22 Troubleshooting VNFM
Debug VNFM
- VNFM logs are located in " /var/vnfm/logs/vnfm.log "
- VNFM boot logs are located in "/usr/share/vnfm/apache-tomcat-9.0.16/logs/catalina.out".
- Tomcat logs are located in " /usr/share/vnfm/apache-tomcat-9.0.16/logs/catalina.out ".
- SNMP notifier logs are located in "/var/vnfm/logs/snmp_notifier.log"
- Alert Manager logs are located in "/var/vnfm/logs/alertmanager.log"
- Prometheus server logs are located in "/var/vnfm/logs/prometheus.log"
- Node Exporter logs are located in "/var/vnfm/logs/node_exporter.log"
- RSync logs are location in "/var/log/rsync.log"
- Reboot logs are location in "/var/vnfm/logs/reboot.log"
- Cloud-init logs of the DSR/SDS VNFs are located in "/var/TKLC/log/cloud-init/cloud-init.log"
Adding Route for a New VIM
root
user mode:
- Open
route-network.sh, and append the new VIM route address to the DataList.For example:
DataList=10.75.167.0/24,10.75.185.0/24 - Execute the
/route-network.sh, and then executeifdown eth1andifup eth1.
Reboot Tomcat
dsrvnfm user mode:
- Go the
/path.The
./dsrvnfmStartup.pyscript is present. - Execute this
command:
./dsrvnfmStartup.py <option for tomcat to start,stop,restart> <ipAddress of vnfm, Don't use [] incase of IPv6>Examples:
./dsrvnfmStartup.py restart 2606:b400:605:b84a:6e41:6aff:fec7:8100./dsrvnfmStartup.py start 10.75.189.201
Resolve HA Alarms on VNF through VNFM Deployed Setup
Perform the following to resolve the HA alarms:
- Check the ping request and
response packets from Server-A and Server-B for which alarm has been raised, by
executing:
tcpdump -i eth1 -n "host <server-A>-imi or <server-B>-imi and port 17401 and udp"For example:
tcpdump -i eth1 -n "host noam00-17badf67-imi or noam01-17badf67-imi and port 17401 and udp" - If ping request or response packets are not coming
from any server, then add security group rule ingress (response) or egress (request)
to that instance.
The following image shows Ingress response:
Figure 22-1 Ingress Response
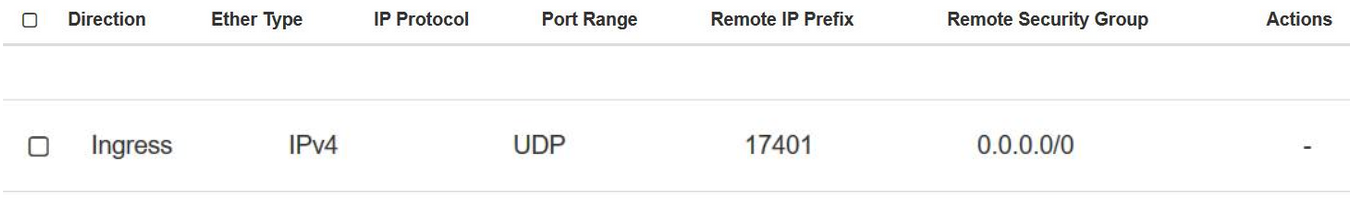
- Check the ping packets again
after adding the rule and ensure that
imirequest and response packets are received from each servers, by executing:tcpdump -i eth1 -n "<server-A>-imi or <server-B>-imi and port 17401 and udp" - Now restart the cmha process
on the node where the alarms are present, by executing:
pm.set off cmha && sleep 5 && pm.set on cmhaNote:
If the Node is HA Active, then restarting cmha will cause switch over.
Adding a Port in Openstack Security Groups
The Security Group Rules define the traffic that is allowed through instances assigned to the security group.
- Open
Security Groups tab on the Openstack Horizon.
A list of available Security Groups appear.
- From the list, click Manage Rules for the required Security Group.
-
Select Add Rule, provide all the required details in the dialog box.
Note:
In the CIDR field, the values for zero address are:- For IPv4 - 0.0.0.0/0
- For IPv6 - ::/0
- Click Add Rule.
Debug SNMP System Alerts
- Check the log files for any errors. For information about list of log files, see How to debug VNFM.
- If default configurations needs to be changed, perform SNMP System Traps Configurations.
Configure Flavor and Instantiation Levels in VNFM
Steps to configure Flavor and Instantiation Levels in VNFM:
The number of VMs to be allocated to each VNF Flavor and Instantiation Levels are present
in the file: /usr/share/vnfm/openstack/VnfSizing.yaml
A sample of the file is provided below:
dsrSignaling:
small:
diameter:
damp: 2
ipfe: 2
stp: 0
sbr: 0
udr: 0
large:
diameter:
damp: 32
ipfe: 4
stp: 0
sbr: 0
udr: 0- In
'dsrvnfm'user mode, edit this file:/usr/share/vnfm/openstack/VnfSizing.yaml - Change the number of VMs under the required VNF Type → Instantiation Level Id → Flavor Id and save the file.
For example: In DSR Signaling, under Diameter Flavor Id, small Instantiation Level Id, the user needs 16 DAMPs, 4 IPFEs, the sample of file would be as below:
Edited Sample File
dsrSignaling:
small:
diameter:
damp: 16
ipfe: 4
stp: 0
sbr: 0
udr: 0
large:
diameter:
damp: 32
ipfe: 4
stp: 0
sbr: 0
udr: 0