Pegging in PeopleSoft Inventory
A material stock request in PeopleSoft Inventory can be used as the following order types for pegging:
Stock Request (demand order type): material stock requests (MSR) shipping from an inventory business unit.
Transfer Demand (demand order type): interunit transfers, a type of MSR, shipping from one inventory business unit to another inventory business unit.
Transfer Supply (supply order type): interunit transfers, shipping from the sending inventory business unit is supply to the receiving inventory business unit.
Note: You can only peg a demand-side material stock request when the line is in an unfulfilled state and the item is a soft-reserve item.
You can access peg chains and create new peg chains by accessing the Pegging Workbench or view peg chains by accessing the Pegging Inquiry page from other PeopleSoft Inventory pages, including:
Create/Update Stock Requests component
Maintain Stock Requests component
Shortage Workbench
Stock Request inquiry page
Fulfillment Status inquiry page
Interunit Receipts page
Note: The link to the Pegging Workbench is only visible if the User Security page gives access to the user ID.
You can peg a material stock request in PeopleSoft Inventory as the demand side of a peg. The stock request could be shipping to a customer, department, or another inventory business unit (demand-side interunit transfer).
This process flow diagram illustrates pegging material stock requests (demand) to an incoming interunit transfers (supply). The sequence of events in the process flow is explained below the diagram:

The sequence of events in the process flow when pegging an MSR to another MSR is:
Peg is created using the Pegging Workbench. A material stock request or an interunit transfer (demand-side) can be pegged to an interunit transfer (supply-side) with stock arriving in the business unit of the demand-side orders.
The supply-side interunit transfer is shipped from the sending business unit.
The supply-side interunit transfer is putaway in the destination business unit. During putaway, the stock is soft-reserved or optionally allocated to the outgoing material stock requests based on your setting in the pegging setup pages. In the IN_PEGGING table, if the pegged quantity (QTY_PEGGED field) is equal to the putaway pegged quantity (QTY_COMPLETE field) then the peg status in this table is updated to complete. If either the demand or supply order has no more open peg quantity, then the peg status on the order itself is also updated to complete.
If the notification framework has been defined for the Message Dashboard, then a notification is sent to the owner of the peg when putaway is complete.
The material stock request (demand-side) is fulfilled and shipped to the customer, department, or another inventory business unit.
This process flow diagram illustrates pegging material stock requests to a requisition or purchase order. The sequence of events in the process flow is explained below the diagram:
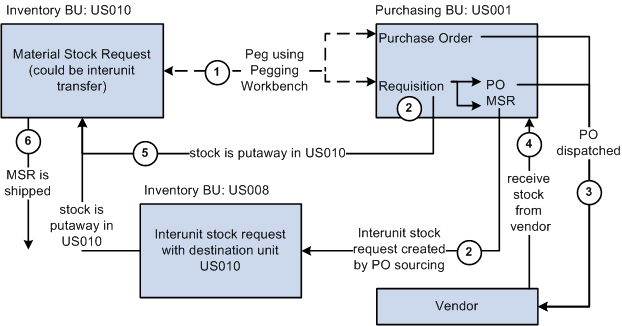
The sequence of events in the process flow when pegging an MSR to a requisition or purchase order is:
Peg is created using the Pegging Workbench. A material stock request can be pegged to a requisition or purchase order.
The requisition goes through the PO sourcing module and is sourced to an interunit stock request or a purchase order or both. The interunit stock request is created in the sending inventory business unit and is pegged to the MSR.
The purchase order is dispatched to the supplier.
The supplier ships the stock and it is received into the Purchasing business unit. If the notification framework has been defined for the Message Dashboard, then a notification is sent to the owner of the peg when stock is received into the Purchasing business unit.
The stock from the supplier or the sending inventory business unit is putaway in the inventory business unit. During putaway, the stock is soft-reserved or optionally allocated to the outgoing material stock requests based on your setting in the pegging setup pages. In the IN_PEGGING table, if the pegged quantity (QTY_PEGGED field) is equal to the putaway pegged quantity (QTY_COMPLETE field) then the peg status in this table is updated to complete. If either the demand or supply order has no more open peg quantity, then the peg status on the order itself is also updated to complete.
If the notification framework has been defined for the Message Dashboard, then a notification is sent to the owner of the peg when the stock completes putaway in the Inventory business unit.
The material stock request (demand-side) is fulfilled and shipped to the customer, department, or another inventory business unit.
This process flow diagram illustrates pegging an MSR to a production ID in PeopleSoft Manufacturing. The sequence of events in the process flow is explained below the diagram:

The sequence of events in the process flow when pegging an MSR to a production ID is:
Peg is created using the Pegging Workbench. A material stock request (demand) can be pegged to a production ID when the Manufacturing business unit is the same as the Ship From Inventory business unit. You can only peg to the primary output of a production ID.
The production is completed and the output placed in the inventory business unit.
During putaway, the stock is soft-reserved or optionally allocated to the outgoing material stock requests based on your setting in the pegging setup pages. Once the production order is closed the peg status is changed to complete on both the demand and supply transactions.
If the notification framework has been defined for the Message Dashboard, then a notification is sent to the owner of the peg when the stock completes putaway in the Inventory business unit.
The material stock request (demand-side) is fulfilled and shipped to the customer, department, or another inventory business unit.
Pegging links the stock coming into the PeopleSoft Inventory business unit to the outgoing orders. This peg prevents the incoming stock from being reserved or allocated to another order. For slow-moving items or customized orders, pegging enables you to keep inventory levels low and still deliver product efficiently to a customer. Pegging can also insure that customers get stock from the same lot or at a special cost.
Pegged supply can be received into a PeopleSoft Inventory business unit from an interunit transfer, a receipt from PeopleSoft Purchasing, or a completion from PeopleSoft Manufacturing. When the supply is received into the inventory business unit, it can be soft-reserved or hard-allocated to the demand line so that no other order can take the material. If the supply is received within the pegging lead days for the outgoing order (demand), then the stock can be placed in a default pegging putaway location so that it is easily found and shipped. In addition, the demand information is printed on the putaway plan.
When the pegged demand line is ready to be picked, the Order Release process attempts to pick from the default pegging putaway location first (unless the line is already allocated). If there is not enough stock in the default location, the Order Release process picks the available stock and then picks the remaining quantity requested from the material storage locations selected by the standard picking method.
Load Staged Items Process
After the items slated for putaway have been inserted into the staging interface tables (STAGED_INF_INV and STGCOST_INF_INV), launch the Load Staged Items process to insert the items into the putaway staging tables (STAGED_ITEM_INV and STAGED_COST_INV). If the supply being putaway is pegged to a demand, then the Load Staged Items process associates the staged putaway to a specific demand and looks for a putaway location by:
Placing the stock in the material storage location specified on the putaway transaction or input by the user online.
If no location is specified on the putaway transaction or online, then the system determines if the pegged order (outgoing demand) is scheduled to ship within the pegging lead days window, if so the pegged supply quantity is received (putaway) into the default pegging location specified. If the pegged order is not within the pegging lead days window, the pegged supply quantity is received into the standard material storage location determined by the putaway processes.
If a default pegging putaway location is needed, the Load Staged Items process looks to the Default Putaway Locations page for a default pegging location defined by business unit and item ID. If none is found, the process looks to the Default Pegging Putaway Location Details page for a pegging location defined by inventory business unit.
One putaway (supply transaction) can be pegged to multiple demand transactions. If a partial receipt of the supply transaction is putaway, then the Load Stage Items process uses the Final Sort Option on the Setup Fulfillment component to determine how the incoming stock is applied to the demand transactions. For example, assume a purchase order with 100 units in total is pegged to one sales order (40 units pegged) and one material stock request (50 units pegged). A partial receipt of 30 units is received and putaway in the inventory business unit. The Load Staged Items process associates the staged putaway to a specific demand. In this case, the process determines how to associate the 30 units by using the Final Sort Option to prioritize the demand transactions.
Directed Putaway
If directed putaway is enabled for the inventory business unit, then the default pegging location is used for putaway of pegged supply following the same rules stated above for the Load Staged Items process. Capacity checking is ignored when placing stock in the default pegging location because it is assumed the shipment will occur in a short time frame. Directed putaway can be launched from a link on an online page. The following pages use default pegging locations during direct putaway:
Interunit and RMA Receiving component. In addition, when receiving interunit transfers that are pegged supply, the InterUnit and RMA Receiving - Receipt Line page displays a link to the Pegging Inquiry component.
Review Plan page
Managing Receipts page in PeopleSoft eProcurement
Maintain Receipts component in PeopleSoft Purchasing
Record Completions and Scrap in PeopleSoft Manufacturing
Complete Putaway Process
The Complete Putaway process is the final stage in inventory putaway that updates the available quantity and inbound cost in the appropriate system tables. In addition, for pegged items, it can reserve or allocate the putaway quantity to an outgoing demand (materials stock request, interunit transfer, sales order, or work order). The Complete Putaway process performs a soft-reserve or hard-allocation based on your setting in the Pegging Setup page or the Pegging Item Setup page.
Once stock has been putaway in the inventory business unit, the Complete Putaway process:
Updates the putaway quantity (QTY_COMPLETE) in the IN_PEGGING record.
If all the pegged quantity has been received and putaway (QTY_COMPLETE=QTY_PEGGED), sets the peg status to complete in the IN_PEGGING record and in the supply and demand transactions.
If the notification framework has been defined for the Message Dashboard, sends a notification to the owner of the peg when putaway is complete.
Reservations Processing
Pegged quantities can only exist in an unfulfilled demand line and are not moved to the releasable state until the peg is at least partially received. When the pegged supply is received and putaway in the inventory business unit, the peg status is changed to complete; enabling the demand line to be picked up by the Reserve Materials process and moved downstream. Keep in mind that the formerly-pegged quantity is reserved or allocated by the Complete Putaway process when the supply is putaway. Partial receipts do not set the peg status to complete.
When a demand line has both pegged and unpegged quantities, then the reservations process only attempts to reserve the unpegged portion of a demand line. For example, if a demand line has a total quantity of 10 units, and 4 are pegged, then the Reserve Materials process attempts to reserve the 6 unpegged units based on the reservation rules. If the unpegged portion of a demand line can be reserved and the peg portion is not yet complete, then the pegged portion is backordered and unpegged portion is reserved and set to releasable. The backorder rules determine if the pegged portion should be backordered or canceled. If a backorder is created, then the peg chain is updated to peg the backorder line to the incoming supply. When the supply comes in, the backorder line is fulfilled.
Picking and Shipping
The Order Release process sets the demand lines to the released fulfillment state for picking and generates the pick plan. For demand lines with a pegged quantity that was reserved during the Complete Putaway process, the Order Release process can now allocate stock from a specific material storage location. Allocation is optional. If you choose to create an allocation, the Order Release process attempts to find stock to allocate to a pegged quantity in:
The default pegging location defined on the Default Putaway Locations page for the inventory business unit and item ID combination.
If no location is specified on the Default Putaway Locations page or no stock is available in the location, then the system looks to the Default Pegging Putaway Location Details page to determine if a default pegging location has been specified for the inventory business unit.
If there is no default pegging location or no stock available in the location, then the system uses the picking method specified on the Order Release process page.
Keep in mind that pegged quantities that were allocated during the Complete Putaway process will keep that allocation when released for picking.
The system can ship order from the unfulfilled state using the Fulfillment Workbench, Front End Shipping process page, Shipping Request process page, the Front-End Shipping transaction, or the Shipping Transaction. These processes do not pick up and ship from the unfulfilled state when the demand line is fully or partially pegged (that is, the peg status is not complete).