5.5.3 IDIH Manual Deployment on OpenStack
Perform the following procedure to perform IDIH Manual Deployment on OpenStack using IDIH VMDK image:
- Log in to OpenStack with valid credentials.
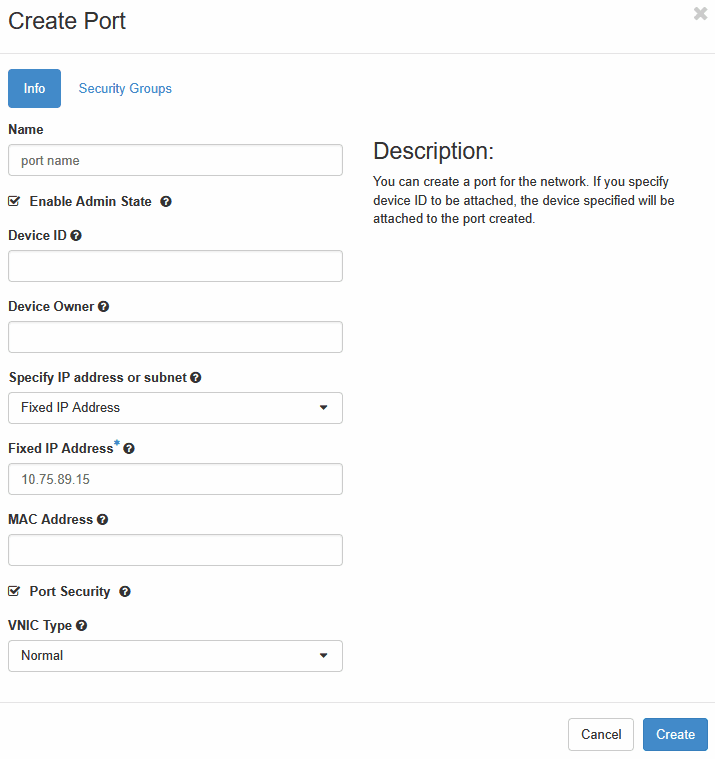
- To create a port:
Note:
The user must select either Fixed IP or Dynamic IP deployment based on the specific requirements. If Fixed IP deployment is selected, it is mandatory to create a port prior to launching an instance.- Navigate to Networks submenu, select
the network Name, select Port
and then select Create Port from the upper menu for
XMI, IMI, and XSI network planning and enter the below details:
- Name
- Select Fixed IP from the drop-down list
- Fixed IP Address
Figure 5-3 Create Port
- Navigate to Networks submenu, select
the network Name, select Port
and then select Create Port from the upper menu for
XMI, IMI, and XSI network planning and enter the below details:
- In the left navigation menu of the OpenStack main page, select Compute, then select Instances.
- On the Instances page, click Launch
Instance. In the Launch Instance dialog box,
enter the following information:
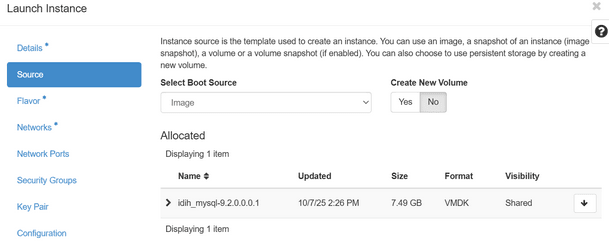
Figure 5-4 Launch Instance Dialog Box

- In the Details submenu, enter the
following details:
- The Project Name is automatically populated.
- Provide an instance name for the MySQL VM (for example
mysql-openstack) and click Next.
- In the Source submenu, enter the
following details:
- From the Select Boot Source drop-down list, select the required IDIH VMDK image.
- Ensure Create New Volume is set
to No to avoid creating a new volume and
click Next.
Figure 5-5 Source
- In the Flavor submenu, before proceeding
to the next step, verify that appropriate flavors are available and select
the recommended flavor for the MySQL VM based on the flavor table
below:
Table 5-11 VM Flavors
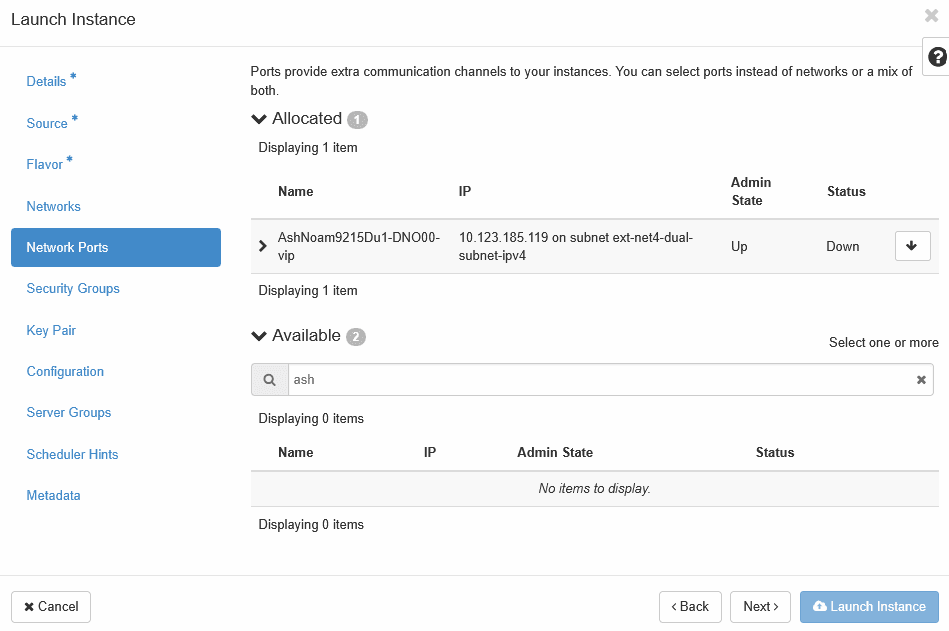
VNFC Type Image Name Flavor Name Minimum vCPUs Minimum RAM (GB) Minimum Disk (GB) EIDIH-KAFKA kafka-9.x.0.0.0.vmdk kafka-eidih 6 16 170 EIDIH-SERVICE service-9.x.0.0.0.vmdk service-eidih 6 16 120 EIDIH-DB mysql-9.x.0.0.0.vmdk mysql-eidih 6 16 220 - If the deployment type is Fixed IP: Navigate to Network Ports, select the newly created port as illustrated below. Refer to the 2nd step for creating a port.
- Select XMI, IMI, and XSI network ports for the VM.
Note:
XSI network port is applicable only for the Kafka VM.Figure 5-6 Network Port
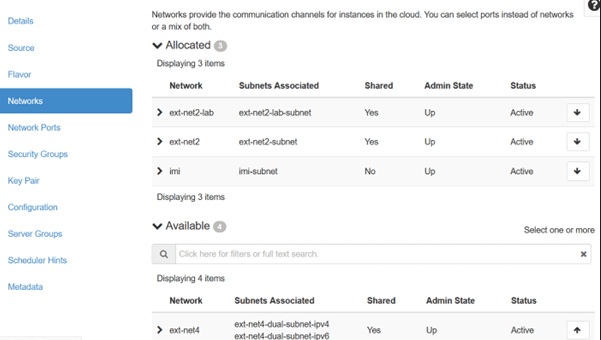
- If the deployment type is Dynamic IP: Navigate to
Networks submenu, select XMI, IMI, and XSI
networks for the VM.
Note:
XSI network is applicable only for the Kafka VM.Figure 5-7 Networks
- Click Launch Instance to create the MySQL VM.
- In the Details submenu, enter the
following details:
- Configure Virtual Machine
Note:
Establish an SSH connection to the VMs XMI IP address. If you are unable to access the XMI IP, proceed with the following steps to configure the XMI network.- Select the created MySQL VM from the instance list and navigate to the Console tab. Log in to the console using valid credentials to configure the XMI network interface.
- Run the following command to view available network
interfaces:
nmcli con showFigure 5-8 Retrieving Name of the XMI Interface
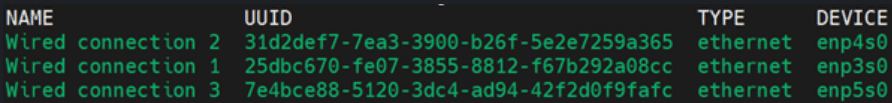
- Retrieve the XMI interface name from the above command, and
configure its metric to 1 to allow SSH connection to the XMI
IP.
nmcli con mod '<name of XMI interface>' ipv4.route-metric 1 nmcli con up '<name of XMI interface>'
- Repeat steps 2 to 4 to configure instances for the Kafka and Service VMs.
- After all the three VMs are created, verify network connectivity by pinging the XMI IP and IMI IP addresses of each VM.
Application Setup
- MySQL Setup
- Log in to the MySQL VM and navigate to the
/optdirectory. - Copy the manual_mysql_setup.sh script to
/optand provide the required permission. - Run the setup
script:
./manual_mysql_setup.sh - When prompted, enter the IMI IP address for the MySQL bind address.
- Upon script completion, MySQL will be configured successfully.
- Log in to the MySQL VM and navigate to the
- Kafka Setup
- Log in to the Kafka VM and navigate to the
/optfolder. - Ensure the Kafka installation script is present and executable.
- Run the following setup
script:
./manual_kafka_setup.sh - During execution, provide the Kafka IMI IP and XSI IP when prompted.
- Kafka and Kraft services will start on the specified IPs.
- (Optional) To use the Kafka XMI IP instead of the default Kafka
IMI IP for communication with DSR.
- Uncomment the following
property:
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL_PLAINTEXT://192.168.1.237:9092,INTERNAL_SSL://192.168.1.237:9093,EXTERNAL://[kafka_xmi]:9094 line in broker.properties file(path: /opt/kafka/config) and replace[kafka_xmi] with Kafka XMI IP - Comment the following property:
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL_PLAINTEXT://192.168.1.237:9092,INTERNAL_SSL://192.168.1.237:9093, EXTERNAL://10.196.84.46:9094 line. - Run the below command to restart Kraft and Kafka
services:
systemctl restart kafka
After running the health checks, Kafka is successfully set up on VM.
- Uncomment the following
property:
- Log in to the Kafka VM and navigate to the
- Service Setup
- Log in to the Service VM and navigate to the
/optdirectory. - Edit the
cnidih_VM.yamlfile. - Replace <REPLACE WITH SOAM VIP> with a valid active SOAM IP.
- Navigate to the Protrace section and set
the
NFCONFIG_CLIENT_ENABLEDproperty to true. - Save and exit.
- Run the service setup
script:
./manual_service_setup.sh - The script will prompt for several inputs during execution:
- Enter Service IMI IP, Service XMI IP, Kafka IMI IP, and
MySQL IMI IP.
Note:
For IPv6 setups, the above IPs must be entered in square brackets ( [] ).After these inputs are provided, the script will start the required services and proceed with the health check.
- Run the following command to verify if all the services
are running:
podman ps -aAccess the UI at:
https://<SERVICE XMI IP>/#/
This completes the setup for MySQL, Kafka, and Services. The IDIH deployment is now ready for use.
- Enter Service IMI IP, Service XMI IP, Kafka IMI IP, and
MySQL IMI IP.
- Log in to the Service VM and navigate to the