Implementing Default User Profile Synchronization
This section provides an overview of default user profile synchronization and discusses how to set up a default user profile synchronization.
When you implement default user profile synchronization among databases, other than the default user profile synchronization exceptions mentioned below, the subscribing databases have no control over the data that they receive and process.
All participating databases use the USER_PROFILE service operation and the USER_PROFILE.VERSION_84 message during the publish and the subscribe processes.
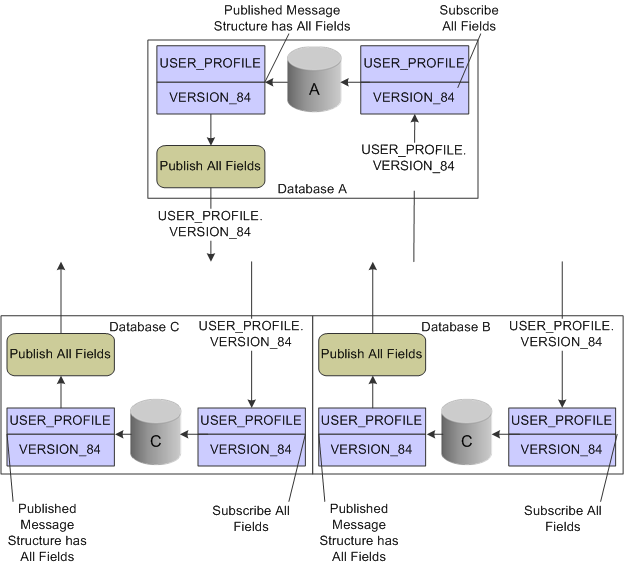
Image: Diagram of the flow of user profile information as it uses standard synchronization among three PeopleSoft databases
This diagram shows the service operations and messages, and the way in which user profile data is published by and subscribed to by three PeopleSoft systems that are using default user profile synchronization.
Default User Profile Synchronization Designed Exclusions
Adding and deleting user profiles on the publishing node cause corresponding changes on the subscribing nodes. Modifying user profiles on the publishing node causes corresponding changes on the subscribing nodes with these exceptions:
Changes to the primary email account are ignored if a primary email exists in the subscribing node.
Changes to a user ID type are ignored if the user ID type is not valid on the subscribing node. Instead, the subscribing node inserts an ID type of None if the subscribing node does not have a row for None already.
In general, changes that produce invalid field values in the subscribing node are ignored by the subscribing node.
To set up standard user profile synchronization, perform these tasks:
Turn on the Pub/Sub servers.
Define the local gateway URL for the integration broker.
In each participating database, activate the domain in integration broker.
In each participating database, create and configure the remote nodes.
In each participating database, configure single signon by setting up each subscribing database as a trusted node.
In each participating database, define the gateway properties; include all PeopleSoft nodes.
In each participating database, activate the USER_PROFILE service operation.
Note: The default setting is Enabled.
In each participating database, configure and activate routings for the USER_PROFILE service operation.
In each subscribing database, select the Generate Any-to-Local check box to create the necessary inbound routings; or create point-to-point inbound routings.
In each publishing database, you must create outbound routings to each subscribing node. For example, if you are in a CRM database publishing to an HCM and a FIN database, you must create two outbound routings.
For each subscribing database, grant permission list security for the USER_PROFILE service operations.