Maintaining Asset Book Information
Add books to assets either by entering the assets through the Asset Express Add component or capitalizing them on the Asset Information page of the Asset Basic Information component.
The pages in the Asset Book Definition component enable you to enter book information that is different from that in your asset profile IDs.
This topic discusses how to maintain Asset Book information.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
ASSET_BOOK_01 |
Identify the asset's books and some of the information needed for calculating depreciation. An asset can be linked to any number of books. Typically, separate books are required for financial and tax purposes. |
|
|
ASSET_DEPR_DETAILS |
Set special depreciation terms and select an accounting method for them. These are commonly used to meet depreciation requirements for specific countries. |
|
|
ASSET_BOOK_02 |
Specify property type, tax depreciation criteria, and tax credit options. If the fields on this page are not available, the book was not set up as a tax book on the Business Unit/Book Definition page. |
Use the Book - Depreciation page (ASSET_BOOK_01) to identify the asset's books and some of the information needed for calculating depreciation.
An asset can be linked to any number of books. Typically, separate books are required for financial and tax purposes.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Book - Depreciation page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
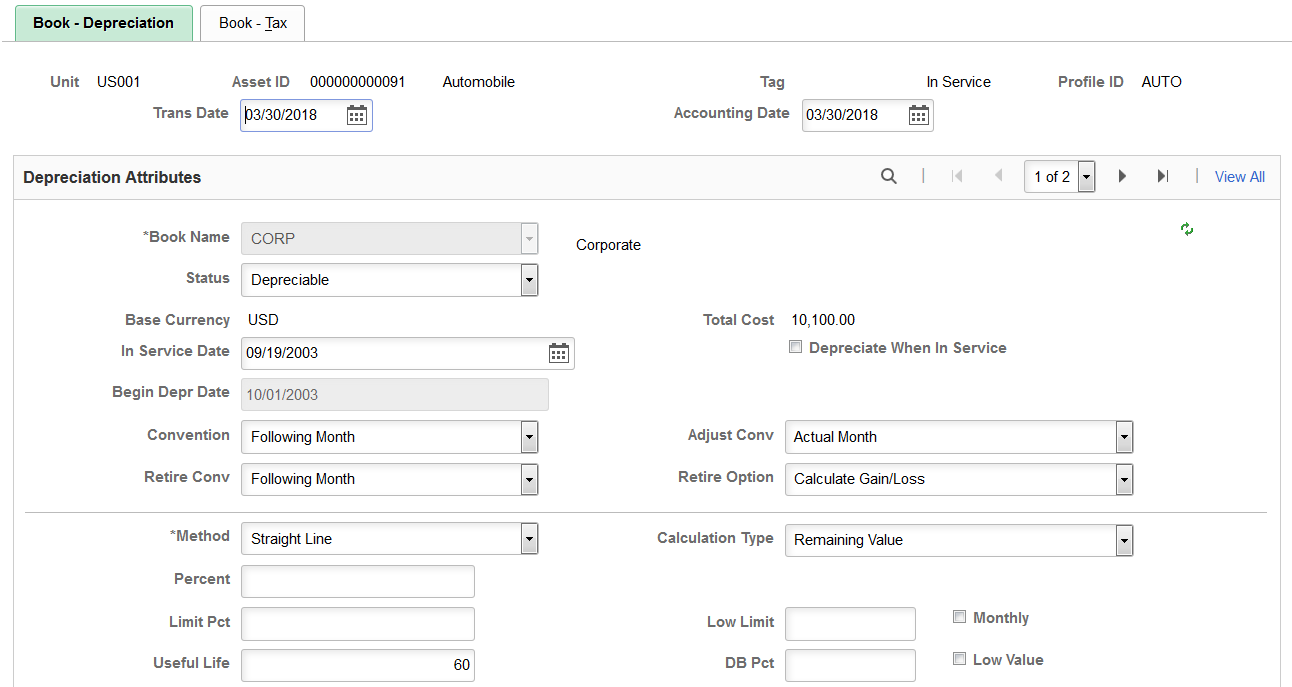
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Book - Depreciation page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
In Service Date |
Enter the date that the asset was made available for use from a financial standpoint. This date and the depreciation convention determine when depreciation starts for this book. This date is reflected in the Begin Depr Date field. |
Depreciate When In Service |
Select to allocate annual depreciation as of the date that you placed the asset in service. If you do not select this option, PeopleSoft Asset Management allocates annual distribution as of the date determined by the depreciation convention. This option is valid only in the year that the asset was acquired. |
Convention |
Enter the convention that the system uses to prorate depreciation for the asset. Asset Management is delivered with most standard depreciation conventions set up in the Depreciation Conventions table. The system derives the beginning depreciation date from the convention and the placed-in-service date. For example, if you began using an asset on May 3, 2006, and selected Actual Month as the depreciation convention, PeopleSoft Asset Management would begin depreciating this asset on May 1, 2006. If you selected Following Month as the convention, depreciation would begin on June 1, 2006. |
Adjust Convention |
Enter the adjustment convention that the system uses to prorate cost adjustments for the asset. |
Retirement Convention |
Enter the retirement convention that the system uses to prorate retirement for the asset. |
Retire Option |
Select the retirement calculation option to be processed for assets within a given book. These retirement options are available at the profile, book and asset levels. See Retire Assets Page. |
Select a depreciation method in the Depreciation Method field. Some depreciation methods require you to enter additional information. Depending on the method that you select, additional fields will display as needed, and as described in the following table:
|
Asset Depreciation Method |
Additional Fields |
|---|---|
|
Declining Balance w/SL by Limit % |
DB Pct (declining balance percent) and Limit Pct (limit percent) |
|
Declining Balance |
Percent, Low Limit, and Monthly |
|
Declining Balance w/SL |
DB Pct |
|
Depreciation Schedule |
Schedule |
|
Flat Rate % |
Percent, Low Limit, and Avg Option (averaging option) |
|
France Derogatory Balance |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life (depreciate past life) |
|
Germany Staffel Method |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life |
|
Japan - Changes 200/250 DB to SL (J9 - Changes 200/250 Declining Balance to Straight Line) |
No additional fields display. However, for this method you must select the Special Depreciation option and input the year of change on the Special Terms - Depreciation Method Information page. Used for assets that were added using the following methods:
|
|
Japan - Changes DB to SL 200 (J8 - Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line 200) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired on or after April 1, 2012. |
|
Japan - Changes DB to SL 250 (J6 - Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line 250) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired on or after April 1, 2007. |
|
Japan - Extended/Strt Line (JE - Extended Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for fully depreciated assets under the Tangible / Strt Line and Tangible / Declining Balance methods that are subject to an extended depreciation useful life of five years using a Straight Line depreciation method starting from the first period of the following fiscal year. |
|
Japan - Lease Depreciation (J4 - Lease Depreciation) |
No additional fields display. |
|
Japan - Intangible/Strt Line (J3 - Intangible/Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life |
|
Japan - Tangible/Declining Bal (J1 - Tangible/Declining Balance) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired before April 1, 2007. |
|
Japan - Tangible/Strt Line (J2 - Tangible/Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired before April 1, 2007. |
|
Japan - Changes DB to SL (J5 - Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life |
|
Japan - Tangible/Strt Line Rev (J7 - Tangible/Straight Line Revenue) |
DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, Depr Pass Life Used for assets acquired on or after April 1, 2007. |
|
Manual Depreciation |
No additional fields display. The manual depreciation method enables you to adjust depreciation amounts using different method. To use manual depreciation, you must first create depreciation entries using another method. Once this has been done, you can make your adjustments. |
|
Straight Line |
No additional fields appear. |
|
Straight Line Percent |
Percent |
|
Sum of the Years |
No additional fields appear. |
|
Units of Production |
UOP ID (units of production ID) |
|
User Defined Method |
Method ID, DB Pct, Percent, Low Limit, and Depr Pass Life |
The following table defines the additional fields:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Limit Pct (limit percent) |
Enter to specify a limit for depreciation as a percentage of cost. |
UOP ID (units of production ID) |
Enter the units-of -production ID, production information, and transaction information to use for the asset. |
DB Pct (declining balance percent) |
Enter the percentage of declining balance depreciation to be taken each year until the amount calculated by the straight line method is greater. |
Percent |
Enter the percentage of original basis to be taken in depreciation each year. |
Low Limit |
Enter an amount. When the asset basis reaches this limit, the remaining basis is taken in depreciation and the asset is fully reserved. Low limit is specific to group assets and flat rate. |
Depr Pass Life (depreciate past useful life) |
Select this if you want to continue to depreciate this asset past its useful life. This option is used for certain countries' governmental regulations and in utilities industries to depreciate an asset to the end of a depreciation calendar. |
Method ID |
Enter the user-defined method to use. |
Schedule |
Enter a schedule to use for depreciation. |
Avg Option (average option) |
Generally, this field is used by utility companies to depreciate composite assets. The averaging options are expressly designed to work with the flat rate depreciation method. |
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Monthly |
Monthly averaging takes an average monthly asset balance and multiplies it by the annual depreciation rate. The result is then applied against a period allocation (1/12, 2/12, 3/12, and so on) to derive a year-to-date (YTD) depreciation amount. The difference between the newly calculated YTD depreciation and the previous YTD depreciation is the amount booked to the current period. This is applicable to the declining balance method only. |
Yearly |
Yearly averaging is similar to monthly averaging except that a yearly average balance is used. Because this amount is not known until the end of the year, it is usually estimated and adjusted periodically as the actual figures become available. |
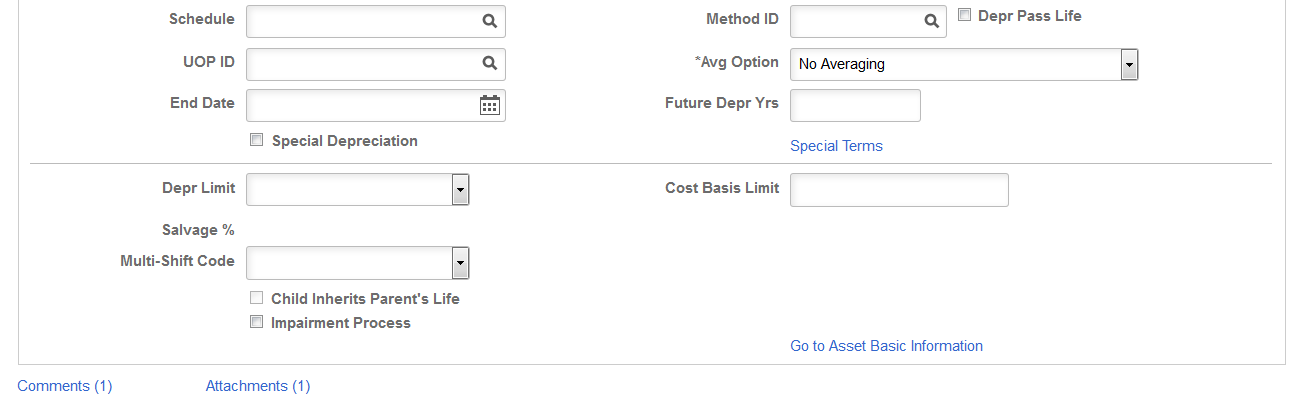
Note: Using the flat rate depreciation method causes any depreciation to be posted to the end of the calendar. If this is not the intention, you must enter a low limit of .01 when you first select the depreciation method in the Asset Book Definition component for the asset. If you have not already done this, update the Depreciation Method field by selecting Flat Rate and entering .01 in the Low Limit field that appears.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Calculation Type |
Select Remaining Value to deduct any accumulated depreciation from the cost basis and depreciate the remaining value over the remaining life of the asset. Most assets are depreciated using this option. Use Life-to-Date to calculate the difference between the depreciation allowed and the depreciation taken. Typically, you use life-to-date calculations when there is a change in accounting principle, such as depreciation method. Changes of this type require an adjustment for the differences in accumulated depreciation to date. For example, if you took 20,000 USD depreciation over a two year period but the amount allowed was 24,000 USD, the difference of 4,000 USD would be expensed as an adjustment to accumulated depreciation in the current period. |
Low Value |
Select to identify assets with costs below a certain level for special depreciation processing. This is a requirement for Germany. |
Useful Life |
Enter the number of periods. This is used to perform the depreciation calculations for the financial books. |
End Depr Date (end depreciation date) |
Enter a value to have depreciation end at a particular time. At the ending depreciation date, the remaining asset basis is taken in depreciation and the asset is fully reserved. |
Future Depr Yrs (future depreciation years) |
Asset Management calculates and stores depreciation until the end of the asset's life. However, for optimal processing performance and greater table efficiency, you can specify a fixed number of years for which depreciation is calculated and stored. Note: It is strongly recommended that you use the Future Depreciation Years option for group assets and for a large number of assets. |
Special Depreciation or Special Terms |
If you are working in a global environment and want to use special depreciation terms to meet specific country requirements, select the Special Depreciationcheck box and click Special Terms to open the Depreciation Method Information page, where you can select global attributes for depreciation. |
Depr Limit (depreciation limit code) |
Depreciation limits generally apply to tax books, but they can also be used for financial books. The tableset delivered with Asset Management contains depreciation limits currently dictated by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service for luxury automobiles. |
Cost Basis Limit |
Enter the limit on the depreciable basis of this asset. If the actual cost of an asset is greater than its depreciable basis, the difference produces a gain when the asset is retired. |
Salvage % (salvage percentage) and Salvage Value |
Enter the residual value of the asset subtracted from the cost to determine the depreciable basis used in depreciation calculations. You can enter it either as a flat rate or as a salvage percentage (a percentage of the asset's total cost). If you use a salvage percentage, the system recalculates the salvage value as you add additional costs for the asset. |
(DEU) Multi-Shift Code |
Enter rates by which depreciation should be increased based on the number of production shifts an asset is used. |
Threshold ID |
If you want to modify an existing asset to use the capitalization threshold by book method, select the Threshold ID to use as the default value for assets within the selected book. This field is available for editing only when:
|
Child Inherits Parent's Life |
Select if the child asset inherits the parents remaining life. When you use parent-child component assets, all child assets have their own cost basis and depreciation attributes that are independent of the parent asset. Because the child's asset life may differ from the life of the parent asset, you may need to specify that a new child asset of a parent asset inherit the remaining life of the parent asset. |
Impairment Process |
Select to make an asset available for impairment processing. |
Comments |
Click the Comments link to access the Book Depreciation - Comments page and view or add relevant supporting comments to an asset transaction. |
Attachments |
Click the Attachments link to access the Book Depreciation - Attachments page and view or add relevant supporting documents to an asset transaction. |
Book Depreciation - Comments Page
Use the Book Depreciation - Comments page (AM_COMMENTS_SEC) and view or add relevant supporting comments to an asset transaction.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Comment |
Enter comments for an asset. |
User ID, Name and Date/Time Stamp |
Displays the user ID, name, and date/time stamp related to the user who added the comment. You can edit the date/time stamp after saving the comment. |
Source |
Displays the transaction source for the asset, such as adjustment, transfer, and so forth. |
Book Depreciation - Attachments Page
Use the Book Depreciation - Attachments page (AM_ADD_ATTACH_SEC) to view or add relevant supporting documents to an asset transaction.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Add Attachment |
Click this button to attach files as supporting documentation for an asset. Supply a description of the file or files that you attach. |
File Name |
Displays the attached file. Click the file-link to access the file. |
Description |
Displays a description of the file attachment when one was provided by the user. |
User, Name, and Date/Time Stamp |
Displays the user ID, name, and date/time stamp related to the user who added the attachment. |
Use the Depreciation Method Information page (ASSET_DEPR_DETAILS) to set special depreciation terms and select an accounting method for them.
These are commonly used to meet depreciation requirements for specific countries.
Navigation:
Select the Special Depreciation check box and then click the Special Terms link on the Book - Depreciation page.
Select one of the following accounting method options:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Allowance |
Special depreciation amounts are not booked with the standard depreciation amounts. Journal entries are generated that include only the standard depreciation. PeopleSoft Asset Management does not support automatic generation of journal entries for the special depreciation allowance accounting method. You may need to run two reports—the Reserve for Special Depreciation report and the Reversal for Special Depreciation report—and then generate the journal entries manually into the General Ledger system. |
Expense |
Total amounts of special depreciation and standard depreciation are booked and journal entries are generated that include the total of the standard and special depreciation amounts. |
Reserve |
Special depreciation amounts are not booked with the standard depreciation amounts. Journal entries are generated that include only the standard depreciation. PeopleSoft Asset Management does not support automatic generation of journal entries for the special depreciation reserve accounting method. You may need to run two reports—the Reserve for Special Depreciation report and the Reversal for Special Depreciation report—and then generate the journal entries manually into PeopleSoft General Ledger. |
Additional fields are provided to comply with the depreciation methods used in countries other than the U.S. If your current depreciation method requires these fields, enter Special Terms, Accel Terms (accelerated terms), Initial Terms, andIncr Rate (increased rate).
When you use additional terms, they affect depreciation calculations as follows:
|
Term |
Depreciation |
|---|---|
|
Special |
Depreciation × Rate |
|
Accelerated |
Depreciation × Rate |
|
Initial |
Cost × Rate |
|
Increase |
Depreciation × Rate |
The Year of Change field is available only if the depreciation method is Japan-Change DB to SL. Enter the year of the change in calculation methods.
Use the Book - Tax page (ASSET_BOOK_02) to specify property type, tax depreciation criteria, and tax credit options.
If the fields on this page are not available, the book was not set up as a tax book on the Business Unit/Book Definition page.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Book - Tax page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
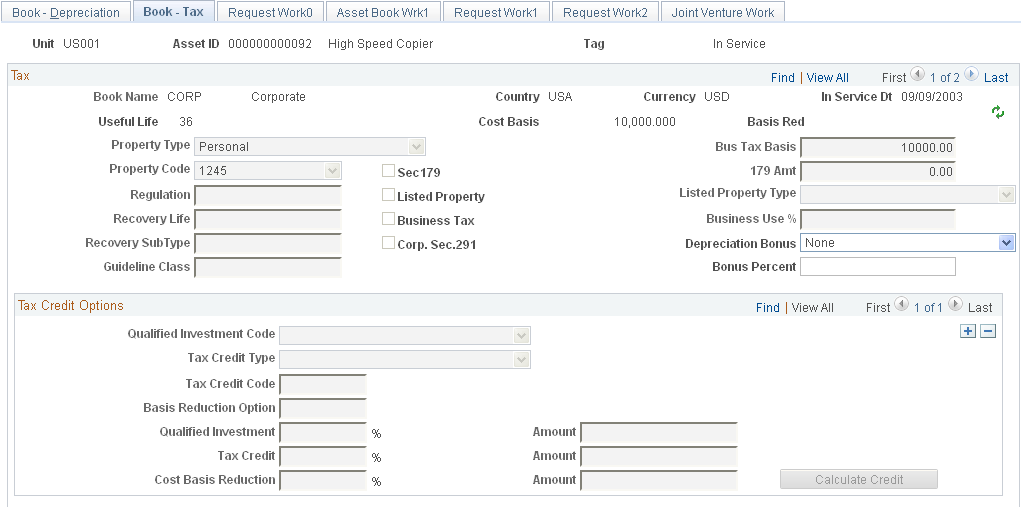
Tax
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Property Type and Property Code |
These fields determine the amount of gain treated as ordinary income upon the disposition of the asset. |
Regulation |
Regulation is an indication of the tax system that you elect. Each tax system has an effective date that is validated against the asset's placed-in-service date. Select a regulation to identify the depreciation system elected for this asset. Options are:
|
Recovery Life and Recovery SubType |
For reporting purposes, you can further classify the asset by specifying the recovery life (expressed in years) and the recovery subtype. For example, the code for a 15-year life might be 15 and the code for low-income housing might be LI. |
Guideline Class |
All current U.S. classifications are set up in the Tax Class table in the delivered tableset |
Section 179 |
You can elect to recover all or part of the cost of certain qualifying property, up to a limit, by deducting it in the year you place the property in service. You can elect the section 179 deduction instead of recovering the cost by taking depreciation deductions. |
Listed Property |
Select the Listed Property check box to define the asset as listed property and select its Listed Property Type. Listed properties are certain kinds of assets that are conducive to mixed business and personal use, such as:
|
(FRA) Business Tax |
Select to indicate that the business tax is applicable. This option enables you to calculate and report a business tax assessed on the gross value of fixed assets. This is a requirement in some countries. |
Corp. Sec. 291 (corporation section 291) |
Select if the organization is a corporation. This check box must be selected if the company is a corporation in order for the Tax Retirement Capital Gains report (AMTX3210) to accurately reflect the correct Sec. 1231/Ordinary gains. |
(USA) Depreciation Bonus |
Select to indicate the specific depreciation bonus definition if the asset qualifies for depreciation bonus treatment. For descriptions of the PeopleSoft delivered field options: See PeopleSoft Asset Lifecycle Management Fundamentals, Establishing Asset Processing, Specifying Tax Attributes in a Profile. You can also define your own depreciation bonus options for selection in this field using the Depreciation Bonus Info page. See PeopleSoft Asset Lifecycle Management Fundamentals, Setting Up Depreciation Processing, Setting Up Depreciation Bonus Information |
(USA) Bonus Percent |
Enter the percent amount of the depreciation bonus to be applied to the books for this profile. The amount depends on the legislation provisions for bonus amount, acquisition date and in-service date of the asset as well as state or local application of the depreciation allowance. |
Tax Credits Options
The rate and amount of the tax credit are based on federal tax law and determined by the qualified investment code, tax credit type, tax credit code, and the basis reduction option in Asset Management.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Basis Red (basis reduction) |
Displays the total reduction of the cost basis, if any. The total reduction amount is updated each time that you change tax credit information. |
Qualified Investment Code |
Corresponds to the option you enter in the Tax field. |
Tax Credit Type |
Although the investment tax credit was essentially repealed on December 31, 1985, certain business incentive credits can still be taken. Currently, you can specify the following credits:
|
Tax Credit Code |
Enter a value in this field to further define the tax credit—for example, a 20 percent rehabilitation tax credit is available for certified historic buildings. |
Basis Reduction Option |
Some credits require a corresponding reduction in the asset's cost basis. In this field, specify whether the basis needs to be reduced. Options are:
|
Asset Management calculates the percentage and computation amount based on the following calculations: