
When a Service Allotment Is Reached
If the current usage reaches the service allotment value for a company for the Web Services Operations allotment, further Web service requests are not processed until the 24-hour window shifts and capacity is released. To help avoid this situation, your administrator can configure email alerts to inform one or more users that your company is approaching the service allotment value.
See Oracle CRM On Demand Online Help for more information on configuring email alerts for service allotments.
For information about best practices, see Best Practices for Adhering to Web Service Allotments.
Calculation of Allotment Usage
The following topics describe how usage is calculated for each allotment.
Web Services Operations Allotment
The Web service operation count is incremented whenever a Web service request is received and executed. A single Web service SOAP request, when processed, might result in one or more Web service operations being executed. For example, The following table shows the number of operations resulting for different types of request.
Table Examples of Number of Operations for Different Web Services Requests
| Type of Request | Number of Operations |
|---|---|
Nonquery operations |
|
Account insert request containing a single Account record (with no child operations) |
1 |
Contact update request containing 10 Contact records (with no child operations) |
10 |
Account update request containing a single Account record with 3 Account Team records |
4 |
Query operations |
|
Simple query for a set of Accounts |
1 |
Query for a set of Accounts and the associated Contacts for each Account |
1 + n, where:
|
Web Services Concurrent Request Allotment
The Web Services Concurrent Request allotment is a measure of the number of Web service requests (including both stateful and stateless requests) being processed by a company concurrently.