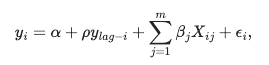空間ラグ・モデル
空間依存性の存在は、観測値が距離を介して相互に関連していることを示し、この依存性を含む空間ラグ・モデルの方がパフォーマンスが向上することが期待されます。 空間ラグ・モデルは、Spatial Autoregressive Model (SAR)とも呼ばれます。
SARモデルでは、ターゲット変数に対する空間依存性が考慮されます。つまり、リージョンのターゲット変数の値は、そのネイバーのターゲット変数に関連しています。
SARモデルでは、従属変数の空間ラグが線形方程式に含められます。 これにより、次の式に示すように、依存変数の空間ラグに関連付けられた余分なパラメータが生成されます。
方程式は、次のように表すことができます:
前述の方程式では、Wは標準化された空間加重マトリックスで、ρは空間自動受信係数と呼ばれます。
SpatialLagRegressorクラスには、隣接する観測間の関係を確立するspatial_weights_definitionパラメータの設定が必要です。 次の表に、SpatialLagRegressorクラスの主なメソッドを示します。
| メソッド | 説明 |
|---|---|
fit |
指定されたトレーニング・データからSpatialLagRegressorモデルをトレーニングします。 モデルには、ターゲット変数の空間ラグのパラメータが含まれます。
|
predict |
ターゲット変数の空間ラグに関連付けられたパラメータを含むトレーニング済パラメータを使用して、指定されたデータのターゲット変数を見積もります。 |
fit_predict |
トレーニング・データを使用して、fitおよびpredictメソッドを順番にコールします。
|
score |
指定されたデータのR平方統計を返します。 |
詳細は、「Oracle Spatial AI Python APIリファレンス」のSpatialLagRegressorクラスを参照してください。
次の例では、block_groups を使用します。 SpatialDataFrame spatial_weights_definitionパラメータを定義するSpatialLagRegressorクラスのインスタンスが作成されます。 次に、データを標準化するための前処理ステップを含む空間パイプラインを作成し、最後のステップで空間ラグ・モデルを適用します。
モデルは、トレーニング・セット(X_train)およびMEDIAN_INCOME列をターゲット変数として使用してトレーニングされます。 最後に、テスト・セット( X_test)を使用してpredictおよびscoreメソッドをコールし、ターゲット変数の値を推定し、モデルのR-Squareスコアをそれぞれ取得します。
from oraclesai.preprocessing import spatial_train_test_split
from oraclesai.weights import KNNWeightsDefinition
from oraclesai.regression import SpatialLagRegressor
from oraclesai.pipeline import SpatialPipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# Define features
X = block_groups[["MEDIAN_INCOME", "MEAN_AGE", "HOUSE_VALUE", "INTERNET", "geometry"]]
# Define training and test sets
X_train, X_test, _, _, _, _ = spatial_train_test_split(X, y="MEDIAN_INCOME", test_size=0.2, random_state=32)
# Create an instance of SpatialLagRegressor
spatial_lag_model = SpatialLagRegressor(spatial_weights_definition=KNNWeightsDefinition(k=5))
# Add the model in a Spatial Pipeline with a preprocessing step
spatial_lag_pipeline = SpatialPipeline([("scaler", StandardScaler()), ("spatial_lag", spatial_lag_model)])
# Train the model with MEDIAN_INCOME as the target variable
spatial_lag_pipeline.fit(X_train, "MEDIAN_INCOME")
# Print the predictions with the test set
spatial_lag_predictions_test = spatial_lag_pipeline.predict(X_test.drop(["MEDIAN_INCOME"])).flatten()
print(f"\n>> predictions (X_test):\n {spatial_lag_predictions_test[:10]}")
# Print the R-squared metric with the test set
spatial_lag_r2_score = spatial_lag_pipeline.score(X_test, y="MEDIAN_INCOME")
print(f"\n>> r2_score (X_test):\n {spatial_lag_r2_score}")プログラムは次の出力を生成します:
>> predictions (X_test):
[ 92285.13545208 100551.0381313 30910.61123168 45166.3218764
177515.68764358 44088.89962954 98205.35728383 27788.19879028
72553.17695035 24875.81828048]
>> r2_score (X_test):
0.6150829472253789