(DEU) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet German Requirements
This topic provides an overview of commonly used German depreciation methods.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
UD_METHOD_DEFN |
Create a user-defined Staffel depreciation method. |
|
|
RUN_AMRETFDA |
Identify run control parameters to automatically retire fully depreciated assets. |
|
|
DEPR_CAP_LIMIT |
Specify asset value minimums and associate warning or error actions with assets whose values fall below those limits. |
|
|
DEPR_TERMS_DEFN |
Define special depreciation terms for accelerated depreciation and associate the terms at the asset or book level. |
|
|
Load History Report Table |
LOAD_AM_HIST_TBL |
Run one of two SQR processes that load asset data into tables where it can be used for reports. The AMLDDPHI.SQR process loads depreciation history data into a table where it can be used to run the Depreciation History reports. The AMASHIST.SQR process loads asset history data into a table where it can be used by Asset History reports. Before running this process, you must run a process to load the depreciation report table. |
|
Asset History Reports |
RUN_AMDE1000 |
Run the Asset History Sheet reports that are attached to annual balance sheets and provide information about the history of an asset and its transactions. |
|
Reconciliation AP/AM (reconciliation accounts payable/asset management) |
RUN_AMDE5000 |
Run a report to help you reconcile accounts payable asset vouchers with Asset Management asset transaction information. |
The Staffel depreciation method is used for depreciating buildings in Germany and other countries. The Staffel depreciation method can be characterized as a "step straight line." For example, for a building with an acquisition cost of $100,000 and a life of 25 years, the depreciation calculation is 10 percent ($10,000) per year for years one through four, 5 percent ($5,000) per year for years five through seven, and 2.5 percent ($2,500) per year for years eight through twenty-five. These percentages vary due to legislation and the acquisition date of the building.
Three Staffel Depreciation Methods
There are three common Staffel depreciation methods.
The first Staffel method is for domestic buildings that are used by an organization for non-habitational purposes (for example, production buildings within Germany) and where the request to build was submitted to the local construction authorities after March 31, 1985, but before February 28, 1989:
|
Year |
Percentage |
|---|---|
|
Years 1–4 |
10% each year |
|
Years 5–7 |
5% each year |
|
Years 8–25 |
2.5% each year |
Non-habitational buildings that do not fulfill the preceding criteria are depreciated according to this criteria:
|
Year |
Percentage |
|---|---|
|
Years 1–8 |
5% each year |
|
Years 9–14 |
2.5% each year |
|
Years 15–50 |
1.25% each year |
Exceptions (all buildings that are used for habitational use and where the request to build was submitted to local construction authorities after February 28, 1989) are depreciated according to this criteria:
|
Year |
Percentage |
|---|---|
|
Years 1–4 |
7% each year |
|
Years 5–10 |
5% each year |
|
Years 11–16 |
2% each year |
|
Years 17–40 |
1.25% each year |
Depreciation periods in Germany are based on calendar years (January 1 – December 31). Because not all buildings are completed or purchased on January 1, if you activate an asset in a different month, you must prorate the depreciation for the first year, including the month of asset addition. For example, the depreciation amount for the first year is 36,000 EU if activated on January 1. But if the asset was activated on August 12, the depreciation amount for the first year is 15,000 EU, reflecting the months August through December.
Also, you must prorate the depreciation in the year of asset retirement (or sale) excluding the month in which it is retired. For example, the depreciation for the last year is 60,000 EU if the asset is retired at the end of the year. But if the asset was retired or sold on August 12, then the depreciation amount must be adjusted to 35,000 EU, reflecting the months January through July.
Creating a User-Defined Staffel Depreciation Method
To calculate depreciation by using the Staffel method, you can create a user-defined depreciation method for this formula. For example, in this case:
The asset basis of the building is $100,000 (EU).
The asset life is 25 years (300 periods).
The depreciation convention is AM (actual month).
The user-defined depreciation method name is Staffel.
To create a Staffel user-defined depreciation method, use the User-Defined Method page. Enter a description for the method ID.
You must define the following four variables to create a Staffel user-defined depreciation method:
This calculation results in the number of remaining periods in weeks:
This is the number of remaining periods in years.
This provides the number of periods for the year to be depreciated / total periods for the year, for example, 6 / 12 for the first year.
This result is:
Finally, to calculate the depreciation proration for the first year and the year of retirement, specify the following in the formula:
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports the German half-year convention. The German half-year convention differs from the U.S. half-year convention in that an asset takes a full year's depreciation if it was acquired in the first half of the year. This convention is delivered in the tables shipped, but you can modify it as necessary to suit a specific requirement.
Geometric digressive depreciation calculates depreciation up to three times the annual straight-line depreciation with a maximum of 30 percent of the asset cost per year. Asset Management supports this depreciation method by providing the declining balance with a Switch to Straight Line depreciation method option. To depreciate assets by using this method, select DB w/SL By Limit% on the Book-Tax page in the Asset Book Definition component, the Depreciation page in the Asset Profiles component, or the Depreciation Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component. Specify 300 as the declining balance percent and 30 as the limit percent.
Use the Capitalization Limits page (DEPR_CAP_LIMIT) to specify asset value minimums and associate warning or error actions with assets whose values fall below those limits.
Navigation:
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports low-value asset processing by providing a capitalization limit table where you can specify asset value minimums and associate warning or error actions with assets whose values fall below those limits. Additionally, you can set the limit at which an asset is marked as a low-value asset.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Capitalization Limits page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
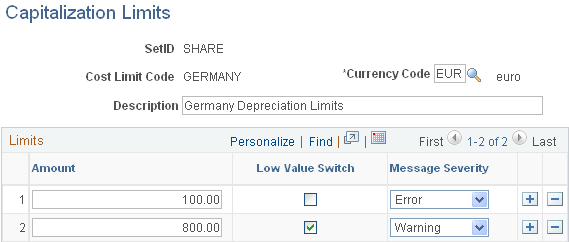
After you have set up the necessary capitalization limits, select Table Lim (table limit) and the correct code as the capitalization limit method on the Business Unit/Book Definition page in the Establish Business Units - Asset Management Definition component.
When you add assets to that business unit and book combination, Asset Management checks the capitalization limits against the amounts that are stored by code in the capitalization limit table.
In Germany, assets marked as low value should be depreciated in one year.
PeopleSoft Asset Management provides the PROGWG asset profile that is defined with depreciation attributes that are appropriate for German low-value asset processing. These include depreciation using the straight-line method and a useful life of 12 periods. Also, Asset Management provides the German First Day Last Period depreciation convention that you can use to generate one accounting entry for the annual depreciation for a low-value asset.
Low-value assets can be retired in mass using the Auto-Retire feature to satisfy the requirement that low-value assets be fully depreciated and retired after the first year of service.
Use the Terms Definition page (DEPR_TERMS_DEFN) to define special depreciation terms for accelerated depreciation and associate the terms at the asset or book level.
Navigation:
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports special depreciation methods that are used in Germany, such as accelerated depreciation, by enabling you to define special terms and associate them at the asset and book level.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Terms Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
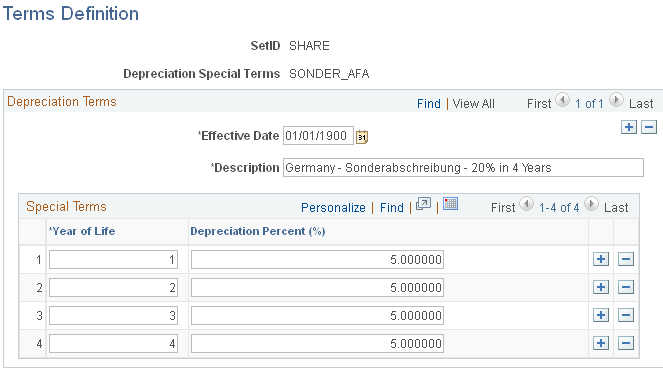
After you have defined special terms, associate them with an asset or book by selecting the Special Depreciation check box on the Depreciation Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component.