Understanding Electronic Data Collection
Electronic data collection enables you to:
Increase the accuracy of data entry.
Decrease the amount of time spent on data entry.
You can use the electronic data collection components to capture data from:
Bar code devices.
External feeds.
Direct data entry.
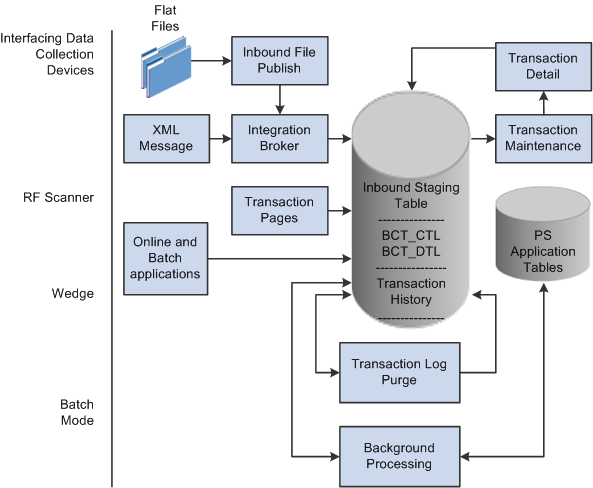
The following diagram shows the data flow for electronic data collection. Data from flat files or XML messages are placed in the inbound staging tables by the PeopleSoft Integration Broker system. Online or batch applications can also place data directly into the inbound staging tables. Background processes apply the data to the PeopleSoft production tables. Any errors are handles by the Transaction Maintenance component. The Purge process will delete all transactions with a status of Complete or Confirmed from the transaction log:
This image illustrates electronic data collection data flow.
The first step in designing an electronic data collection system is to select the data collection devices you will use to process bar code material movement transactions. PeopleSoft provides support for three bar code technologies:
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) systems are used when immediate access to the database is required. This technology requires RF terminals and controllers. RF data collection applications, developed in-house or by third-party suppliers, produce transactions that are passed to the PeopleSoft applications through PeopleSoft Integration Broker using XML messages.
Batch
Batch systems are used when real-time updates are not needed. Batch-oriented data collection applications, developed in-house or by a third-party supplier, produce transactions that are collected in an ASCII text file. The text file is loaded into the PeopleSoft system using the Inbound File Publish utility.
Keyboard Wedge
Keyboard wedges can be used when the person collecting the bar-coded information has access to a workstation running the PeopleSoft application. A wand or a laser gun connects to the keyboard wedge that inputs the bar-coded information directly into the transaction pages. The computer interprets information entered using the keyboard wedge in the same manner as information entered using the keyboard.