5.5.1 IDIH Deployment on KVM with RAW Images
Perform the following procedure to set up the VMs (Virtual Machine):
- Log in to KVM host machine.
- Navigate to a directory where enough space is available.
Refer the following table for flavors:
Table 5-11 IDIH Flavor Value
Flavor Name VCPUs RAM(GB) Root Disk(GB) Ephemeral Swap Disk kafka_flavor 6 16 170 0 0 Mysql-DB-DataNode 6 16 220 0 0 service_profile 6 16 120 0 0 - Create empty qcow2 image files for MySQL, Kafka, and services.
qemu-img create -f qcow2 idih-mysql.qcow2 220Gqemu-img create -f qcow2 idih-kafka.qcow2 170Gqemu-img create -f qcow2 idih-service.qcow2 120G
- Copy the
OracleLinux-R8-U9-x86_64-dvd.isofile to host machine. - Create MySQL VM, Kafka VM, and Service VM by running the following
commands on host
machine.
virt-install \ --name idih-mysql \ --ram 16384 \ --vcpus 6 \ --disk path=idih-mysql.qcow2,size=220,format=qcow2 \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant ol8.0 \ --network network=default \ --graphics none \ --location OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso \ --extra-args 'console=ttyS0' virt-install \ --name idih-kafka \ --ram 16384 \ --vcpus 6 \ --disk path=idih-kafka.qcow2,size=170,format=qcow2 \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant ol8.0 \ --network network=default \ --graphics none \ --location OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso \ --extra-args 'console=ttyS0' virt-install \ --name idih-service \ --ram 16384 \ --vcpus 6 \ --disk path=idih-service.qcow2,size=120,format=qcow2 \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant ol8.0 \ --network network=default \ --graphics none \ --location OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso \ --extra-args 'console=ttyS0'Note:
The installation process is interactive, and the user must complete all the steps marked with [ ! ] by selecting the options one at a time.Figure 5-1 Installation
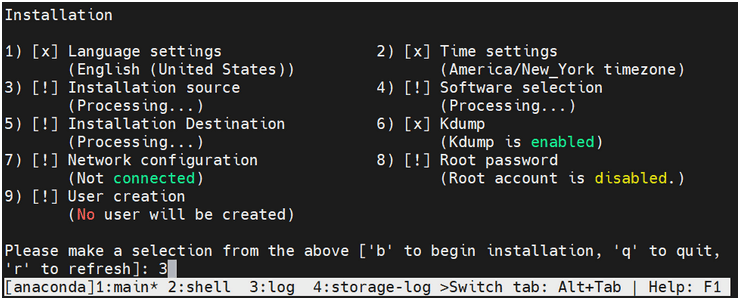
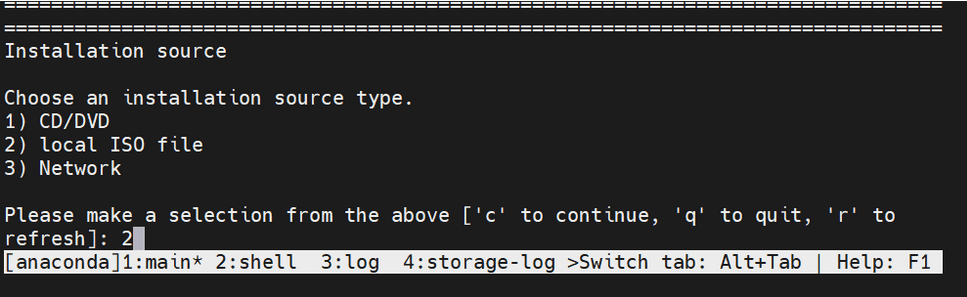
- Select a source type from the following installation sources:
- CD/DVD
- Local ISO file
- Network
Figure 5-2 Installation Source
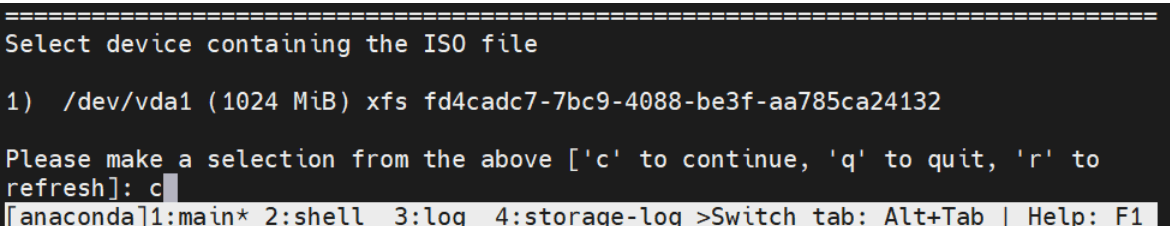
- Select a device containing the ISO file. After selection of ISO file,
the installation process initiates.
Figure 5-3 ISO File
- Wait for the processing to complete. Press "r" to
refresh and check if step 3 is completed before proceeding to step 4.
Figure 5-4 Installation process

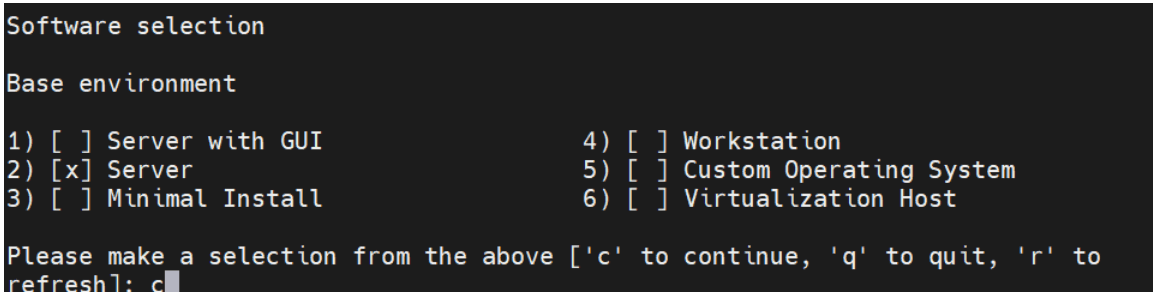
- Select a software from the following base environment:
- Server with GUI
- Server
- Minimal Install
- Workstation
- Custom Operating System
- Virtualization Host
Figure 5-5 Software Selection
- Select Additional Software for the selected
environment:
Figure 5-6 Additional Software
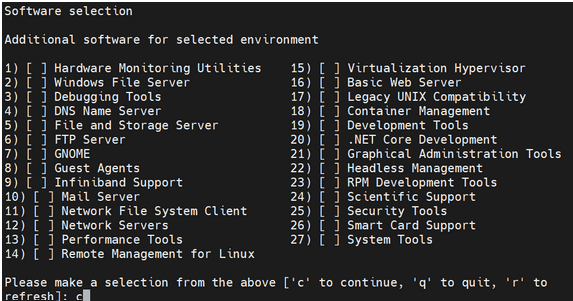
- Wait a moment for the processing to complete, then press "r" to refresh and confirm that step 4 is marked as complete.
Figure 5-7 Installation
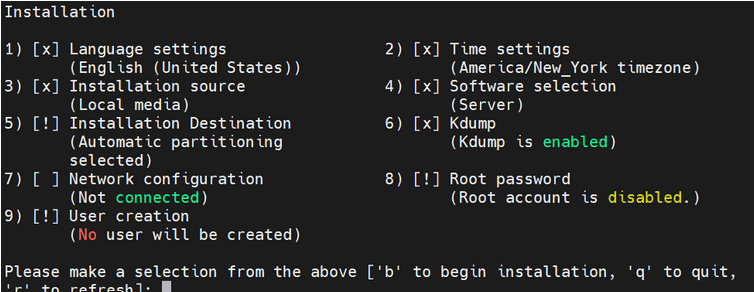
- Proceed with the next steps, and once all the steps are marked with
[x], press "b" to start the installation.
Figure 5-8 Installation

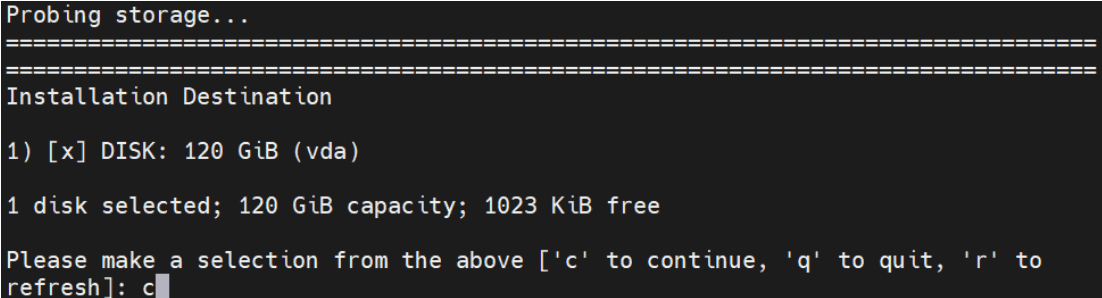
Installation Destination is selected during the probing storage.
Figure 5-9 Probing storage
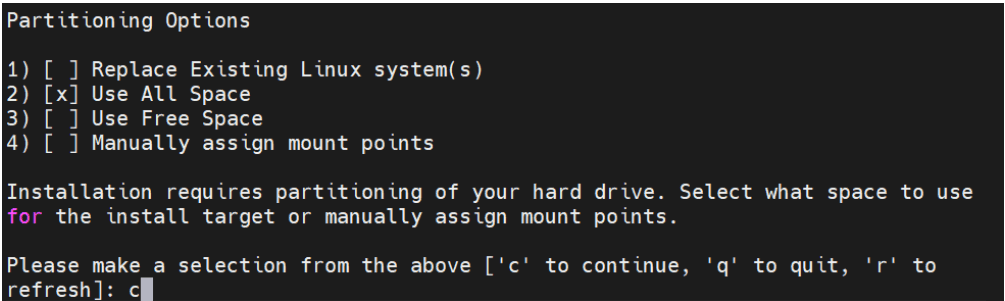
- For partitioning options, select the space to be used for the install
target or manually assign mount points.
Figure 5-10 Partitioning Options
- Select a Partition Scheme Configuration from the following options:
- Standard Partition
- LVM
- LVM Thin Provisioning
Figure 5-11 Partitioning Scheme Options
- Set a strong password for the root user and confirm.
Figure 5-12 Set password for root user
After selection of the password, the installation procedure initiates.
Figure 5-13 Begin Installation
Writing network configuration in progress.
Figure 5-14 Writing network configuration
- Press Enter Key to quit.
- User must add 3 network interfaces for each VM, xmi, imi, and xsi. Shut
down the VM and follow the following steps if you encounter a "No PCI
slots available" error while adding any interface.
Note:
This step is optional, user must add controller only if they encounter "No PCI slots available"error while adding an interface. - Run the following command to add the
controller:
virsh edit <vm-name> and add below controller after index=7 <controller type='pci' index='8' model='pcie-root-port'> <model name='pcie-root-port'/> <target chassis='8' port='0xf'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x01' function='0x7'/> </controller> - Turn on the VM after controller is added.
- Log in to the host machine with a valid username and password.
Figure 5-15 Login Page
After signing in, the system will automatically open the Overview page.
Figure 5-16 Overview
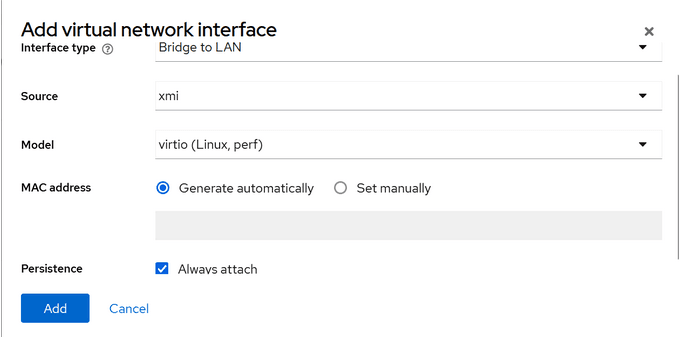
- Click Virtual machines and search for the
idih-mysqlVM. Go to Network interfaces section, click Add Network Interface, select value as shown in the following screenshot, and click Add.Figure 5-17 Add Virtual Network Interface
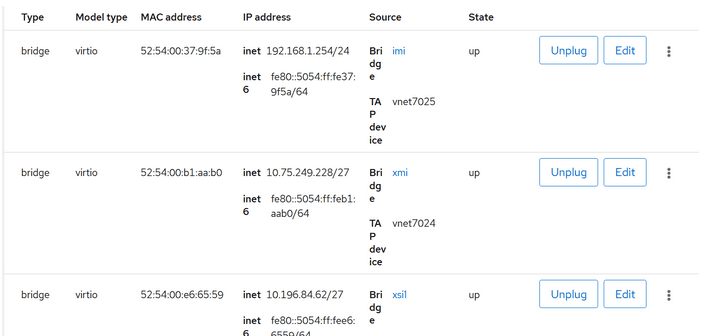
- Apply the same process to the IMI and XSI interfaces. The following
screenshot displays all the interfaces.
Figure 5-18 Interfaces
- Log in to the VM through CLI. You can change the hostname of the VM by
editing the following command. Provide a name of your
preference.
- vi /etc/hostname - Assign a valid IP address for all the three interfaces for the three VMs created.
- Run
ifconfigcommand and take a note of device names -enp1s0, enp7s0, and enp8s0. Here, enp1s0 represents xmi, enp7s0 represents imi, and enp8s0 represents xsi. - Run the following command, it will display the status as "disconnected"
for all the interfaces.
nmcli dev status - To assign an IP addresss to enp1s0, run the following
command:
If you get an error, then most likely the device is not up. You can bring it up by running the following command:nmcli con edit enp1s0
.nmcli dev up enp1s0 - After the device is up, re-run the following command. Prompt must be
visible as shown in the below screenshot:
nmcli con edit enp1s0. nmcliFigure 5-19 Prompt
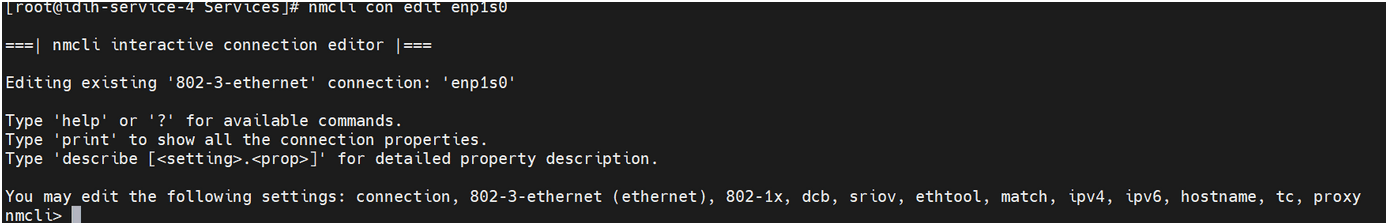
- Perform the following steps to assign the IP address to
enp1s0:- Set ipv4.addresses <ip-address>
- set ipv4.gateway <gateway-ip>
- Save and quit.
- You can type print in
nmcliprompt to verify the assigned IP. - Apply the same steps for enp7s0 and enp8s0 interfaces.
- Perform the following steps to assign the IP address to
- Ensure that
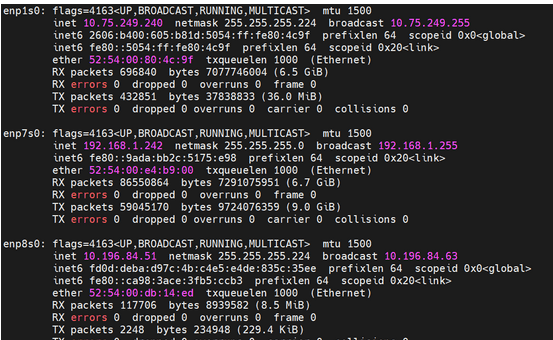
onboot=yesin the following/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp1s0ile. - Restart the VM and check if IP addresses are assigned with help of
ifconfig.Figure 5-20 ifconfig
- Repeat steps 8 to 13 for IDIH Kafka and IDIH Service VMs.
- Ensure that you are able to reach the IMI IPs of Mysql VM and Kafka VM from Service VM.
Installation Package Download and Extraction
The installation TAR file can be downloaded on any of the three VMs. After downloaded, extract (untar) the TAR file.
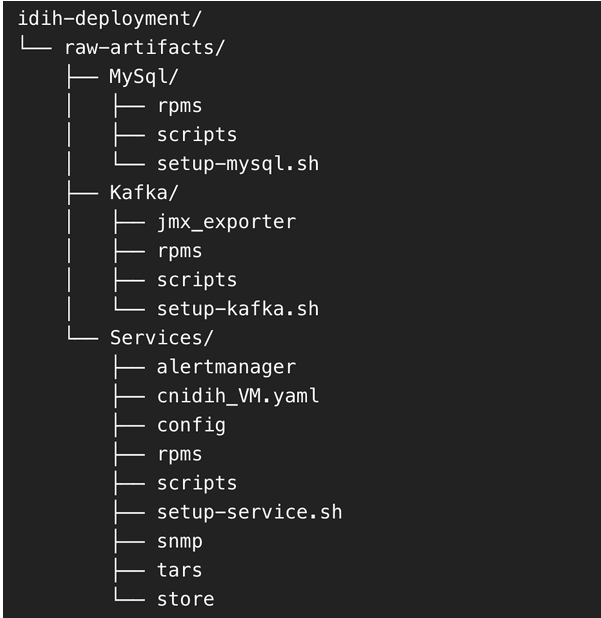
Directory Structure
After extraction, the directory structure will appear as follows:
Figure 5-21 Directory Structure
Deployment of Components Across VMs
Distribute the extracted directories to their respective VMs as follows:
- Copy the MySql directory to the MySQL VM at any preferred location.
- Copy the Kafka directory to the Kafka VM at any preferred location.
- Copy the Services directory to the Services VM at any preferred location.
MySQL Setup
Perform the following steps to set up MySQL on the MySQL VM:
- Access the MySQL VM:
- Log in and navigate to the MySQL directory.
- Run the MySQL Setup Script
- Locate
setup-mysql.sh. - Run the below command to run the script:
./setup-mysql.sh
- Locate
- Configuration During Execution: Enter the IMI IP of the
MySQL VM when prompted for the MySQL bind address.
Completion: After the script is complete, MySQL will be successfully set up on the VM.
Kafka Setup
Perform the following steps to set up Kafka on the Kafka VM:
- Access the Kafka VM: Log in and navigate to the Kafka directory.
- Run the Kafka Setup Script:
- Locate the setup-kafka.sh script
- Run the below command for the
script:
./setup-kafka.sh
- Configuration during execution:
- When prompted, enter the Kafka IMI IP and Kafka XSI IP. when prompted by the script.
- Kafka and Kraft services will be initiated on the specified IPs.
After the successful health check is completed, Kafka will be successfully set up on VM.
- Optional step, only if you need to use Kafka XMI IP instead of the
default Kafka IMI IP for communication with DSR.
- Uncomment:
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL_PLAINTEXT://192.168.1.237:9092,INTERNAL_SSL://192.168.1.237:9093,EXTERNAL://[kafka_xmi]:9094 line in broker.properties file(path: /opt/kafka/config) and replace[kafka_xmi] with Kafka XMI IP - Comment:
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL_PLAINTEXT://192.168.1.237:9092,INTERNAL_SSL://192.168.1.237:9093, EXTERNAL://10.196.84.46:9094 line. - Run the below commands to restart Kraft and Kafka
services:
systemctl restart kafka
After successful execution of the health check, Kafka is successfully set up on VM.
- Uncomment:
Service Setup
Perform the following steps to set up the services on the Service VM:
- Access the Service VM
- Navigate to the directory where the
setup-service.shscript is located. - Move the store Directory to the
/opt/path using the following command:mv store /opt/ - Edit the Docker-compose file:
- Navigate to the
Services/ directory. - Edit
cnidih_VM.yamlfile:- <REPLACE WITH SOAM VIP> must be replaced with a valid active SOAM IP.
- Navigate to Protrace section and enable the
following property
NFCONFIG_CLIENT_ENABLEDto True. - Save and exit.
- Run the following command for the Service Setup
Script:
./setup-service.sh
- Navigate to the
- Configuration during execution
- The script will prompt for several inputs during
execution:
- Enter Service IMI IP, Service XMI IP, Kafka IMI IP,
and MySQL IMI IP.
Note:
For IPv6 setups, the above IPs must be entered in square brackets ( [] ).After these inputs are provided, the script will start the required services and proceed with the health check.
- Run the following command to verify if all services
are
running:
podman ps -aAccess the UI at:
https://<SERVICE XMI IP>/#/
Conclusion: This completes the setup for MySQL, Kafka, and Services. The deployment is now ready for use.
- Enter Service IMI IP, Service XMI IP, Kafka IMI IP,
and MySQL IMI IP.
- The script will prompt for several inputs during
execution: