Understanding Workers in CRM
These topics discuss:
Workforce administration.
Options for creating workers.
Job information and effective dates.
Worker refers to anyone who performs work for an organization, including employees and contractors. Employees who are not part of the CRM workforce are considered CRM customers in the sense that they might call the help desk or HR help desk for assistance with problems. These topics focus on maintaining the information that is necessary to administer workers who are part of the CRM workforce and to assign them to field service and support tasks.
In CRM, workers are represented as Person business objects with a role type of Worker. The Person table (RD_PERSON) contains a record for each worker, with Person ID as the key field. Attributes that are specific to the person's role as a worker, such as employee status, job location, work function, and so forth, are stored in the Worker table (RB_WORKER).
Workers are not tracked as business contacts, although you can assign the Contact role to a worker.
See Person (<Role>) - Person: Primary Page.
Worker User Preferences and Security
Workers often have access to the CRM system to perform their functions. You can control worker access to data for system functions.
Worker Foundational Data
Worker foundational data is the control information (or prompt tables) from which you select when creating a worker. This data describes the organization infrastructure in which workers perform. You can maintain these tables in CRM, PeopleSoft Human Capital Management (PeopleSoft HCM), or a third-party system and move the data to CRM by implementing enterprise integration points (EIPs).
This is the worker foundational data that you must set up before creating workers:
Job codes.
Use the Job Code Table EIP to integrate with an HR system.
Department tables.
Use the Department Table EIP to integrate with an HR system.
Locations.
Competency information.
Worker competency information determines which workers are best qualified for assignment to a case or service order. Use the Competency Type, Rating Model, and Competency EIPs to integrate with an HR system.
Navigation
CRM provides two ways to access pages that you might use when setting up worker data: the left-hand menu and the Worker Administration Center. This topic lists the left-hand menu navigation.
After you set up the foundational data, you create workers in several ways:
Use the Person or Worker component to create and maintain worker records in CRM.
When you create a worker in the Worker component, you can create a new worker, copy data from an existing worker, or copy data from a template worker.
Integrate worker data with PeopleSoft HCM or a third-party HR system.
You implement the Personal Data, Workforce Data, and Person Competencies EIPs to populate the Person, Worker, and Worker Competency tables in the CRM system .
If you integrate with an HR system that maintains worker data, do not modify the personal data, job detail, and competencies that are entered in the human resource system. You should use the Worker pages in CRM to maintain only user profiles, notes, and worker data that is used by the CRM assignment engine.
Use quick create functionality.
The Quick Create component requires that you enter the minimum required information and is used to quickly enter data. Quick create of workers is also supported through HRHD 360-Degree View and Worker 360-Degree View.
Copying Existing and Template Workers
Creating a worker by copying an existing worker and creating a worker by copying a template worker are similar processes. The difference is in the way in which you identify the information to copy. When you copy an existing worker, you must search through the entire Worker table to identify the worker to copy; but when you copy a template worker, you can select the worker to copy from a drop-down list box that contains only workers who are designated as template workers.
Template workers are workers whose information represents a model to use when you create other workers. You can set up dummy workers, such as CSR Level 1, as template workers. You can also identify employees who are good template workers. For example, employee John Smith is a good template worker for CSR Level 1. You designate a worker as a template worker when you enter the job detail for the worker. Whether you designate real employees or set up dummy workers for templates is an implementation consideration.
When you create a worker by copying an existing worker or a template worker, all active worker roles are copies to the new worker. Current active job details for all assignments are copied, but not historical or future job details.
Worker Toolbar
The worker toolbar contains a Create from Current button that you can use to create a new worker from a worker whose data you are currently viewing and a Copy Data button that you can use to copy the worker's data to another worker.
A worker's job assignments and their relation to the organization can change over time. For example, a worker can be promoted, perform a different job, or change from employee to contingent worker status. Changes in a worker's job and organizational relationships are represented in the database by effective-dated assignment and job detail rows.
The current row is the most recent row for which the effective date is before the current date. Future-dated rows are all rows for which the effective date is after the current date, and historical rows are all rows for which the effective date is before the effective date of the current row.
Image: Effective-dated job information
This diagram illustrates the use of effective dates in managing a worker's assignments, roles, and job information:
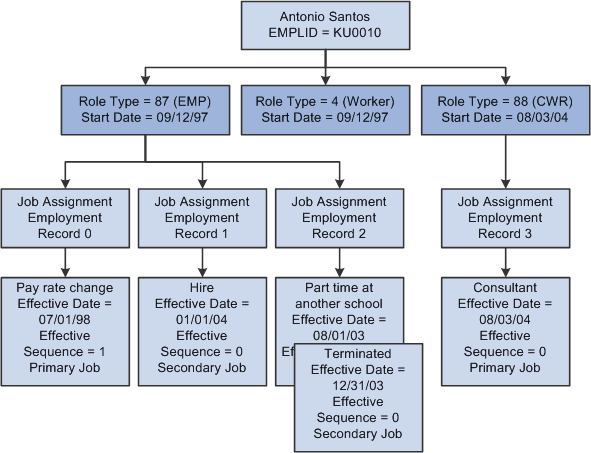
In this example, Antonio Santos was hired on September 1997. Antonio is assigned the Worker and Employee roles as of his hire date, and the effective date of both roles is set to the date of hire. Initially, the end date for both roles is set to 12/31/2999.
Assignments and Roles
All workers have the Worker role by default, and must also have either the Employee or Contingent Worker role on each assignment. The Worker role is terminated only when all assignments for the worker are terminated.
Each worker can have multiple assignments, and an assignment can have multiple effective-dated job detail records for it. You can add a new job assignment without changing existing job records. The first job record that you add for new job assignments always has the Hire action code, and you must specify the worker's role for each assignment. An assignment is terminated when all active job records that relate to it are terminated.
Jobs
There are two levels of primary jobs. One at the job level is user-selected and could be called the primary job. Another primary job is system-defined and could be called the primary job assignment. The primary job assignment is determined by an algorithim and takes into consideration the primary job. A worker can have only one primary job assignment.
By default, the first job record added for a role is marked as the Primary job record for that role. The primary job assignment is used by the Assignment Engine when assigning workers to cases or service orders.
If a worker requires new job data for an existing assignment, for example, a new supervisor ID, job code, or location, you create a new effective-dated job record for that assignment. When Antonio receives a pay increase, a new job record is inserted, effective July 1, 1998 to reflect the change. The new current record becomes the primary record. A background job runs to mark the primary flag on future job records.
Inactivating Provider Group Memberships for Worker Terminated in HCM
If a worker is scheduled to be terminated in an integrated HCM system on a future date, the same status change in the corresponding CRM worker record is handled in the background through the WORKFORCE_SYNC EIP and reflected on the record properly when the termination date arrives. In a situation where the worker is a member of a provider group, such relationship needs to be inactivated as well.
CRM delivers an application engine (AE) program to dissociate terminated workers from their provider groups. This program, named PGRP_JOB, is scheduled to run nightly to identify terminated workers and inactivate any of their existing provider group memberships. When the update is completed, the status of a terminated worker is set to Inactive on the Provider Groups page of the related provider group. Similarly, the status of the provider group is set to Inactive on the Groups page of the terminated worker's record.