This chapter details the steps involved in adding various client data objects into the model.
Topics:
· Adding Dimension Tables and Key Dimension (Leaf) Registration
· Adding Custom Instrument Tables
· Adding Custom Transaction Tables
· Adding Management Ledger Class tables
· Object Registration and Validation
· Defining Alternate Rate Output Columns
· Modifying the Precision of Balance Columns In Ledger Stat
ID numbers can have a maximum length of 25 digits.
Dimension Leaf values can have a maximum of 14 digits.
Only 26 key (processing) dimensions are allowed in the database. Examples of seeded key leaf types are Common COA ID, Organizational Unit ID, GL Account ID, Product ID, and Legal Entity ID.
The maximum number of columns that the Oracle database allows in a unique index is 32. This is the overriding constraint. After subtracting IDENTITY_CODE, YEAR_S, ACCUM_TYPE_CD, CONSOLIDATION_CD, and ISO_CURRENCY_CD, this leaves 27 columns available for Key Processing Dimensions (leaf dimensions). BALANCE_TYPE_CD is now part of the unique index so this brings the maximum number of leaf columns down to 26.
Balances stored in Instrument tables are limited to 999,999,999,999.99. Balances stored in the LEDGER_STAT table are limited to 99,999,999,999.9999. The maximum precision for a balance used in a calculation process is 15 digits, with the range of 1.7e-308 to 1.7e+308. Calculation precision on larger numbers is compromised.
By default, rates stored in instrument tables are limited to 999.9999 and -999.9999. More precision can be achieved by increasing the number of decimals in the column. Internally, rates are stored with the same precision as balances.
Hierarchies with 15+ level is NOT supported within any Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) - ALM/FTP/PFT/HM processes.
The following section details the process in which users can add custom key dimensions to the OFSAA application. Users can view the registered dimension within the AMHM screens. Also, users can add members and hierarchies for the dimension through AMHM screens.
For Simple dimensions, entries should also be made in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES for each Instrument and Transaction Table in which that new dimension will occur.
Registering a new Key Dimension (called as Leaf in OFSA 4.5) requires the following steps:
· Add a set of dimension tables to store leaf values in ERwin model.
· Add the key dimension column to required Entities in ERwin model.
· Assign the Processing Key Column Property (Key Dimension Columns only).
· Upload the model.
· Register the Key Dimension.
· Modify Unique indexes (Key Leaf Dimension only).
· Validate tables.
Each of these steps is discussed in detail in the following sections.
Additionally, perform the following steps to avoid the errors running due to Allocations that use a Portfolio table.
1. Insert a row into REV_COLUMN_REQUIREMENTS for the custom dimension column.
2. Add the custom dimension to the Portfolio classification by following the instructions in the section Adding a new user defined column as a Portfolio column for use in all Instrument tables.
NOTE
For more information on limitation for number of key (processing) dimensions, see the Doc ID 1478920.1.
If an allocation using a Portfolio with expression fails, then you should do manual entries for standard columns in REV_COLUMN_REQUIREMENTS through sql script which comes as part of installer.
Each key dimension contains a set of the following tables:
· DIM_<DIMENSION>_B: Stores leaf and node member codes within the dimension.
· DIM_<DIMENSION>_TL: Stores names of leaf and node and their translations.
· DIM_<DIMENSION>_ATTR: Stores attribute values for the attributes of the dimension.
· DIM_<DIMENSION>_HIER: Stores parent-child relationship of members and nodes that are part of hierarchies.
NOTE
Replace <DIMENSION> with the keyword representing the key dimension.
Seeded key dimension tables are present in 'ALM-FTP-PFT-HM-BSP – Dimensions' subject area within the ERwin model. The above tables need to be created for the new dimension. For more information on creating dimension tables in ERwin, see leaflet (Adding And Customizing Leaf.pdf).
NOTE
For ease of use, user can copy an existing set of dimension tables such as for ORG_UNIT dimension and rename the tables (in both physical and logical view) to represent the new dimension.
Table structure of one of the seeded key dimension is given following with remarks on how this can be used as the basis for modeling new key dimensions.
Stores the ID of the members (leaf and nodes) of the dimension.
|
Column Name |
Logical Column Name |
Data type |
NULL |
Column Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ORG_UNIT_ID |
Organization Unit ID |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Leaf column which stores the id for the organization unit dimension |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. |
|
ORG_UNIT_DISPLAY_CODE |
Organization Unit Display Code |
NUMBER(14) |
NULL |
Leaf column which stores the display code for the organization unit dimension |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. |
|
ENABLED_FLAG |
Enabled Flag |
VARCHAR2(1) |
NOT NULL |
Store if the item is enabled or not |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LEAF_ONLY_FLAG |
Leaf or Node Flag |
VARCHAR2(1) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates if the member is leaf only or not |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
DEFINITION_LANGUAGE |
Definition Language |
VARCHAR2(4) |
NOT NULL |
Language that is used to define |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATED_BY |
Created By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who created this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATION_DATE |
Creation Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item created |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_BY |
Last Modified By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who modified this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_DATE |
Last Modified Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item modified |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
ORG_UNIT_CODE |
ORG_UNIT_CODE |
VARCHAR2(20) |
NULL |
This column is used by staging and contains the alpha-numeric codes for each dimension member. Staging dimension table contains unique alpha-numeric codes and a unique numeric identifier is generated while loading into ALM-FTP-PFT-HM-BSP dimension table. |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. |
Stores the names and descriptions of the members (leaf and nodes) of the dimension in various languages.
|
Column Name |
Logical Column Name |
Data type |
NULL1 |
Column Description |
Remarks1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LANGUAGE |
Language |
VARCHAR2(4) |
NOT NULL |
Language |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
ORG_UNIT_ID |
Organization Unit ID |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Leaf column which stores the id for the organization unit dimension |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. |
|
ORG_UNIT_NAME |
Organization Unit Name |
VARCHAR2(150) |
NOT NULL |
Leaf column which stores the name for the organization unit dimension |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
Description |
VARCHAR2(255) |
NULL |
Description of an Item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATED_BY |
Created By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who created this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATION_DATE |
Creation Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item created |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_BY |
Last Modified By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who modified this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_DATE |
Last Modified Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item modified |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
Stores the values of the attributes of the members (leaf and nodes) of the dimension.
|
Column Name |
Logical Column Name |
Data type |
NULL |
Column Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ORG_UNIT_ID |
Organization Unit ID |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Leaf column which stores the id for the organization unit dimension |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. |
|
ATTRIBUTE_ID |
Attribute ID |
NUMBER(22) |
NOT NULL |
Stores attribute id number for a member of a dimension |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
DIM_ATTRIBUTE_NUMERIC_MEMBER |
Numeric Dimension Value |
NUMBER(22) |
NULL |
This field stores the number values for the attribute of a member |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
DIM_ATTRIBUTE_VARCHAR_MEMBER |
Varchar Dimension Value |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NULL |
This field stores the varchar values for the attribute of a member |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
NUMBER_ASSIGN_VALUE |
Numeric Value Of A Member |
NUMBER(22) |
NULL |
This field stores the number values for the attribute of a member |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
VARCHAR_ASSIGN_VALUE |
Varchar Member Value |
VARCHAR2(1000) |
NULL |
This field stores the varchar values for the attribute of a member |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
DATE_ASSIGN_VALUE |
Date Value |
DATE |
NULL |
Date value that is assigned |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
Stores the parent-child relationship of various nodes and leaf within hierarchies of the dimension.
|
Column Name |
Logical Column Name |
Data type |
NULL |
Column Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HIERARCHY_ID |
Hierarchy ID |
NUMBER(10) |
NOT NULL |
Unique Id that is generated for every hierarchy that is created |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
PARENT_ID |
Parent ID |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Column that store the id of the child member |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CHILD_ID |
Child Member ID |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Store child id number for a dimension |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
PARENT_DEPTH_NUM |
Parent Depth Number |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Stores parent depth number |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CHILD_DEPTH_NUM |
Child Depth Number |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Stores child depth number |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
DISPLAY_ORDER_NUM |
Display Order Number |
NUMBER(14) |
NOT NULL |
Stores the display order number for the member |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
SINGLE_DEPTH_FLAG |
Single Depth Flag |
VARCHAR2(1) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates if the hierarchy is of single depth or not |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATED_BY |
Created By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who created this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATION_DATE |
Creation Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item created |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_BY |
Last Modified By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who modified this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_DATE |
Last Modified Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item modified |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
Simple dimensions are created to store CODE and Descriptions. These tables are used by the User Interfaces to list values in drop downs / radio buttons, and so on. For Simple dimensions, entries should also be made in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES for each Instrument and Transaction Table in which that new dimension will occur. The entries in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES are used by Data Element Filters as well as the procedures for Synchronize Instruments and Synchronize Stage.
Each simple dimension contains a set of the following tables:
· CD table: Stores the members for a simple dimension.
· MLS table: Stores the members' multi lingual description.
If you use simple dimensions where _CD column is VARCHAR2, you will need to classify the tables as follows:.
FSI_ACCUMULATION_TYPE_CD, FSI_BILLING_METHOD_CD
The CD table should be classified as
|
Value |
Details |
|---|---|
295 |
Codes User Defined base tbl |
|
198 |
Codes Reserved (base tbl) |
The MLS table should be classified as
|
Value |
Details |
|---|---|
2968 |
MLS Descriptions User Defined |
|
197 |
MLS Descriptions Reserved |
Table structure of one of these seeded simple dimensions is given in the following section with remarks on how this can be used as the basis for modeling new simple dimensions.
Stores the ID of the members (leaf and nodes) of the dimension.
|
Column Name |
Logical Column Name |
Data type |
NULL |
Column Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DIM_CD |
Dimension Code |
NUMBER(5) |
NOT NULL |
Leaf column which stores the code for the dimension. |
Stores the Dimension Code. |
|
LEAF_ONLY_FLAG |
Leaf or Node Flag |
VARCHAR2(1) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates if the member is leaf only or not |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
ENABLED_FLAG |
Enabled Flag |
VARCHAR2(1) |
NOT NULL |
Store if the item is enabled or not |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
DEFINITION_LANGUAGE |
Definition Language |
VARCHAR2(4) |
NOT NULL |
Language that is used to define |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATED_BY |
Created By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who created this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATION_DATE |
Creation Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item created |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_BY |
Last Modified By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who modified this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_DATE |
Last Modified Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item modified |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
<DIM>_DISPLAY_CD |
Dimension Display Code |
VARCHAR2() |
NULL |
Leaf column which stores the display code for the dimension |
Column name and description should reflect the new dimension. Datatype and other constraints should be retained. The length of this column is customizable. |
Stores the members' multi lingual description.
|
Column Name |
Logical Column Name |
Data type |
NULL |
Column Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DIM_CD |
Dimension Code |
NUMBER(5) |
NOT NULL |
Leaf column which stores the code for the dimension. |
Stores the Dimension Code. |
|
LANGUAGE |
Language |
VARCHAR2(3) |
NOT NULL |
Language |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
<DIM> |
Dimension |
VARCHAR2(40) |
NOT NULL |
Name of the Dimension |
Stores the name of the Dimension. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
Description |
VARCHAR2(255) |
NULL |
Description of an Item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATED_BY |
Created By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who created this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
CREATION_DATE |
Creation Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item created |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_BY |
Last Modified By |
VARCHAR2(30) |
NOT NULL |
Indicates who modified this item |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
|
LAST_MODIFIED_DATE |
Last Modified Date |
TIMESTAMP |
NOT NULL |
Indicates when was this item modified |
Internally used and hence should be retained in the same form within the new dimension table. |
Example for FSI_<DIM>_CD table:
CREATE TABLE <XXXXX>_FSI_<DIM>_CD ACME_FSI_ACCT_STATUS_CD
(<DIM>_CD NUMBER(5) ACCT_STATUS_CD
,LEAF_ONLY_FLAG VARCHAR2(1)
,ENABLED_FLAG VARCHAR2(1)
,DEFINITION_LANGUAGE VARCHAR2(4)
,CREATED_BY VARCHAR2(30)
,CREATION_DATE DATE
,LAST_MODIFIED_BY VARCHAR2(30)
,LAST_MODIFIED_DATE DATE
<dim>_display_CD VARCHAR2()
);
Example for FSI_<DIM>_MLS table:
CREATE TABLE <XXXXX>_FSI_<DIM>_MLS ACME_FSI_ACCT_STATUS_CD
(<DIM>_CD NUMBER(5) ACCT_STATUS_CD
,LANGUAGE VARCHAR2(3)
,<DIM> VARCHAR2(40) ACCT_STATUS
,DESCRIPTION VARCHAR2(255)
,CREATED_BY VARCHAR2(30)
,CREATION_DATE DATE
,LAST_MODIFIED_BY VARCHAR2(30)
,LAST_MODIFIED_DATE DATE
);
Dimension column can be added to the following set of Client Data Objects:
· Tables classified as Instruments and Instrument Profitability
· Tables classified as Transaction Profitability
· Management Ledger table
· Result tables of Asset Liability Management
Dimension can be of the types – Ledger Only, Instruments Only, or Both. If the dimension is classified as 'Ledger Only', the dimension column needs to be added only to Ledger Stat table.
If the dimension is classified Instruments only, the dimension column needs to be added to instruments and Transactions tables. If the dimension is classified as 'Both', the dimension column needs to be added to Ledger Stat table and other tables classified as Instruments and Transactions.
· For adding key dimension column to tables that are classified as 'Instruments' and 'Instrument Profitability', add the column to LEAF_COLUMNS super-class table.
· For adding key dimension column to tables that are classified as 'Transaction Profitability', add the column to TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS super-class table.
· For adding key dimension column to Ledger Stat table, add the column to LEDGER_LEAF_COLUMNS super-class table.
NOTE
Columns of super-class tables that are linked to sub-class table are rolled down to the sub-class table during 'Model Upload' operation.
NOTE
Columns of super-class tables that are linked to sub-class table are rolled down to the sub-class table during 'Model Upload' operation.
If both super-class and sub-class tables have some common columns, then the sub-class table column is retained and the column from the super-class table will be ignored.
If both sub and super entities have common columns with same properties (such as datatype, size, and so on ), then there is no issue with model upload process. If sub and super entities have the common columns with different properties, then there will issue with model upload process.
If you use Asset Liability Management, then add the Dimension column directly to the following tables. Use the same column properties as the other dimension columns on the table when adding them. Add the column to the same indexes as the existing dimension columns.
1 FSI_O_RESULT_DETAIL_TEMPLATE
2 FSI_O_CONS_DETAIL_TEMPLATE
3 FSI_O_RESULT_MASTER
4 FSI_O_CONSOLIDATED_MASTER
'Processing Key' is a column level User Defined Property (UDP) in ERwin model. This property can have two values – Yes or No. Only those objects where the column was added to the unique index are affected.
For tables classified as 'Transaction Profitability, this property needs to be set as 'Yes' for one or more of the key dimension columns.
For Ledger Stat table, this property needs to be set as 'Yes' for all key dimension columns.
Assigning Processing Key Property is not required for Simple Dimension.
ERwin model with the above changes needs to be uploaded in OFSAAI environment. Uploading the model creates these additional tables and sets these properties within the atomic schema.
After upload, user can verify the changes in the schema as well as query OFSAAI metadata tables like REV_COLUMN_PROPERTIES for viewing properties assigned to each column.
For more information on data model upload process, see OFSAAI User Guide.
Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications Infrastructure (OFSAAI) provides an Leaf Registration procedure to add the new Key Dimension Column to the Dimensions metadata registry (REV_DIMENSIONS_B, REV_DIMENSIONS_TL).
This procedure performs the following:
· Registers key and simple dimension.
· Invalidates all Client Data Objects when key dimension is registered.
You can execute this procedure either from SQL*Plus or from within a PL/SQL block or from Batch Maintenance window within OFSAAI framework.
To run the procedure from SQL*Plus, login to SQL*Plus as the Schema Owner. The function requires 19 parameters. The syntax for calling the procedure is:
function rev_leaf_registration(batch_run_id varchar2,
mis_date varchar2,
memDataType varchar2,
dimName varchar2,
description varchar2,
memberBTableName varchar2,
memberTLTableName varchar2,
hierarchyTableName varchar2,
attributeTableName varchar2,
memberCol varchar2,
memberDispCodeCol varchar2,
memberNameCol varchar2,
memberDescCol varchar2,
dimTypeCode varchar2,
simpleDimFlag varchar2,
keyDimFlag char,
writeFlag varchar2,
catalogTableType char,
flattenedTableName in varchar2,
membercodecol in varchar2
)
· batch_run_id : any string to identify the executed batch.
· mis_date : in the format YYYYMMDD.
· memDataType : member data type of Dimension as in NUMBER,VARCHAR2,CHAR.
· dimName : name of the dimension to be added (less than 21 chars).
· description : description of the dimension (less than 255 chars).
· memberBTableName : Member Base Table Name input as either null or a value with suffix '_CD' or '_B'.
· memberTLTableName : Member TL Table Name input as either null or name of the table.
· hierarchyTableName : Hierarchy Table Name input as either null or name of the table.
· attributeTableName : Attribute Table Name input as either null or name of the table.
· memberCol : Member Column Name input as either null or name of the column.
· memberDispCodeCol : Member Display Code Column Name input as either null or name of the column. For simple dimensions, enter the same field as the memberCol. Do not user display column for simple dimensions.
· memberNameCol : Member Name Column input as either null or name of the column.
· memberDescCol : Member Description Column input as either null or name of the column.
· dimTypeCode : Code for the dimension Type as in 'PROD for product type', 'ORGN for Organizational Unit', 'CCOA for Common Chart of Accounts', 'FINELE for Financial Element', 'GL for General Ledger Account', 'OTHER for any other type'.
· All user defined dimensions will haveDIMENSION_TYPE_CODE as 'OTHER'. User defined dimensions which are product related will have DIMENSION_TYPE_CODE as 'PROD'.
· simpleDimFlag : 'Y' or 'N' to determine Simple Dimension.
Simple dimensions are created to store CODE and Descriptions. These tables are used by the User Interfaces to list values in drop downs / radio buttons, and so on. Simple dimensions are not reverse populated.
Example: Country, Currencies, Customer Type.
· keyDimFlag : 'Y' or 'N' to determine Key Dimension.
Key dimensions are dimensions which get reverse populated to the legacy tables.
Example: Product, Org Unit, General Ledger.
· writeFlag : 'Y' or 'N' to determine whether Dimension should appear in drop down list in Dimension Management > Members.
· catalogTableType : 'L', 'B', or 'I' to determine table type for key dimensions.
· For a Simple Dimension, this value should be set to Null.
· flattenedTableName : Flattened Table Name input as either null or name of the table.
· membercodecol: Alphanumeric Code column. Populates the MEMBER_CODE_COLUMN column in REV_DIMENSIONS_B. The value provided should be a valid code column from the relevant DIM_<DIMENSION>_B (key dimension) or FSI_<DIM>_CD (simple dimension) table. For simple dimensions use the display code column.
Example for Key Dimension:
Declare
num number;
Begin
num := rev_leaf_registration('BATCH_NO_01',
'20101216',
'NUMBER',
'SIMPLE DIMENSION',
'SIMPLE DIMENSION DESC',
'FSI_DIM_SIMPLE_CD',
'FSI_DIM_SIMPLE_MLS',
'null',
'null',
'SIMPLE_CD',
'SIMPLE_CD',
'SIMPLE_NAME_Dim',
'SIMPLE_DESCRIPTION',
'OTHER',
'Y',
'N',
'Y',
'B',
'FLATTEN_PROD_TABLE',
'SIMPLE_DISPLAY_CODE');
End;
Example for Simple Dimension:
Declare
num number;
Begin
num := rev_leaf_registration('BATCH_NO_01',
'20101216',
'NUMBER',
'SIMPLE DIMENSION',
'SIMPLE DIMENSION DESC',
'FSI_DIM_SIMPLE_CD',
'FSI_DIM_SIMPLE_MLS',
'null',
'null',
'SIMPLE_CD',
'SIMPLE_DISPLAY_CODE',
'SIMPLE_NAME_Dim',
'SIMPLE_DESCRIPTION',
'OTHER',
'Y',
'N',
'Y',
'B',
'FLATTEN_PROD_TABLE');
End;
To execute the procedure from OFSAAI Batch Management, create a new Batch with the Task as TRANSFORM DATA and specify the following parameters for the task:
· Datastore Type: Select appropriate datastore from list
· Datastore Name: Select appropriate name from the list
· IP address: Select the IP address from the list
· Rule Name: batch_leaf_registration
· Parameter List: Member Data type , Dimension Name, Dimension Description, Member Base Table Name, Member Translation Table Name, Hierarchy Table Name, Attribute Table Name, Member Column , Member Display Code Column, Member Name Column, Member Description Column , Dimension Type Code , Simple Dimension Flag , Key Dimension Flag , writeFlag, Catalog Table Type , Flatten Table Name
For tables of 'Transaction Profitability' classification, key dimension column can be part of the unique index. If this column is intended to be part of the unique index, alter the unique index in the schema.
For Ledger Stat table, all key dimension columns should form part of the unique index. Hence, alter the unique index in the schema to include this column.
Since leaf registration invalidates all Client Data Objects, Object Registration Validation procedure needs to be executed to validate the required tables. For more information on Executing Object Registration Validation, see Object Registration and Validation.
Instrument and Account objects are tables storing financial services information about customers and accounts. These are most commonly used objects for OFSAA processing and reporting operations. There are seeded instrument tables that are packaged as part of each OFSAA. You can customize or remove any of them during implementation. In some cases, you might also require to add a custom instrument table.
For Simple dimensions, entries should also be made in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES for each Instrument Table in which that new dimension will occur. The entries in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES are used by Data Element Filters as well as the procedures for Synchronize Instruments and Synchronize Stage.
Topics:
· Steps in Creating Custom Instrument Table
· Setting Table Classifications
· Object Registration Validation
Most instrument tables are used for OFSAA processing. OFSAA processing mandates the instrument table to have a certain set of columns. These columns have been put together in super-class entities. The following are the seeded super-class entities:
· LEAF_COLUMNS: contains the key dimension columns that are part of the Instrument tables.
· BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ: contains the basic instrument columns like ID_NUMBER, IDENTITY_CODE, and so on.
· MULTI_CUR_REQ: contains the columns required for multi-currency processing.
· CASH_FLOW_EDIT_REQ: contains the columns required for Cash flow Edit processing.
· CASH_FLOW_PROC_REQ: contains the columns required for Cash flow processing.
· TP_BASIC_REQ: contains the columns required for Transfer Pricing processing.
· TP_OPTION_COSTING_REQ: contains the columns required for Transfer Pricing Option Cost processing.
· PORTFOLIO_REQ: contains the columns required for Portfolio table classification.
· TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS: contains the key dimension columns that are part of the transaction tables.
· LEDGER_LEAF_COLUMNS: contains the key dimension columns that are part of the Ledger Stat table.
· BASIC_LEDGER_CLASS_REQ: contains the columns required for Ledger Class tables example _Ledger.
NOTE
Column Precision for Instrument Table:
You can increase the size of the columns to make them hold a value of larger precision, but the new size will impact FTP and ALM engines as follow:
Values/fields read by the engine are restricted to the size that the c++ variables can hold within the engine memory. In fact, having a value larger than the allowed precision can cause the engine to read the value incorrectly.
Changing the size of the fields that these engines write into does not affect the precision of the results
An upgrade could rollback such changes unless you remember to do a model merge.
Instrument table can link to any of the above super-class entities based on its purpose. For example, if the instrument table is used for Cash Flow Processing, then this table should be linked to the following super-class entities:
· BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ
· MULTI_CUR_REQ
· LEAF_COLUMNS
· CASH_FLOW_EDIT_REQ
· CASH_FLOW_PROC_REQ
NOTE
CASH_FLOW_PROC_REQ is required for all instrument tables where conditional assumptions will be applied.
See the following mapping table that specifies the list of super-class entities required for each table classification:
|
Type of Client Data Object |
Table Classification |
List of Super class entities |
|---|---|---|
|
Instrument |
Instrument |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ LEAF_COLUMNS |
|
Instrument |
ALM Standard |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ LEAF_COLUMNS MULTI_CUR_REQ CASH_FLOW_EDIT_REQ CASH_FLOW_PROC_REQ |
|
Instrument |
TP Cash Flow |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ LEAF_COLUMNS MULTI_CUR_REQ CASH_FLOW_EDIT_REQ CASH_FLOW_PROC_REQ TP_BASIC_REQ |
|
Instrument |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ LEAF_COLUMNS MULTI_CUR_REQ CASH_FLOW_EDIT_REQ TP_BASIC_REQ |
|
Instrument |
TP Option Costing |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ LEAF_COLUMNS MULTI_CUR_REQ CASH_FLOW_EDIT_REQ TP_BASIC_REQ TP_OPTION_COSTING_REQ |
|
Instrument |
Instrument Profitability |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ MULTI_CUR_REQ PORTFOLIO |
|
Instrument |
Portfolio |
BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ LEAF_COLUMNS MULTI_CUR_REQ PORTFOLIO |
|
Transaction |
Transaction Profitability |
TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS |
|
Ledger Stat |
Ledger Stat |
LEDGER_LEAF_COLUMNS |
The following are the steps involved in creating a custom instrument table:
· Create a new subject area within the ERwin model.
· Move the required super-class tables as part of the subject area.
· Create the custom instrument table in ERwin. Specify logical name, physical name and description for the table. Define any columns that do not come from any of the standard super-class tables as part of the custom instrument table. Specify logical, physical names, domain and other column properties for each column.
· Create subtype relationship between the custom instrument table and various super-class entities.
NOTE:
User defined tables ( custom ) tables should not have "PORTFOLIO" keyword in the name of the table.
Table Classifications can be set for any Client Data Object. Table classification set against each Client Data Object is validated through Object Registration Validation process.
The following are the steps involved in setting table classification properties for the custom instrument table:
· Choose Physical View within the ERwin model.
· Go to UDP tab within Table Properties window.
· Specify 'Yes' against required Table Classifications properties.
Once the model is prepared using the above steps, user should upload the ERwin model. After uploading the model, user can check if the custom instrument table has been created in the schema with columns from super-class entities that have been linked to the custom instrument table as well as the columns present in the custom instrument table. Model upload also creates metadata entries within the following Object Registration tables:
· REV_TABLES_B: Contains the list of table names.
· REV_TABLES_TL: contains the list of table display names and descriptions in various languages.
· REV_TAB_COLUMNS: contains the list of column names.
· REV_TAB_COLUMNS_MLS: contains the list of column display names and descriptions in various languages.
· REV_COLUMN_PROPERTIES: stores the column properties associated with each column.
· REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT: stores the table classification associated with each table.
NOTE
In case custom instrument table contains the column in the same name as that of the super-class table, then column present in the custom instrument table will take precedence over the equivalent column of the super-class table. In case multiple super-class tables contain the same column, user should ensure that all the columns have same datatype, as any column can be selected and it is not resolved in any specific order.
Physical order of the columns within the custom instrument table is determined in the following way:
Columns present in the custom instrument table.
Columns present in each of the linked super-class table. In case multiple super-class tables are linked to the custom instrument table, columns are rolled down from all super-class tables without any specific order.
Within any table, ERwin maintains three different column orders:
1. Logical Order: Order of the columns as seen in Logical view of the model
2. Physical Order: Order of the columns as seen in Physical view of the model.
3. Database Order: Order of the columns as seen in the Database schema.
Instrument tables require unique index on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE column. This unique index needs to be created on the custom instrument table, post-model upload operation.
Transaction tables require unique index on ID_NUMBER, IDENTITY_CODE and one of the key dimension columns. This unique index needs to be created on the custom transaction table, post-model upload operation.
NOTE
The unique index may not contain any non-Key Dimension columns other than ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE.
It enables users to define rules with a cross-instrument definition, since the Portfolio table classification contains columns (potentially including user-defined columns) that are common to all instruments. Any other specific instrument table selection (such as Mortgages, and so on) would limit the rule definition to the specific instrument table. During processing of a Portfolio selection from an assumption rule, the engine will substitute the name of a specific table (that is, instruments selected in the parent process rule).
Portfolio is available as a table selection in various modules including Infrastructure objects such as Filters and Expression rules. It is also available in application objects such as Profitability Management Allocation rules, and so on. To add a new user-defined column as a Portfolio column, use the following steps:
1 Include the column in the PORTFOLIO super-type table in the Erwin Data Model to ensure that the column rolls down to all subtype tables.
3. Complete incremental model upload to add the column to all subtype Portfolio tables.
4. Manually insert a row into the Atomic schemaREV_PROPERTY_COLUMNS table with TABLE_PROPERTY_CD = 40:
For example, if your new column is APPLE_BRANCH_CD
Insert into REV_PROPERTY_COLUMNS
(TABLE_PROPERTY_CD,COLUMN_NAME,PROTECTED_FLG) values
(40,'APPLE_BRANCH_CD',1);
COMMIT;
Data Element Filters created with custom columns will appear in Conditional Assumptions (within Funds Transfer Pricing) when properly registered. When creating a custom column in Instrument table(s)/Cash Flow related table(s), that is, those containing BASIC_INSTRUMENT_REQ/CASH_FLOW_PROC_REQ in the data model, the custom column must have one of the Domains listed as follows: BALANCE, CHAR,CODE, CODE_NUM, DATE, DESCRIPTION, FLAG, NUMBER, NUMERIC, RATE, SWITCH, VARCHAR2, CHAR_RANGE, PCT.
Since leaf registration invalidates all Client Data Objects, Object Registration Validation procedure needs to be executed to validate the required tables. For more information on Object Registration Validation procedure, see Object Registration and Validation.
Transaction tables are used within Profitability Management processing. There are seeded transaction tables that are packaged as part of Profitability Management application. You can customize or remove any of them during implementation. In some cases, you might also require to add a custom transaction table.
For Simple dimensions, entries should also be made in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES for each Transaction Table in which that new dimension will occur. The entries in REV_DESCRIPTION_TABLES are used by Data Element Filters as well as the procedures for Synchronize Instruments and Synchronize Stage.
Topics:
· Steps In Creating Custom Transaction Table
· Setting Table Classifications
· Object Registration Validation
Profitability Management processing mandates the transaction table to have a certain set of columns. These columns have been put together in super-class entities. The following are the seeded super-class entities:
TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS – contains the key dimension columns that are part of the Transaction tables.
The following are the steps involved in creating a custom transaction table:
· Create a new subject area within the ERwin model.
· Move TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS into the new subject area.
· Create the custom transaction table in ERwin. Specify logical name, physical name and description for the table. Define any columns that do not come from any of the standard super-class tables as part of the custom transaction table. Specify logical, physical names, domain and other column properties for each column.
· Create subtype relationship between the custom transaction table and TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS super-class entity.
Table Classifications can be set for any Client Data Object. Table classification set against each Client Data Object is validated through Object Registration Validation process.
The following are the steps involved in setting table classification properties for the custom transaction table:
· Choose Physical View within the ERwin model.
· Go to UDP tab within Table Properties window.
· Specify 'Yes' for 'Transaction Profitability' user defined property.
Once the model is prepared using the above steps, user should upload the ERwin model. After uploading the model, user can check if the custom transaction table has been created in the schema with columns from super-class entities that have been linked to the custom transaction table as well as the columns present in the custom transaction table. Model upload also creates metadata entries within the following Object Registration tables:
· REV_TABLES_B: Contains the list of table names.
· REV_TABLES_TL: contains the list of table display names and descriptions in various languages.
· REV_TAB_COLUMNS: contains the list of column names.
· REV_TAB_COLUMNS_MLS: contains the list of column display names and descriptions in various languages.
· REV_COLUMN_PROPERTIES: stores the column properties associated with each column.
· REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT: stores the table classification associated with each table.
· REV_TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_TL: contains the list of table classification, language name and description associated with each table.
· REV_TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_B: contains the list of table classification.
NOTE
For Mortgages, TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_CD = 618 and TABLE_CLASSIFICATION = 'Mortgages' in REV_TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_TL and REV_TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_B tables.
For Embedded Options, TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_CD = 617 and TABLE_CLASSIFICATION = 'Embedded Options' in REV_TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_TL and REV_TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_B tables.
· REV_COLUMN_PROPERTY_CD: contains the column property Ids and currency basis associated with each column.
· REV_COLUMN_PROPERTY_MLS: contains the column properties, language name and description associated with each column.
NOTE
For Economic Value, COLUMN_PROPERTY_CD = 86 and COLUMN_PROPERTY = 'Economic Value' in REV_COLUMN_PROPERTY_MLS and REV_COLUMN_PROPERTY_CD tables.
NOTE
In case custom transaction table contains the column in the same name as that of the super-class table, then column present in the custom transaction table will take precedence over the equivalent column of the super-class table.
Physical order of the columns within the custom transaction table is determined in the following way:
Columns present in the custom transaction table.
Columns present in each of the linked super-class table.
Within any table, ERwin maintains three different column orders:
1. Logical Order: Order of the columns as seen in Logical view of the model.
2. Physical Order: Order of the columns as seen in Physical view of the model.
3. Database Order: Order of the columns as seen in the Database schema.
'Processing Key' user defined property needs to be set for the following columns within the transaction table:
· ID_NUMBER
· IDENTITY_CODE
· Leaf columns that are part of the unique index
The following are the steps to set this property in ERwin:
· Choose Physical View within the ERwin model.
· Choose TRANS_LEAF_COLUMNS super-class table.
· Choose the leaf column that needs to be set 'Processing Key' property.
· Go to UDP tab in Column Properties window for this column.
· Specify 'Yes' against 'Processing Key' user-defined property.
· Choose the custom transaction table.
· Go to UDP tab in Column Properties window for ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE columns.
· Specify Yes for Processing Key user-defined property.
Transaction tables require unique index on the following columns:
· ID_NUMBER
· IDENTITY_CODE
· At-least one of the key dimension columns.
This unique index needs to be created on the custom transaction table, post-model upload operation.
Since leaf registration in-validates all Client Data Objects, Object Registration Validation procedure needs to be executed to validate the required tables. For more information on Object Registration Validation procedure, see Object Registration and Validation.
Lookup tables are used within OFSAA Profitability Management application. Lookup tables have to be created and registered within OFSAAI, in order to display them in Lookup Table Driver definition of OFSAA Profitability Management application.
Topics:
· Steps to Create Lookup Table
· Registering Lookup Tables and Validation
· Lookup Table Driver Definition
Lookup table has to be created in the ERwin model. The following are the steps:
· Open the ERwin model in ERwin Data Modeler tool.
· Create a new subject area.
· Create a table and add columns to the table.
· Lookup table needs to at-least have one primary key column.
· Lookup table needs to at-least have one numeric non-key column. Such numeric columns will be the return value of the lookup.
· Specify logical names, comments and primary key for the table.
· Specify logical names, domains and comments for the column.
· Domains for the columns can be LEAF, BALANCE, RATE and so on.
· Save the model.
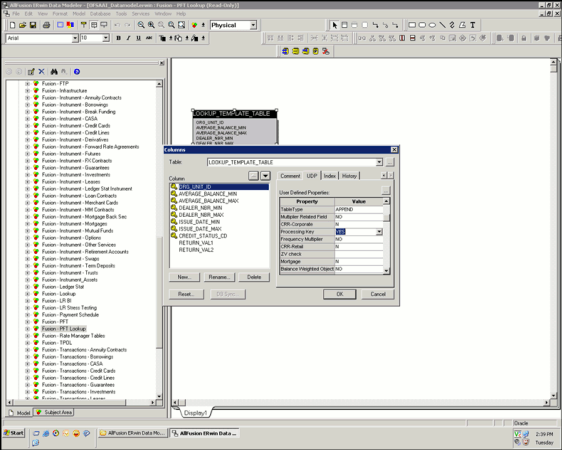
'Processing Key' is a column level User Defined Property (UDP) in ERwin model. This property can have two values – Yes or No. 'Processing Key' property needs to be set for all the primary key columns of the lookup table.
'Balance Range' is a column level User Defined Property (UDP) in ERwin model. This property can have two values – Yes or No. Balance Range property needs to be set for the columns that can have range values in the lookup.
The following are the steps for setting the above properties:
· Open the ERwin model in ERwin Data Modeler tool.
· Go to the Subject Area where lookup table was created.
· Choose the table and open the columns of the table.
· Go to UDP tab within the column properties for each column.
· Specify the value for the required user defined properties.
· Save the model.
'UDP_LOOKUP_RANGE_MINIMUM' is a column level User Defined Property (UDP) in ERwin model. This property can have two values – Yes or No. UDP_LOOKUP_RANGE_MINIMUM property needs to be set for the columns that can have minimum values for a range in the lookup.
'UDP_LOOKUP_RANGE_MAXIMUM' is a column level User Defined Property (UDP) in ERwinModel. This property can have two values – Yes or No. UDP_LOOKUP_RANGE_MINIMUM property needs to be set for the columns that can have maximum values for a range in the lookup.
Table Classifications can be set for any Client Data Object. Table classification set against each Client Data Object is validated through Object Registration Validation process.
The following are the steps involved in setting table classification properties for the custom lookup table:
· Choose Physical View within the ERwin model.
· Go to UDP tab within Table Properties window.
· Specify Yes for PA Lookup Tables user-defined property.
Upload the model and execute the object registration validation.
Post registration and validation, the lookup table is available within Lookup Table Driver definition of OFSAA Profitability Management application.
Following is the criteria for columns to be displayed in the Source - Lookup Mapping grid:
· Column needs to be Primary Key or be part of composite primary key.
· Processing Key user defined property should be set for the column under UDP tab as shown following.

Description of Data Modeler for Mapping of Column to Processing Key follows
Following is the criteria for columns to be part of the Range:
· Balance Range user defined property should be set for the column under UDP tab as displayed.
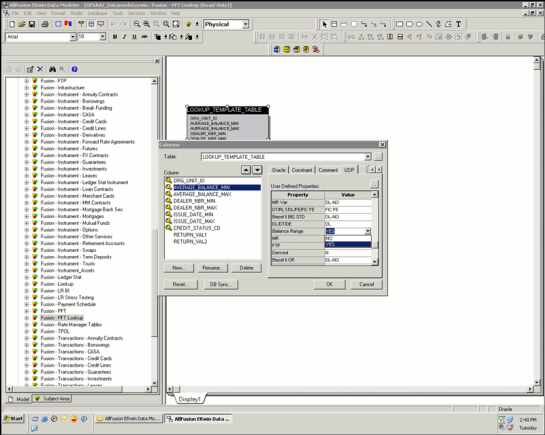
Description of Data Modeler for Mapping of Column for Range Property follows
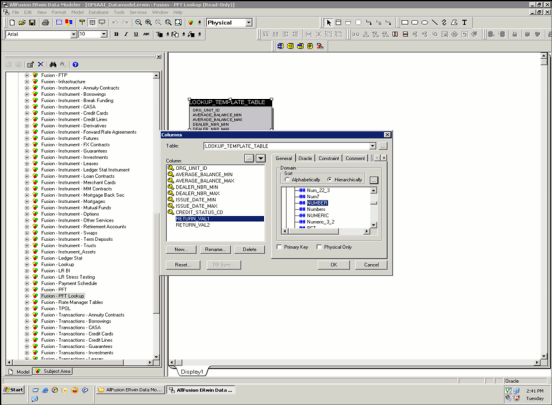
Following is the criteria for columns to be part Lookup Return Value:
· Column should not be primary key/processing key or be part of composite primary key.
· Column domain should be defined as NUMBER under General Tab as displayed.
Beginning with release 8, OFSAA Profitability Management supports a Management Ledger table class. Management Ledger tables provide substantially identical functionality to the traditional Ledger/Stat table. Like Ledger/Stat, you may also customize the dimensionality of Management Ledger tables. Additionally, in addition to the seeded Management Ledger table (FSI-D-MANAGEMENT-LEDGER), you may also construct and customize additional ledger tables of the Management Ledger table class.
The seeded FSI-D-MANAGEMENT-LEDGER table is loaded from STG_GL_DATA via a standard T2T rule (T2T_MANAGEMENT_LEDGER). If you choose to build additional Management Ledger tables, you will need to cloneT2T_MANAGEMENT_LEDGER to target your new ledger table.
NOTE:
All Custom Dimensions should be added to the PK for STG_GL_DATA.
And all Custom Dimensions should be added to Unique Index of FSI_D_MANAGEMENT_LEDGER.
The following topics are covered in this section:
· Steps to create Custom Ledger Class Table
· Setting Table Classifications
· Setting Processing Key Property
· Object Registration Validation
Profitability processing mandates the Ledger class table to have a certain set of columns. These columns have been put together in super-class entities.
The following are the seeded super-class entities:
· BASIC_LEDGER_CLASS_REQ: Contains the columns required for Ledger Class tables.
· The FSI_D_MANAGEMENT_LEDGER.ENTERED_BALANCE column stores entered or transacted balances that correspond to the local currency in which the transactions were booked in your General Ledger.
· The FSI_D_MANAGEMENT_LEDGER.FUNCTIONAL_BALANCE column stores balances in the Functional currency of your General Ledger
NOTE
When Initially loading data from Staging fo Management Ledger, Entered and Functional currency balances should correspond to the values originally booked into your General Ledger.
For a mono-currency implementation:
· The Entered balance should equal the Functional balance on each Management Ledger row
· The ISO_CURRENCY_CD for each Management Ledger row should match your Functional Currency (from FSI_DB_INFO).
For multi-currency implementations:
· When a Management Ledger row's ISO_CURRENCY_CD is the same as your Functional Currency, the Entered balance will equal the Functional balance
· The Entered balance will equal the Functional balance for all statistical rows (ISO_CURRENCY_CD = 002)
· Generally, the Entered balance will NOT equal the Functional balance for Management Ledger rows where ISO_CURRENCY_CD is different than your Functional Currency
· The ratio of Entered balance to Functional balance - the observed exchange rate for the row is determined within your source General Ledger. Typically, ending balances will match end-of-month exchange rates while P&L balances may reflect weighted monthly average exchange rates.
NOTE
For more information on how Entered & Functional balances are used with applications, see the Multicurrency in OFS Profitability Management User Guide.
The following are the steps involved in creating a custom Ledger Class table: Create subtype relationship between the custom Ledger Class table and BASIC_LEDGER_CLASS_REQ super-class entity.
NOTE
FINANCIAL_ELEM_ID, ORG_UNIT_ID, GL_ACCOUNT_ID, COMMON_COA_ID, and LEGAL_ENTITY must be present in any Management Ledger table.
1 Create a new subject area within the ERwin model.
5. Create the custom Ledger Class table in ERwin. Specify logical name, physical name and description for the table. Define any columns that do not come from any of the standard super-class tables as part of the custom Ledger Class table. Specify logical, physical names, domain and other column properties for each column.
6. Move BASIC_LEDGER_CLASS_REQ into the new subject area.
Table Classifications can be set for any Client Data Object. Table classification set against each Client Data Object is validated through Object Registration Validation process.
The following are the steps involved in setting table classification properties for the custom Ledger Class table:
· Choose Physical View within the ERwin model.
· Go to UDP tab within Table Properties window.
· Specify 'Yes' for 'Ledger Class ' user defined property. Once the model is prepared using the above steps, user should upload the ERwin model. After uploading the model, user can check if the custom Ledger Class has been created in the schema with columns from super-class entities that have been linked to the custom Ledger Class table as well as the columns present in the custom Ledger Class table. Model upload also creates metadata entries within the following Object Registration tables:
§ REV_TABLES_B: Contains the list of table names.
§ REV_TABLES_TL: contains the list of table display names and descriptions in various languages.
§ REV_TAB_COLUMNS: contains the list of column names
§ REV_TAB_COLUMNS_MLS: contains the list of column display names and descriptions in various languages.
§ REV_COLUMN_PROPERTIES: stores the column properties associated with each column.
§ REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT: stores the table classification associated with each table.
— In case custom Ledger Class table contains the column in the same name as that of the super-class table, then column present in the custom Ledger Class table will take precedence over the equivalent column of the super-class table.
— Physical order of the columns within the custom Ledger Class table is determined in the following way:
— Columns present in the custom Ledger Class table.
— Columns present in each of the linked super-class table.
Within any table, ERwin maintains three different column orders:
— Logical Order: Order of the columns as seen in Logical view of the model.
— Physical Order: Order of the columns as seen in Physical view of the model.
— Database Order: Order of the columns as seen in the Database schema.
'Processing Key' user defined property needs to be set for the following columns within the Ledger Class table:
· Leaf columns that are part of the unique index
The following are the steps to set this property in ERwin:
· Choose Physical View within the ERwin model.
· Choose BASIC_LEDGER_CLASS_REQ super-class table.
· Choose the leaf column that needs to be set 'Processing Key' property.
· Go to UDP tab in Column Properties window for this column.
· Specify 'Yes' against 'Processing Key' user-defined property
· Choose the custom Ledger Class table.
· Go to UDP tab in Column Properties window for the columns.
· Specify 'Yes' against 'Processing Key' user-defined property.
Ledger Class tables require unique index on the following columns:
· IDENTITY_CODE
· FISCAL_YEAR
· CONSOLIDATION_CD
· ISO_CURRENCY_CD
· LEGAL_ENTITY_ID
· BALANCE_TYPE_CD
· FISCAL_MONTH
· Key dimension columns
This unique index needs to be created on the custom Ledger Class table, post-model upload operation.
1 Select the subject area within the ERwin model.
7. Delete the table. Before deleting the table, check the dependent tables.
Since, leaf registration in-validates all Client Data Objects, the Object Registration Validation procedure needs to be executed to validate the required tables.
Table Classifications provide a means to designate how tables are used within the OFSAA suite of applications. Each table classification identifies a specific purpose for which an assigned table is allowed to be used.
Some Table Classifications have requirements that must be satisfied in order for an object to be assigned to the classification. These requirements are designated by Table Properties associated to the Table Classifications. These Table Properties are either specific column name requirements or logic validations.
Table Classification assignments are stored inREV_TABLE_CLASS_ ASSIGNMENT.
NOTE
FSI_D_CUSTOMER table should be registered against Other table Class and Profitability-Other Class in REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT table.
Below SQL statements shouldbe executed explicitly to make the required entries in REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT :
Insert into REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT (TABLE_NAME,OWNER,TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_CD,PROTECTED_FLG,VALIDATED_FLAG)
values ('FSI_D_CUSTOMER','<DB OWNER>',30,0,'Y');
Insert into REV_TABLE_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT (TABLE_NAME,OWNER,TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_CD,PROTECTED_FLG,VALIDATED_FLAG)
values ('FSI_D_CUSTOMER','<DB OWNER>',350,0,'Y');
where <DB OWNER> is atomic schema user name.
Object Registration is a process of classifying a table with one or more table classifications depending on the purpose of the table. This step is performed within the ERwin model by setting various User Defined Properties for a client data object. Validation procedure validates table class assignment for a client data object and needs to be executed after model upload operation.
Topics:
· User-Assignable Table Classification
· Requirement For Table Classification
· Executing the Validation Procedure
User-Assignable Table Classifications are those that can be assigned by the administrator to user-defined and client data objects, including the OFSAAI Instrument tables. These Table Classifications identify processing and reporting functions for the OFSAA. Some of these Table Classifications have requirements that must be met in order for the classification to be assigned to a table or view.
All User-Assignable Table Classifications are available for assignment within the ERwin model. The following table lists the User-Assignable Table Classifications:
|
Code |
Table Classification Name |
|---|---|
|
20 |
Instrument |
|
50 |
Ledger Stat |
|
100 |
Portfolio |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
|
210 |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
|
295 |
Codes User Defined (base tbl) |
|
296 |
MLS Descriptions User Defined |
|
300 |
Transaction Profitability |
|
310 |
Instrument Profitability |
|
320 |
User Defined |
|
330 |
Data Correction Processing |
|
360 |
RM Standard |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
|
500 |
PA Lookup Tables |
|
600 |
Derivative Instruments |
|
530 |
Break Funding |
|
197 |
MLS Descriptions Reserved |
|
198 |
Codes Reserved (base tbl) |
|
21 |
Insurance Policy UDP |
|
40 |
Portfolio Supertype UDP |
|
301 |
Insurance Transaction Profitability UDP |
|
311 |
Insurance Policy Profitability UDP |
|
351 |
Insurance Profitability - Other Class UDP |
|
702 |
Processing - EPM Prepayment UDP |
OFSAAI requires specific table structures, column names and column characteristics for OFSAA operations. These structures and requirements are embodied by the User-Assignable Table Classifications.
Each Table Classification comprises individual Table Properties that define the requirements for that classification. Table Properties are two distinct types: those encompassing specific column requirements and those encompassing logic requirements via stored procedures.
The following table provides the validation checks that are being done for each of the table classification:
|
TABLE_CLASSIFICATION_CD |
TABLE_CLASSIFICATION |
TABLE_PROPERTY |
DESCRIPTION5 |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
50 |
Ledger Stat |
Ledger Leaf Column Class |
Fields that are part of core modeling dimensions for Fusion PFT |
Checks if columns of super-type Ledger Leaf Column Class is present |
|
100 |
Portfolio |
Portfolio Requirements |
Dynamic list of Portfolio fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Portfolio Requirements is present |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Basic Instrument Requirements is present |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
Cash Flow Proc. Requirements |
Fields required by TP and ALM Cash Flow processing |
Checks if columns of super-type Cash Flow Proc. Requirements is present |
|
|
|
|
|
Note, this is required if Conditional Assumptions are being defined against the table. |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
Cash Flow Edit Requirements |
Fields required by Cash Flow Edits in addition to Cash Flow fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Cash Flow Edit Requirements is present |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of super-type Multi-Currency Requirements is present |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
TP Basic Requirements |
Non-cash flow Transfer Pricing fields |
Checks if columns of super-type TP Basic Requirements is present |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
Validate Instrument Leaves |
Validates that a table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
200 |
TP Cash Flow |
Validate Instrument Key |
Validate the unique key for Instrument (PA, TP, ALM) tables |
Validation . Instrument table should have index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE column |
|
210 |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Basic Instrument Requirements is present |
|
210 |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of super-type Multi-Currency Requirements is present |
|
210 |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
TP Basic Requirements |
Non-cash flow Transfer Pricing fields |
Checks if columns of super-type TP Basic Requirements is present |
|
210 |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
Validate Instrument Leaves |
Validates that a table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
210 |
TP Non-Cash Flow |
Validate Instrument Key |
Validate the unique key for Instrument (PA, TP, ALM) tables |
Validation . Instrument table should have index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE column |
|
300 |
Transaction Profitability |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Basic Instrument Requirements is present |
|
300 |
Transaction Profitability |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of super-type Multi-Currency Requirements is present |
|
300 |
Transaction Profitability |
Validate Instrument Leaves |
Validates that a table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
300 |
Transaction Profitability |
Validate Transaction Key |
Validate the unique key for Transaction Profitability tables |
Transaction table should have composite index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE and all the processing key columns. |
|
310 |
Instrument Profitability |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Basic Instrument Requirements is present |
|
310 |
Instrument Profitability |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of super-type Multi-Currency Requirements is present |
|
310 |
Instrument Profitability |
Validate Instrument Leaves |
Validates that a table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
310 |
Instrument Profitability |
Validate Instrument Key |
Validate the unique key for Instrument (PA, TP, ALM) tables |
Validation . Instrument table should have index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE column |
|
330 |
Data Correction Processing |
Validate Processing Key |
Validate the unique key for Processing tables |
Processing Key Column for a table have a matching unique index |
|
360 |
ALM Standard |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Basic Instrument Requirements is present |
|
360 |
ALM Standard |
Cash Flow Proc. Requirements |
Fields required by TP and ALM Cash Flow processing |
Checks if columns of super-type Cash Flow Proc. Requirements is present |
|
360 |
ALM Standard |
Cash Flow Edit Requirements |
Fields required by Cash Flow Edits in addition to Cash Flow fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Cash Flow Edit Requirements is present |
|
360 |
ALM Standard |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of super-type Multi-Currency Requirements is present |
|
360 |
ALM Standard |
Validate Instrument Leaves |
Validates that a table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
360 |
ALM Standard |
Validate Instrument Key |
Validate the unique key for Instrument (PA, TP, ALM) tables |
Validation . Instrument table should have index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE column |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Basic Instrument Requirements is present |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
Cash Flow Edit Requirements |
Fields required by Cash Flow Edits in addition to Cash Flow fields |
Checks if columns of super-type Cash Flow Edit Requirements is present |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of super-type Multi-Currency Requirements is present |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
TP Option Costing Requirements |
Fields required for Transfer Pricing Option Costing processing |
Checks if columns of super-type TP Option Costing Requirements is present |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
TP Basic Requirements |
Non-cash flow Transfer Pricing fields |
Checks if columns of super-type TP Basic Requirements is present |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
Validate Instrument Leaves |
Validates that a table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
370 |
TP Option Costing |
Validate Instrument Key |
Validate the unique key for Instrument (PA, TP, ALM) tables |
Validation. Instrument table should have index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE column |
|
500 |
PA Lookup Tables |
Validate PA Lookup |
Procedure to check if there is a primary key for the lookup tables. |
Validation. All Lookup table should have a primary key present |
|
530 |
Break Funding |
Break Funding Requirements |
Fields required as part of TP break funding |
Checks if columns of super-type Break Funding Requirements is present |
|
301 |
Insurance Transaction Profitability UDP |
Validate Policy Table Leaves |
Validates that a policy table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation. Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns should be of data type NUMBER |
|
301 |
Insurance Transaction Profitability UDP |
Validate Policy Trans Key |
Validate the unique key for Policy Transaction tables |
Transaction table should have composite index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE and all the processing key columns. |
|
301 |
Insurance Transaction Profitability UDP |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of supertype Basic Instrument Requirements are present |
|
301 |
Insurance Transaction Profitability UDP |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of supertype Multi-Currency Requirements are present |
|
311 |
Insurance Policy Profitability UDP |
Multi-Currency Requirements |
Fields required for Multi-Currency |
Checks if columns of supertype Multi-Currency Requirements are present |
|
311 |
Insurance Policy Profitability UDP |
Basic Instrument Requirements |
Instrument Required fields |
Checks if columns of supertype Basic Instrument Requirements are present |
|
311 |
Insurance Policy Profitability UDP |
Validate Instrument Key |
Validate the unique key for Instrument (PA, TP, RM) tables |
Transaction table should have composite index present on ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE and all the processing key columns. |
|
311 |
Insurance Policy Profitability UDP |
Validate Policy Table Leaves |
Validates that a policy table has all 'B' leaves |
Validation . Check if the table has all the key dimension leaf columns. The leaf columns must be of data type NUMBER |
|
351 |
Insurance Profitability - Other Class UDP |
Profitability - Other Class |
Validate the unique key for Profitability - Other Class tables |
Validate the unique key for Profitability - Other Class tables |
Specific column requirements for each table property can be obtained by querying REV_COLUMN_REQUIREMENTS table.
The OFSA_TAB_CLASS_REQ package contains all of the procedures and supporting functions that validates if a table meets the requirements for a particular Table Classification.
The package performs the following validations:
· VALIDATE_INST_KEY
This procedure validates if a table has ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE, or ID_NUMBER, IDENTITY_CODE and AS_OF_DATE as its unique index and if the Processing key designated in Column Properties is ID_NUMBER, IDENTITY_CODE.
· UPDATABLE_INST_REQ_FIELDS
This procedure checks that all of the Instrument Required Fields are also listed as updatable in USER_UPDATABLE_COLUMNS for the specified table or view.
· VALIDATE_INST_LEAVES
This procedure will validate a table has all the required leaf columns
· VALIDATE_TRANS_KEY
This procedure validates if a table has ID_NUMBER and IDENTITY_CODE and one or more 'B' Leaf Columns in its unique index and that these columns match the Processing key designated in Column Properties.
· VALIDATE_CORR_KEY
This procedure will validate a table has a unique index with updatable columns.
All the above procedures return a success or failure status. The REV_TAB_CLASS_ASSIGNMENT table is updated as 'Y' if a table is successfully validated and 'N' in case of failure.
You can execute this procedure either from SQL*Plus or from within a PL/SQL block or from Batch Maintenance window within OFSAAI framework.
To run the procedure from SQL*Plus, login to SQL*Plus as the Atomic Schema Owner. The syntax for calling the procedure is:
set serveroutput off
Declare
Output number;
Begin
Output := fsi_batchtableclassreq(pbatchid, pmis_date);
End;
NOTE
Since the package contains huge number of dbms_output statements, user should either increase the output buffer size or disable the server output.
For Example:
set serveroutput off
Declare
Output number;
Begin
Output :=
fsi_batchtableclassreq('INFODOM_INSTRUMENT_TABLE_VALIDATION_20131205_1',
'20131205');
End;
To execute the procedure from OFSAAI Batch Maintenance, create a new Batch with the Task as TRANSFORM DATA and specify the following parameters for the task:
· Datastore Type: Select appropriate datastore from list
· Datastore Name: Select appropriate name from the list
· IP address: Select the IP address from the list
· Rule Name: Batch_Table_Class_Req
· Parameter List: Batch Identifier and MISDATE
The OFSA_TAB_CLASS_REQ packages throws the following exceptions.
· Exception 1: FAILED: Table Property 1030 - Validate Correction Key
This exception occurs when no valid unique index found.
· Exception 2: FAILED: Table Property 1030 - Validate Correction Key
This exception occurs when Processing Key Column Properties do not match unique index
· Exception 3: FAILED: Table Property 1030 - Validate Transaction Key
This exception occurs when no valid unique index found.
· Exception 4: FAILED: Table Property 1000 - Validate Instrument Leaves
This exception occurs when one or more Leaf Columns are missing or incorrectly registered. Check if the datatype of the LEAF columns is NUMBER and domain of these columns is LEAF.
This section details the steps required for defining Alternate Rate Output columns within the OFSAA Fund Transfer Pricing Application.
The following topics are covered in this section:
· Setting User Defined Properties in ERwin
· Uploading the model and object registration
The following are the user-defined properties that are available for identifying columns required for alternate rate output:
· Transfer Pricing Output (Column Property – 80)
· Option Cost Output (Column Property – 81)
· Other Adj Spread Output (Column Property – 82)
· Other Adj Amount Output (Column Property – 83)
· Economic Value Output (Column Property – 86)
· Liquidity_rate_column (Column Property – 95)
· Liquidity_amount_column (Column Property – 96)
· Basis_rate_column (olumn Property – 97)
· Basis_amount_column (Column Property – 98)
· Pricing_rate_column (Column Property – 99)
· Pricing_amount_column (Column Property – 100)
User needs to assign one of the above properties to the columns that need to be used as Alternate Rate Output columns within the Fund Transfer Pricing application.
The following are the steps to set the user-defined property to the column:
1 Open the ERwin file in ERwin Data Modeler tool.
8. Go to Main Subject Area.
9. Go to Physical View.
10. Choose the entity that contains the alternate rate output column. This entity can also be a super-type (like TP_BASIC_REQ).
11. Select the column and open the column properties for the column.
12. Go to UDP tab within column properties.
13. Select YES for one of the above user-defined properties.
14. Save the model.
NOTE
Setting the user-defined property of the columns within a super-type entity will apply to all the entities that are related to the super-type.
Upload the model in OFSAAI and perform object registration. After uploading the model, you can execute the following query to check if the user-defined properties are set for the columns.
select * from rev_column_properties where column_property_cd in (80,81,82,83)
where TABLE_NAME = <<table_name>>
Replace <<table_name>> with the relevant table name and column name in the above query and execute the same. Above query returns the columns that are used for alternate rate outputs.
User Defined Properties are set for tables and columns within ERwin.
The following user defined properties can be set for the table:
|
UDP Name |
Description |
List of values |
|---|---|---|
|
Instrument |
Property to identify if the table is classified as a basic instrument table. (that is, Instrument table classification code 20) |
YES / NO |
|
TP Cash Flow |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'TP Cash Flow' for the purpose of generating Transfer Pricing rates using cash flow methods. |
YES / NO |
|
TP Non Cash Flow |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'TP Non-Cash Flow' for the purpose of generating Transfer Pricing rates using non cash flow methods. |
YES / NO |
|
Transaction Profitability |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Transaction' for the purpose of executing allocation rules. |
YES / NO |
|
Portfolio |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Portfolio'. |
YES / NO |
|
User Defined |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'User Defined' table for storing multi-lingual descriptions for codes. |
YES / NO |
|
Ledger Stat |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Ledger Stat' for the purpose of executing allocation rules. |
YES / NO |
|
ALM Standard |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'ALM Standard' for the purpose of executing ALM cash flow engine to generate cash flows. |
YES / NO |
|
TP Option Costing |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'TP Option Costing' for the purpose of generating Transfer Pricing rates with option costing. |
YES / NO |
|
Break Funding |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Break Funding' for the purpose of generating Break funding charges using Transfer Pricing engine. |
YES / NO |
|
MLS Descriptions Reserved |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Reserved' table for storing multi-lingual descriptions for codes. |
YES / NO |
|
Codes Reserved (base tbl) |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Reserved' table for storing codes of simple dimensions. |
YES / NO |
|
Codes User Defined (base tbl) |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'User-defined' table for storing codes of simple dimensions. |
YES / NO |
|
PA Lookup Tables |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Lookup Table' for the purpose of defining lookup table allocation rules. |
YES / NO |
|
Instrument Profitability |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Instrument' for the purpose of executing allocation rules. |
YES / NO |
|
Derivative Instruments |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Derivatives' for the purpose of executing ALM cash flow engine to generate cash flows for derivative instruments. |
YES / NO |
|
Data Correction Processing |
Property to identify if the table is classified as 'Data Correction Processing' for the purpose of executing Cash Flow Edits engine. |
YES / NO |
The following user defined properties can be set for the column:
|
UDP Name |
Description |
List of values |
|---|---|---|
|
Balance Range |
Property to identify if the column within a table classified as 'PA Lookup Table' must be displayed under 'Range' within Lookup table definition. |
YES / NO |
|
Balance |
Property to identify if the column is of type 'Balance'. |
YES / NO |
|
Standard Rate |
Property to identify if the column is of type 'Standard Rate'. |
YES / NO |
|
Balance Weighted Object |
Property to identify if the column is of type 'Balance Weighted Object'. |
YES / NO |
|
Processing Key |
Property to identify if this column is used as a 'Processing Key' within the instrument, transaction and ledger_stat table. |
YES / NO |
|
Frequency Multiplier |
Property to identify if the column is used to store 'Frequency'. This property is used in Filters UI within OFSAAI. |
YES / NO |
|
Multiplier Related Field |
Property to specify the name of the column that is used to store the multiplier for the corresponding 'Frequency' column. This property is used in Filters UI within OFSAAI. |
Text |
|
Related Field |
Property to specify the name of the column that is used to store the multiplier for the corresponding 'Term' column. This property is used in Filters UI within OFSAAI. |
Text |
|
Term Multiplier |
Property to identify if the column is used to store 'Term'. This property is used in Filters UI within OFSAAI. |
YES / NO |
|
Column Alias |
Property to specify an alias for the column. This is used within the staging loader program for loading LEDGER_STAT table. |
Text |
|
Statistic |
Property to identify if the column is of type 'Statistic'. |
YES / NO |
|
Transfer Pricing Output |
Property to identify if the column must be set as an alternate output column for writing transfer rates by transfer pricing engine. |
YES / NO |
|
Option Cost Output |
Property to identify if the column must be set as an alternate output column for writing option costing output by transfer pricing engine. |
YES / NO |
|
Other Adj Spread Output |
Property to identify if the column must be set as an alternate output column for writing other adjustment spread by transfer pricing engine. |
YES / NO |
|
Other Adj Amount Output |
Property to identify if the column must be set as an alternate output column for writing other adjustment amount by transfer pricing engine. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_LOOKUP_RANGE_MINIMUM |
Property to identify minimum range column within a table classified as 'PA Lookup Table'. For eg: LOOKUP_TEMPLATE_TABLE.AVERAGE_BALANCE_MIN column. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_LOOKUP_RANGE_MAXIMUM |
Property to identify maximum range column within a table classified as 'PA Lookup Table'. For eg: LOOKUP_TEMPLATE_TABLE.AVERAGE_BALANCE_MAX column. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_EXPORT_PFT_OUTPUT |
Property to identify PFT Output Columns in instrument tables and FSI_D_INST_SUMMARY table. For eg: CALL_CENTER_EXP, COMPLAINCE_EXP etc. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_EXPORT_FTP_OUTPUT |
Property to identify FTP Output Columns in instrument tables and FSI_D_INST_SUMMARY table For eg: OTHER_ADJUSTMENTS_AMT, OTHER_ADJUSTMENTS_RATE etc. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_EXPORT_FTP_OTHERS |
Property to identify columns used by FTP in instrument tables and FSI_D_INST_SUMMARY table For eg: AVG_BOOK_BAL, CUR_BOOK_BAL etc. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_EXPORT_EPM_KEY_DIMS |
Property to identify EPM Key Processing dimension columns in instrument tables and FSI_D_INST_SUMMARY table. For eg: COMMON_COA_ID, PRODUCT_ID etc. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_EXPORT_EPM_KEY_COLUMNS |
Property to identify mandatory key columns for EPM in instrument tables and FSI_D_INST_SUMMARY table. For eg: AS_OF_DATE, ISO_CURRENCY_CD, IDENTITY_CODE, INSTRUMENT_TYPE_CD etc. |
YES / NO |
|
UDP_EXPORT_EPM_OTHERS |
Property to identify other columns for EPM in instrument tables and FSI_D_INST_SUMMARY table. For eg: ACCOUNT_OFFICER_CD, INTEREST_INC_EXP etc. |
YES / NO |
Perform the following steps to modify the Precision
1 Open the ALM, FTP, or PFT model using All Fusion ERwin Data Modeler.
15. Switch to ALM-FTP-PFT-HM-BSP – Ledger Stat subject area.
16. Select Logical view.
17. Edit the Ledger Stat table by double clicking the table in the Logical Layer.
18. Change the data type in Datatype tab to the revised precision and scale (example, NUMBER (22, 3)) for the following columns:
§ Month 01 Amount, Month 02 Amount, Month 03 Amount and so on
§ YTD 01 Amount, YTD 02 Amount, YTD 03 Amount and so on.
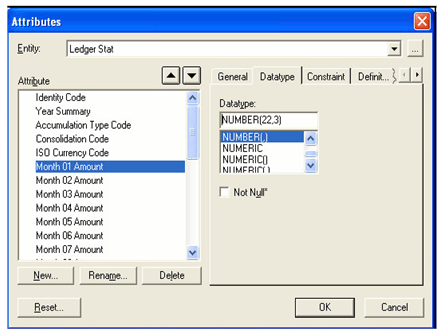
Description of Attribute window follows
19. Save the changes.
20. Select the Physical view.
21. Click LEDGER_STAT table and view the datatype of columns – MONTH_01 till MONTH_12 and YTD_01 till YTD_12. The data type of these columns should display the new precision and scale.
22. Save the model as xml in All Fusion Repository Format.
23. Perform incremental model upload.
NOTE
In case, users decrease the precision and scale for the columns, such columns should not have any values during model upload.