Usage Models
When looking at your requirements, you must understand how you intend to use Siebel Financial Services EAI’s integration capabilities. You need to determine how the integration will behave under different circumstances. In other words, in what way are you planning to use this integration? This is referred to as the usage model.
There are two basic usage models, real time and batch, as shown in the Siebel Financial Services Interfaces image in Design Decisions. Batch mode has a single mode, and real time has two modes, either tightly-coupled or loosely-coupled. To help you determine the appropriate usage model, ask yourself the following questions.
How do I plan to integrate Siebel Financial Services applications with other applications?
Do I want to do it in real-time or in batch mode?
If I want to do it in real-time, do I want the solution to be tightly-coupled or loosely-coupled?
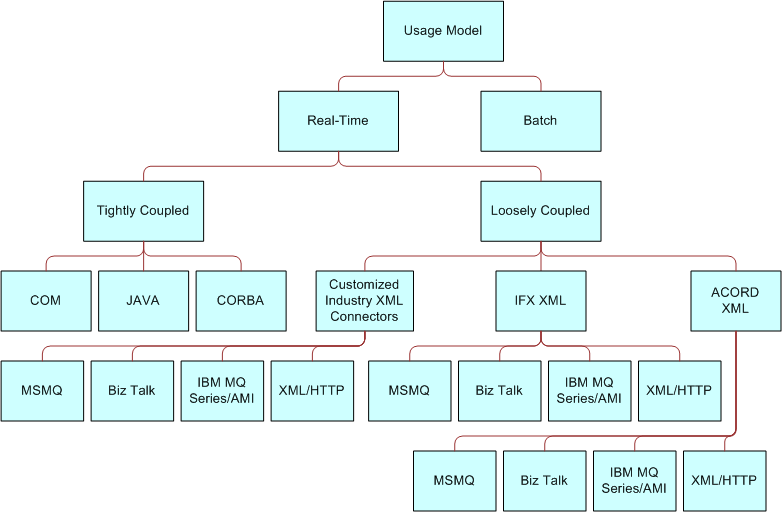
Real Time
With a real time model, you can choose to deploy Siebel Financial Services applications as a client or as a server. As a client, Siebel Financial Services applications access another program or initiate a transaction on an external system. Typical scenarios include:
-
Sending an insurance policy created from Siebel Financial Services applications to a Policy Management system and receiving the policy status in return.
-
Accessing a mainframe banking application to retrieve customer bank deposits in real time and display it within the Siebel user interface.
-
Sending claims to independent claims agents over corporate firewalls without compromising security.
-
Accessing an external rating engine system to calculate a quote and then displaying the information in the Siebel system.
As a server, Siebel Financial Services applications are accessed by an external program to query, insert, update, or delete data without any initiation from the Siebel system. Typical scenarios include:
-
An external EJB Web application accessing a Siebel Financial Services application to retrieve contact information.
-
Call center software extracting customer service request information from a Siebel Financial Services application.
Batch
Batch processing typically is used for periodic uploads or downloads of large amounts of information into the Siebel database. A typical batch scenario includes:
-
Uploading a batch of product catalog and item information into a Siebel Financial Services application from an external system or downloading a batch of all opportunities from Siebel Financial Services applications to another database.
-
Downloading all the new contact and accounts for that day from the Siebel application to an external Customer Information File (CIF).