
This chapter provides an understanding of the Oracle Financial Services Analytical Application Reconciliation.
Topics:
· Overview
The GL structure is designed in such a way that, it facilitates verification of the differences which arise by comparing the GL source systems with the banks operational systems (Product Processor within OFSAA). At a global level, you must input GL and Product Processor setting details which form a base at a reconciliation level. The input provided in the Settings window is reflected at a global level.
Figure 1: Settings window Process Flow

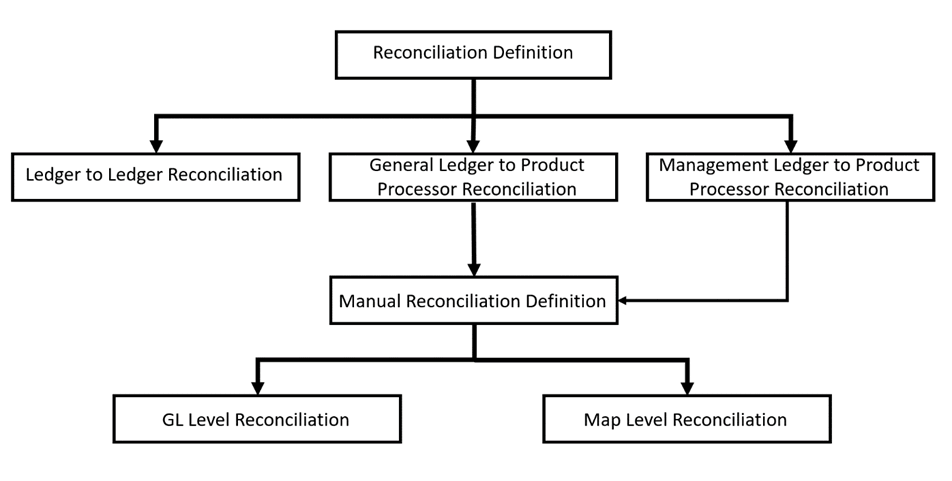
The predefined reconciliation definition types that can be used during a reconciliation definition are:
· General Ledger to Product Processor
· Ledger to Ledger
· Management Ledger to Product Processor
The reconciliations are defined, which forms a part of execution and data verification. This can be defined as Manual Reconciliation Definition, as shown in Figure 2. This reconciliation is defined in the Reconciliation Management screen. For more information on Manual Reconciliation Definition, see the Key Terms and Concepts.
Figure 2: Reconciliation Definition Process Flow
After reconciliations are defined, executions are performed from the Process Modelling Framework of OFSAA infrastructure. When reconciliation differences arise, then adjustment entries are passed (either manually or by the application).
Figure 3: Reconciliation Rule Definition Process Flow

NOTE:
It is imperative to map each function to a specific user role to be able to work with the OFSAA Reconciliation Framework application. The responsibility to map the various function codes of the OFSAA Reconciliation Framework application (such as Add, View, and Delete access) to a particular user role lies with the System Administrator.
To create application users in the OFSAA setup, see the User Administrator section in the Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications Infrastructure User Guide.
For details, see the User Administrator section in the Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications Infrastructure User Guide.
Beginning with the OFSAA 8.1.0.0.0 release, with the installation of the OFSAA Reconciliation Framework application pack, preconfigured Application user groups are seeded. These user groups are unique to every OFSAA Application Pack and have application roles pre-configured.
For more information on seeded User Groups, see OFSAA Reconciliation Framework application pack User Group Names.
Map the application user (s) to the respective Application User Group (s) and subsequently authorize the entitlements by logging in as SYSAUTH (System Authorizer) user.
For details, see the Mapping/Unmapping Users section in the Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications Infrastructure User Guide.
The User UserGroup Map facilitates you to map user(s) to a specific user group which in turn is mapped to a specific Information Domain and role. Every UserGroup mapped to the infodom must be authorized. Else, it cannot be mapped to users.
TheUser UserGroup Map screen displays details such as User ID, Name, and the corresponding Mapped Groups. You can view and modify the existing mappings within the User UserGroup Maintenance screen.
With the installation of the OFSAA Reconciliation Framework Pack, pre-configured Application user groups are seeded. These user groups are unique to every OFSAA Application Pack and have application roles pre-configured.
You can access the User UserGroup Map by expanding the User Administrator section within the tree structure of the LHS menu.
After the user is created for Reconciliation Framework, map them to the following user groups:
1. Recon Administrator
2. Recon Framework Analyst
3. Recon Framework Authorizer
4. Adjustment Super Group
This section aims to explain the key terms and concepts of the OFSAA Reconciliation Framework.
Topics:
· Manual Reconciliation Definition
There are two consolidation types supported by the application:
· Solo
When a legal entity is selected with consolidation type as Solo, then all the exposures of that particular legal entity are selected for processing. Manual reconciliation definition can process solo legal entity data.
When a parent legal entity is selected as Consolidated, then all the exposures of that legal entity and exposure of each level (or levels) of descendant child legal entities (without intra-group exposures) are selected for processing. In intra-group exposures, the counterparty is a child descendant of any level. For an intra-group scenario (where GL structure has specific intra-group GL code in addition to regular GL codes), intra GL codes are considered only from the GL side for processing. Non-Intra is a scenario where no GL codes are present for reconciliation definition.
Figure 4: Consolidated Process Flow
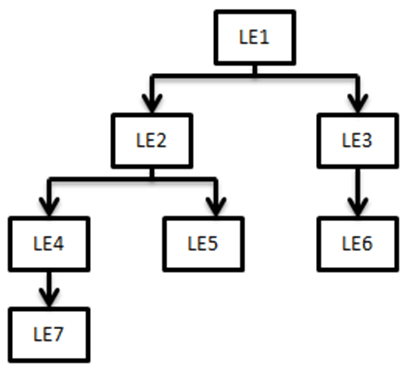
In this case, LE 1 is the parent legal entity, and LE2 and LE3 are the immediate child legal entities of LE1. Similarly, LE4 and LE5 are immediate child legal entities of LE2, but second-level descendant legal entities of LE1.
If you select LE2 (parent) for consolidated treatment, then exposure to LE 4, LE 5, and LE7 are considered as intra-group exposures.
NOTE:
The application only aggregates data on the PP side for a consolidation reconciliation type; such aggregation is only to reconcile data and does not consider minority or majority holdings.
Intra-group exposures are identified by the customer reference ID in the Product Processor. For LE2, if the customer reference ID is LE4, LE5, and LE7, then these are considered as intra-group exposures. Exposures to LE3 or LE6 are not considered as intra-group exposures as they are not the child descendant of LE 2. If you select LE7 for consolidated treatment, then no exposures are considered as intra-group exposure since LE7 has no child legal entity.
NOTE:
Intra-group exposures are identified by the customer reference ID in the PP table.
This feature is used to find child legal entities under the hierarchy node of a Legal Entity that is selected at the definition level. If this feature is used when defining the GL Reconciliation rule, then all child nodes will participate in the reconciliation process.
In manual reconciliation definition, user input is sought on the GL side and PP side to determine the course of reconciliation. This is applicable for both GL level and map level reconciliation. In GL level reconciliation, unique GL codes are identified from the GL code mapping. In the map level, GL codes do not form a part of the reconciliation definition. A manual reconciliation definition can be used for a solo or consolidated legal entity. Reconciliation definition for a consolidated GL, having an intra-group GL structure, is computed from GL data and not from PP data. Therefore, any account present in the PP but unavailable in GL is not captured in the reconciliation definition.
In GL level reconciliation the difference between GL system and Product Processors systems at each reconciliation dimension node level within a GL code is identified. For manual reconciliation definition, unique GL codes are identified from the GL side. If it is at the solo level, then exposures originating in the legal entity are selected. If it is at the consolidated level, then exposures originating in the selected legal entity and its child entities (with or without intra-group exposures depending on GL structure) are selected.
The adjustment entry allocation depends on the reconciliation type selected. In GL level reconciliation after a definition is executed, the differences that emerge as a part of the reconciliation definition (GL PP level reconciliation) are reported in the adjustment entry table. This table shows all the entries of an executed map which requires adjustment. In GL level reconciliation, the difference in amount can either be posted to Product Processors or an external table. For more information on the external table, see the Data Requirement.
NOTE:
In GL level reconciliation the adjustment allocation is always automatic, that is, you do not have the option of editing the allocation ratio.
In map level reconciliation the difference between GL data and PP data at each reconciliation dimension node level across all PPs, are identified. Unlike GL level reconciliation, map level reconciliation is computed at an aggregate level of the reconciliation definition; by ignoring the GL code and by considering reconciliation dimensions. Map level reconciliation is applied at the legal entity level - either solo or consolidated. If it is at the solo level, then exposures originating in a particular legal entity are selected. If it is at the consolidated level, then exposures originating in the selected legal entity and its child entities (excluding intra-group exposure depending on GL structure) are selected.
NOTE:
In a map level reconciliation, adequate filters for the PP data must be selected to ensure that actual data selected on both sides are the same.
The adjustment entry allocation depends on the reconciliation type selected. In map level reconciliation, once a definition has executed the differences that emerge as a part of the reconciliation (General Ledger Product Processor level reconciliation) are reported in the adjustment entry table. This table shows all the entries of an executed map which requires adjustment. In map level reconciliation, the difference in amount can either be posted to Product Processors or an external table. In map level reconciliation, the adjustment allocation can either be automatic or manual.
The common icons which you come across in the GL reconciliation UIs are as follows.
Buttons Name |
Icon |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Pagination Options |
|
It helps in navigating from one page to another. |
View |
|
It helps to view details of GL reconciliation parameters. |
Edit |
|
It allows you to update details of GL reconciliation parameters. |
Add |
|
Helps in defining new GL reconciliation parameters |
Copy |
|
It helps to copy the details of GL reconciliation parameters. |
Delete |
|
Click this icon to delete the GL reconciliation parameters. |
Search |
|
The search feature allows you to search for the entry you are looking for instead of manually searching for data. |
Reset |
|
The Reset icon refreshes the field name back to the default blank field. |