5.5.2 IDIH Manual Deployment on VMware
Virtual Machine Setup
Create three separate virtual machines (VMs) with the latest OL8 ISO image from the yum-oracle repository (for example, OL8.10 https://yum.oracle.com/ISOS/OracleLinux/OL8/u10/x86_64/OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso).
- Create three virtual machines with the following configuration:
- If the image is not already onboarded on VMware then user must upload it.
- To upload the image:
- From the main menu, navigate to
Libraries, Content
Libraries, Media and
Other, then click ADD and
add the following details:
- Catalog: Select ISO
- Name: Specify the name of the image you are uploading. Example: OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso.
- Click Select media to upload and upload the image. Wait for the image to be uploaded.
- From the main menu, navigate to
Libraries, Content
Libraries, Media and
Other, then click ADD and
add the following details:
- Login in to the VMware console and select the appropriate datacenter,
then navigate to Compute and Virtual
Machines, click NEW VM and enter
the following details:
- Name: Provide an appropriate name for each of the following 3 VMs (serviceVM, kafkaVM, and MySqlVM).
- Computer Name: Same as above
- Type: Select New.
- Power on: This field is automatically enabled.
- Guest OS family: Select Linux
- Guest OS: Select Oracle Linux 8 (64 bit).
- Boot image: Whichever image uploaded for OL8 ISO (example: OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso).
- Boot Firmware: Select BIOS.
- Enter Boot Setup: Do not enable.
- CPU: Enter 6,
Cores Per Socket: 1,
Number of sockets is automatically
populated based on the CPU value, Memory:
16, Storage: 120GB for Service VM,
similarly 170 GB for Kafka VM, and 220GB for MySql VM. Select
VM default policy.
Note:
Do not enable Use custom storage policy. - Networking
- Configure Kafka, MySql, and Service VMs:
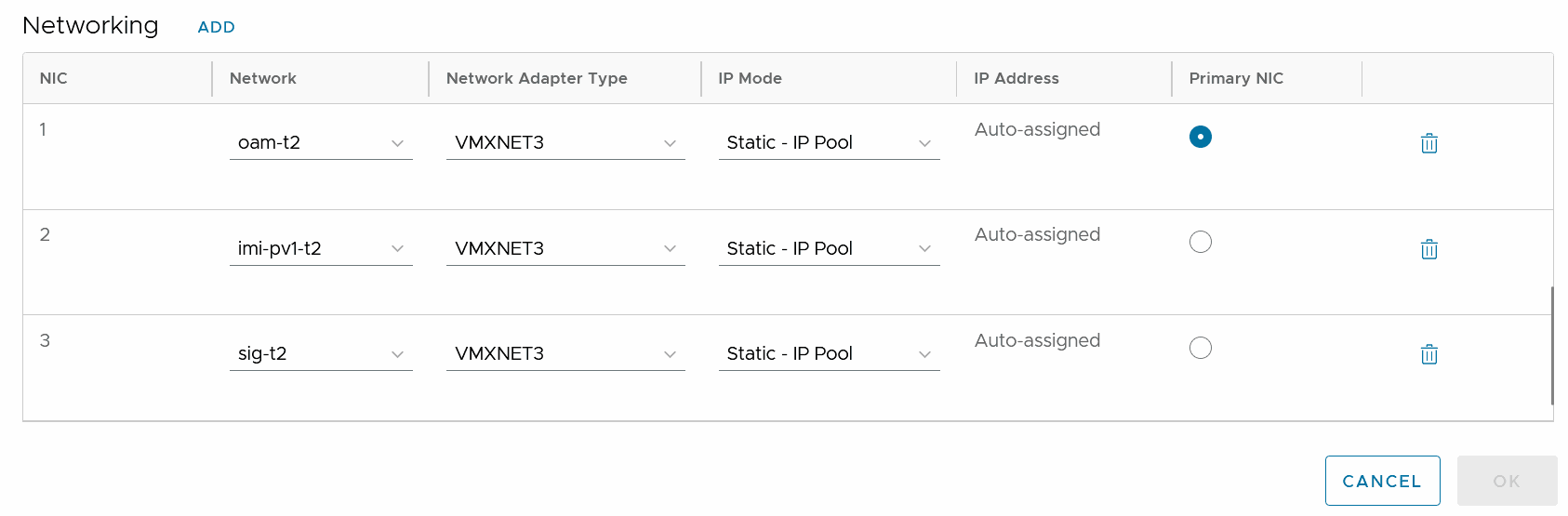
- Click Add beside Networking to add the configuration.
- Select the Network,
Network Adapter Type, and
IP Mode as per the image
shown below and click
OK.
Figure 5-1 Networking
Note:
Service and MySql requires XMI and IMI network, Kafka VM requires all the three interfaces (XMI, IMI, and XSI).
- Configure Kafka, MySql, and Service VMs:
- After creating the new VM, user must select the VM which is created
(wait for a few minutes to display on the homepage) and click LAUNCH
WEB CONSOLE from the upper menu bar then perform the following
steps to install the OS:
- Wait for the GUI to appear (wait for a few minutes) and select the language English and click Continue.
- In the Installation Summary page,
click Root Password under USER
SETTINGS and set changeme as the
password for the root user and click Done.
Note:
The user must click Done twice to set the root password. - Under the SYSTEM, click Installation Destination, verify if the VMWare Standard Disk is selected under the Local Standard Disk and under the Storage Configuration automatic must be selected by default and click Done.
- Now user will be back to the Installation
Summary page, click Begin
Installation.
Note:
The Begin Installation will take 15 to 20 minutes for the setup. - Select Reboot System, it will take a few minutes to restart.
- Click License Information and accept the license, click Done and then click FINISH CONFIIGURATION.
- Keep clicking Next until the About You page appears, here user may give any name and username for the system, avoid whitespaces, click Next and set the password changeme, and then click Next.
- Click Start Using Oracle Linux Server.
- Now user will get the VM GUI, click
Activities from the top left menu and open a
New Terminal and perform the following
configuration:
- Perform the following commands to configure all the
interfaces with these IPs:
Run the following command to log into the root user:
sudo su -Perform the following command to connect all the interfaces:nmcli device status #Get the disconnected interface names nmcli device connect <interface-name> #Connect the interfaces. Example: nmcli device connect ens192User must modify all the interfaces one by one with the proper assigned IP and CIDR block:nmcli connection modify <interface-name> +ipv4.address <ip-address>/<interface-CIDR-Block>" # Ex: nmcli connection modify ens192 +ipv4.address 10.75.190.130/26Note:
Do not obtain VM IPs from inside the VM using any networking command such as "ip route" or "hostname -I" as there could be stale IPs present. To retrieve the correct IPs assigned to the VM, select VM, Hardware, and NICs to get the IPs from VMware.Perform the following command to retrieve the modified interfaces:nmcli connection up <interface-name>" Example: nmcli connection up ens192
- Perform the following commands to configure all the
interfaces with these IPs:
- Now the VM is accessible from outside, perform the following
commands to expand the disk partition for the root:
cd / fuser -km /home umount -l /home lvremove /dev/ol/home lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/ol/root xfs_growfs /
- Installation Package Download and Extraction:
- Download the installation TAR file on any of the three VMs.
- Extract the TAR
file:
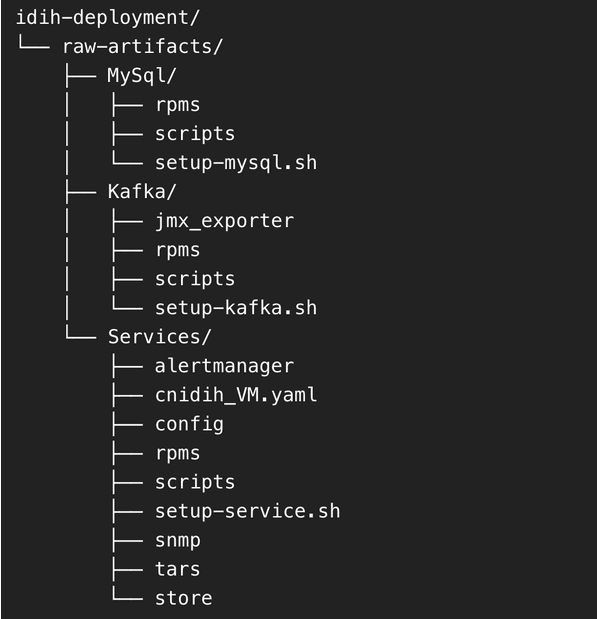
tar -xvf <tar-file-name>.tar - Directory Structure: After extraction, the directory
structure will be as follows:
Figure 5-2 Directory Structure
- Deployment of components across VMs:
- Distribute directories:
- MySQL directory to MySQL VM
- Kafka directory to Kafka VM
- Services directory to Service VM
- MySQL Setup
Perform the following procedure to set up MySQL on the MySQL VM:
- Access the MySQL VM:
- Log in and navigate to the MySQL directory.
- Run the MySQL Setup Script:
- Locate
setup-mysql.sh. - Run the below command to run the
script:
./setup-mysql.sh
- Locate
- Configuration During Execution: Enter the
IMI IP of the MySQL VM when prompted for the MySQL bind
address.
Completion: After the script is complete, MySQL will be successfully set up on the VM.
- Access the MySQL VM:
- Kafka Setup
- Access the Kafka VM: Log in and navigate to the Kafka directory.
- Run the Kafka Setup Script:
- Locate the setup-kafka.sh script
- Run the below command for the
script:
./setup-kafka.sh
- Configuration during execution
- When prompted, enter the Kafka IMI IP and Kafka XSI IP. when prompted by the script.
- Kafka and Kraft services will be initiated on the specified IPs.
After the successful health check is completed, Kafka will be successfully set up on VM.
- Optional step, only if you need to use Kafka XMI IP
instead of the default Kafka IMI IP for communication with
DSR.
- Uncomment:
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL_PLAINTEXT://192.168.1.237:9092,INTERNAL_SSL://192.168.1.237:9093,EXTERNAL://[kafka_xmi]:9094 line in broker.properties file(path: /opt/kafka/config) and replace[kafka_xmi] with Kafka XMI IP - Comment:
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL_PLAINTEXT://192.168.1.237:9092,INTERNAL_SSL://192.168.1.237:9093, EXTERNAL://10.196.84.46:9094 line. - Run the below commands to restart Kraft and
Kafka
services:
systemctl restart kafka
After successful execution of the health check, Kafka is successfully set up on VM.
- Uncomment:
- Service Setup
- Access the Service VM
- Navigate to the directory where the
setup-service.shscript is located. - Move the store Directory to the
/opt/path using the following command:mv store /opt/ - Edit the Docker-compose file:
- Navigate to the
Services/ directory. - Edit
cnidih_VM.yamlfile:Note:
Uncomment the below command if you are using IPv6 setup, ensure indentation of both the properties must be at same level.networks: cnidih-network: enable_ipv6: true external: true- <REPLACE WITH SOAM VIP> must be replaced with a valid active SOAM IP.
- Navigate to Protrace section and
enable the following property
NFCONFIG_CLIENT_ENABLEDto true. - Save and exit.
- Run the following command to uninstall the
libraries:
sudo yum remove -y slirp4netns dnsmasq criu containers-common fuse3-libs fuse-common fuse3 containernetworking-plugins fuse-overlayfs libnet podman podman-catatonit conmon shadow-utils-subid podman-plugins runc protobuf-c podman-gvproxy container-selinux libslirp podman-docker - Run the following command for the Service
Setup
Script:
./setup-service.sh
- Navigate to the
- Configuration during execution: The script will
prompt for several inputs during execution:
- Enter Service IMI IP, Service XMI IP, Kafka
IMI IP, and MySQL IMI IP.
Note:
For IPv6 setups, the above IPs must be entered in square brackets ( [] ).After these inputs are provided, the script will start the required services and proceed with the health check.
- Run the following command to verify if all
services are
running:
podman ps -aAccess the UI at:
https://<SERVICE XMI IP>/#/
Conclusion: This completes the setup for MySQL, Kafka, and Services. The deployment is now ready for use.
- Enter Service IMI IP, Service XMI IP, Kafka
IMI IP, and MySQL IMI IP.
- Distribute directories: