Defining Case EIP Functionality
This topic discusses:
Assumptions about the case EIP.
Case EIP functionality.
Delivered EIPs.
Technical process flows.
Error handling.
When considering the Case EIP, you must be aware of the following:
To create a support case, these customer information fields must be provided: Customer BO ID, Customer Role Type ID, Display Template Family CodeID, and Contact BO ID.
Note: The Display Template Family Code is required for creating a case, not for updating it. If a default Display Template Family Code is specified in the user default setup, the third-party vendor does not have to provide it; case creation will occur. If no business unit or display template is provided in the incoming request message and if the user does not have defaults defined, the system sends an error message back to the third-party vendor.
The third-party system needs to send the appropriate business unit, vertical, and market values in the request, unless these values can be provided by default from user reference.
The Case EIP is developed using PeopleTools Integration Broker technology.
The Case EIP does not use bulk loading.
The Case EIP feature is intended to automatically create and update cases from third-party systems; it is not for data-conversion purposes.
The Case EIP and related case component interfaces are meant for the agent-facing case, not for self-service.
When creating a note for a case using the Case EIP, the system leaves the customer, contact, and employee information blank.
The Case EIP cannot create a note for a different customer, contact, or employee.
A case may use attributes.
An attribute can be of any data type (string, number, date, and so on). The system stores different data types in the matching data type field in the request message. It is the responsibility of the third-party system to provide the correct data format for attributes when creating attributes for a case.
The case component can be configured to enable or disable functionality and to hide or unhide fields on the Case page.
The case component is rendered based on the display template. When customers send a request to create a case, it is assumed that they will not send information that has been disabled or hidden. The Case EIP will not do additional validation that is based on configuration settings.
The Case EIP provides a bi-directional EIP in PeopleSoft CRM for PeopleSoft Support, HelpDesk, HelpDesk for Human Resources, Service Center for Higher Education, and all PeopleSoft CRM verticals. It provides a transactional framework that enables your call center to send and receive case information to and from any third-party applications.
Image: Case EIP process flow
This diagram illustrates the Case EIP process flow.
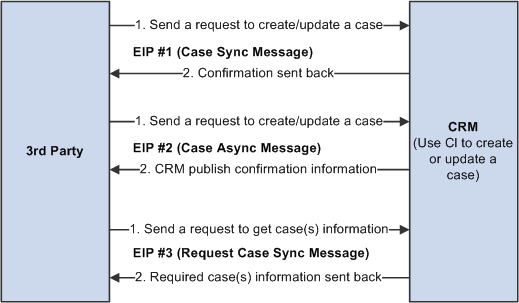
The following EIPs, as shown in the previous diagram, are provided:
EIP #1 - Case Synchronous EIP.
EIP #2 - Case Asynchronous EIP.
EIP #3 - Request Case Information EIP (Synchronous).
Note: If the request contains a case ID, a new case is not created. The existing PeopleSoft CRM case is updated with the pertinent information supplied in the request. If the case ID passed in is invalid, no case is updated and an error message is sent back.
Warning! When you create a case, make sure the value of the CASE_ID field in the request message is empty or 0. When you update a case, make sure the CASE_ID value is a valid value that exists in the CRM RC_CASE table.
Case Synchronous EIP
The third-party application sends a request to CRM to create or update a case and waits for the response. Once the system processes the case in CRM, confirmation information is sent back to the third-party application.
This EIP has one web service (RC_CASE_REQUEST_SYNC), which contains one service operation (RC_CASE_REQUEST_SYNC) with two messages:
RC_CASE_REQUEST_SYNC - Inbound synchronous request message.
RC_CASE_RESPONSE_SYNC - Outbound synchronous response message.
The processing details are as follows: when a request message is received, the on request event calls an appropriate case component interface (CI) to process information from the request message and saves the information into the Case component. The system sends a response message back to the third-party system with confirmation information. The response message may contain information that CRM populates, such as case ID, assigned provider group, and agent.
Since the third-party system is waiting for the response from CRM, the system processes only one case per message.
Case Asynchronous EIP
The third-party system sends a request to create or update a case, and it is not waiting for the response. Once the case is created or updated, CRM publishes confirmation information back to the third-party.
This EIP has two web services:
RC_CASE_REQUEST_ASYNC, which contains one service operation (RC_CASE_REQUEST_ASYNC) with the message RC_CASE_REQUEST_ASYNC (inbound asynchronous message).
RC_CASE_RESPONSE_ASYNC - which contains one service operation (RC_CASE_RESPONSE_ASYNC) with the message RC_CASE_RESPONSE_ASYNC (outbound asynchronous message).
The processing details are as follows: when CRM receives the request, it calls the appropriate case CI to create or update a case and then publishes case information back to the third party.
Since the third-party system is not waiting for the response from CRM, the request message may include information from multiple cases in one message. CRM processes them one by one. The system issues a commit at the end of each successful case.
Request Case Information EIP (Synchronous)
The third-party system sends a request to CRM to find case information. The request may contain multiple cases. CRM processes the request and sends the information for the case or cases back to the third-party system.
This EIP has one web service (RC_CASE_INQUIRY_REQ_SYNC), which contains one service operation (RC_CASE_INQUIRY_REQ_SYNC) with two messages:
RC_CASE_INQUIRY_REQ_SYNC - Inbound synchronous request message.
RC_CASE_INQUIRY_RESP_SYNC - Outbound synchronous response message.
The processing details are as follows: the request message may have one or more Case IDs, the on request event is triggered, and the CRM system processes the rowset of the message to populate case information, one by one. The system uses a direct SQL query instead of a CI.
The logic of EIP #1 (Case Synchronous EIP) and #2 (Case Asynchronous EIP) are the same except for the way in which they are initiated.
EIP #1 is triggered from an OnRequest event. The system generates a sync response message and returns it to the third-party system.
EIP #2 is triggered from an OnNotify event. The system publishes a response message for the third-party application.
EIP #1 and #2 share the same PeopleCode function, ProcessCaseEIP is defined in the FUNCLIB_RC_EIP.CASE_EIP field formula.
Image: Process flow for EIP #1 and EIP #2Process Flow Diagram for EIP #1 and EIP #2process flowsEIP #1 and EIP #2
The following diagram illustrates the technical process flow for both EIP #1 and EIP #2.
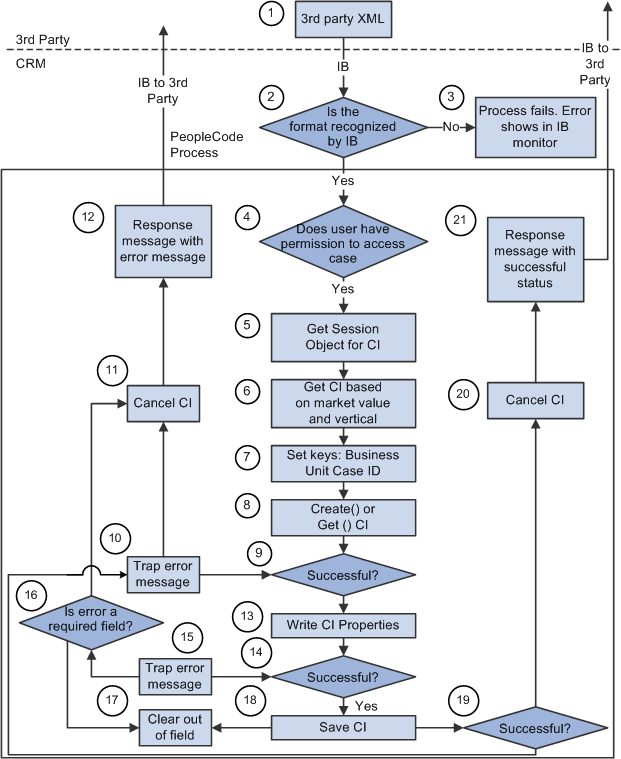
This list indicates where you are in the process flow diagram:
1. The third-party sends an XML request to CRM by way of the integration gateway by using a web service.
3. If integration broker (IB) does not recognize the format, the message is trapped in integration broker.
The process fails (this is standard integration broker functionality).
See PeopleTools: Integration Broker Service Operations Monitor
See PeopleTools: Integration Broker Testing Utilities and Tools
4. OPRID, which is required, is used to validate whether the user has access to the requested case.
Once the user passes security checking, the system creates a case or updates it through integration broker. The integration broker user ID is used to create or update a case. This is the user ID that is used to start the application server.
5. If the user passes the security check, the system obtains a session for component interface processing.
6. When creating a case, BUSINESS_UNIT is required.
The system automatically assigns the next new CASE_ID. If BUSINESS_UNIT is not supplied when creating a case, CRM uses the default business unit from user preferences. When updating a case, only CASE_ID is required since it is a unique identifier.
7. Based on the Case ID value, the system decides whether to insert or update a case.
When no Case ID is provided, CRM creates a case by calling the create() method of CI. When the Case ID is provided, CRM checks whether the Case ID exists in CRM. If it exists, the case is updated by calling the get() method; otherwise, the system does not do any case processing. The system generates a response message with CASE_EIP_STATUS = 1 (failed) and CASE_EIP_ERROR_MSG - Update failed. Case 123 does not exist in CRM. PeopleCode function IsCaseExist in FUNCLIB_RC_EIP. The CASE_ID FieldFormula checks if the case exists.
8. If the create() or get() method fails, the system generates an error message in RC_CASE_EIP_ERR for the response message.
The system cancels the CI to reset the instance (process 11), and sends the response message with the error message back to the third-party (process 12).
9. Once the create() or get() method passes successfully, CRM sets the CI properties as supplied in the request message.
When the third-party application sends a request to create a support case or a Higher Education case for a company contact or consumer, CRM requires customer and contact information.
For customer information, the third-party application can either provide CUST_ID or BO_ID_CUST.
If BO_ID_CUST is provided, CRM uses it directly to create a case.
Conversely, if only CUST_ID is provided, CRM uses the RD_COMPANY table to derive BO_ID_CUST in order to create a case.
The function to get BO_ID_CUST is based on CUST_ID is the PeopleCode Function GetCustBObyID in FUNCLIB_RC_EIP.CASE_ID FieldFormula.
For contact information, the third-party application can either provide the PERSON_ID or BO_ID_CONTACT.
When BO_ID_CONTACT is provided, CRM uses it directly; otherwise, contact PERSON_ID is used to derive BO_ID_CONTACT from the RD_PERSON table.
The function to get BO_ID_CONTACT is based on PERSON_ID, the PeopleCode Function GetPersonBObyID in FUNCLIB_RC_EIP.CASE_ID FieldFormula.
Considerations for HelpDesk or HelpDesk for Human Resources Cases, or for Service Center for Higher Education Case for Worker
The third-party application must provide employee information when it sends a request to create a help desk case. To create a case, the third-party application must also supply the EMPLID, as CRM uses it to derive appropriate BO_ID_CUST with ROLE_TYPE_ID_CUST.
BO_ID_CUST and ROLE_TYPE_ID_CUST need to be populated internally for a case.
Note: Tip: When creating a support case for a customer, make sure BO_ID_CUST (or CUST_ID), ROLE_TYPE_ID_CUST, BO_ID_CONTACT (or CONTACT_PERSON_ID), ROLE_TYPE_ID_CNTCT is provided. When creating a HelpDesk case for an employee, make sure the EMPLID is provided. The POI (person of interest) is supported for PeopleSoft HelpDesk for Human Resources cases only. Third-party vendors must pass a valid worker for creating an IT help desk case, and a valid worker or POI for creating a HelpDesk for Human Resources case. Higher Education cases support company contact, consumer, and worker. When creating a Higher Education case, provide either customer or employee information based on what type of case you want to create.
15. If the setting of a CI property for a field fails, the system traps an error message in the &PSMessage object with information on which field caused the error.
Image: Process flow for EIP #3Process Flow Diagram for EIP #3 process flowsEIP #3
The following diagram illustrates the technical process flow for EIP #3.
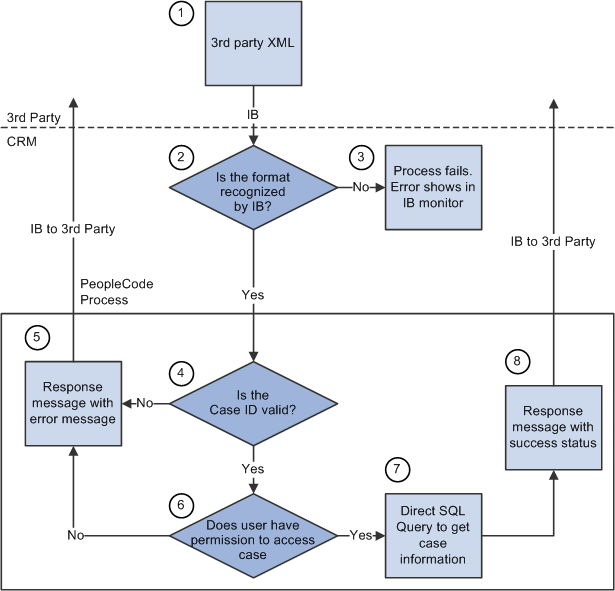
1. The third-party application sends an XML request to CRM by way of the integration gateway.
2. If the integration broker (IB) does not recognize the format, the request is trapped in integration broker.
The case process fails.
3. When a message is passed in from integration broker, the PeopleCode process begins.
The system checks if the case ID exists in PeopleSoft CRM. If the case does not exist in PeopleSoft CRM, the system sends back a response message with an error message (process 5).
4. If the case exists in CRM, PeopleSoft CRM checks if the user has access to the case component based on the market and vertical, and the system gathers market and vertical information.
If a user does not have access, a response message is sent back immediately with the access denied error message (process 5).
The function to check access permission is:
IsUserAuthorized in FUNCLIB_RC_EIP.CASE_ID FieldFormula.
5. Once the user passes the security check, the system executes a direct SQL query to get all case related information and send it back to the third party (process 8).
When a required field contains an invalid value in a request message, or the save event fails, the process fails. The system copies the request message over to response message, and the response message is sent back to the third party with an error message.
When a non-required field contains an invalid value, the system ignores that field and case processing continues. The system sends back a warning message.
Here are some tips:
Always check fields CASE_EIP_STATUS and CASE_EIP_GEN_MSG first in the response message.
When the status is 0 or 2, the response message contains case information that is stored in the PeopleSoft CRM system. When the status is 1 (that is, when the case has failed), nothing is saved in PeopleSoft CRM, and the response message contains a copy of the request information, not the case information stored in CRM. This functionality aids in error handling.
When CASE_EIP_STATUS fails or a warning is issued, the system logs a detailed error or warning message in the rowset RC_CASE_EIP_ERR of the response message.