Understanding Assignment Searches
This topic discusses:
Fit scores.
Activity.
Assignment criteria.
Candidate selection and fit score generation.
In PeopleSoft Customer Relationship Management (PeopleSoft CRM), you can perform assignment searches to find the provider groups and group members that are best suited to a case or service order. The system returns a list of eligible candidates ranked by fit score, which is an evaluation of how well each provider group or group member matched criteria on the case or service order.
In addition to fit score, the system displays current availability and, for group member assignment searches that are performed for a case, the number of open cases that are currently assigned to the group member.
The system doesn't restrict the workforce assignment only to what it suggests. You can select the provider group and group member that the system recommends, any provider group and group member on the list (regardless of the fit score, current availability, or case load), or any provider group and group member that does not appear on the list, to be assigned to a case or service order.
Note: If you use auto-assignment to assign a provider group member to a case and multiple members tie for the highest fit score, the system assigns the member with the lowest case load. If two or more members tie for highest fit score and lowest case load, the system selects the first person in the list. In this situation the system makes an arbitrary assignment based on the member with the lowest person ID.
The system displays the activity from the service order.
Because a competency may be required for more than one activity, this column indicates the activity to which the competency applies. This column does not appear when you perform the assignment search from a case.
PeopleSoft CRM uses the assignment engine to generate recommendations for provider group and group member assignments. The assignment engine uses this information in the assignment evaluation process:
General assignment criteria.
Case-specific assignment criteria.
Service order-specific assignment criteria.
Weighting factors.
Assignment search data model.
General Assignment Criteria
For each worker or provider group, you can define a list of values that the worker or provider group specializes or supports under these criteria: customer, location, product, product group, region, site, department, person type, security role.
When you perform an assignment search on a service order or case, the assignment engine matches the values of these criteria that are available on the service order or case to the values that are available on workers and provider groups. The weight, or relative importance, of each assignment criteria match determines a candidate's fit score.
Failure to match an assignment criteria value on a case or service order lowers the fit score but does not exclude a provider group or group member from the list of eligible candidates. However, if you do not select the Display Provider Groups and Group Members with no Criteria Matches check box on the Assignment Setup page, then a provider group or group member must match at least one criteria or competency value to be included in the list.
The assignment engine uses a different set of assignment criteria values when searching for a case in PeopleSoft HelpDesk or Support, or for a service order in PeopleSoft Integrated FieldService.
The table below illustrates:
For help desk cases, the assignment engine matches values for department, location, product, product group, person type, problem type, and category, type, and detail (CTD) competencies.
For help desk change requests, the assignment engine matches values for department, location, product, product group and security role. Help desk change requests are matched only against provider groups.
For support cases, the assignment engine matches values for customer, site, region, product, product group, problem type, and CTD competencies.
For service orders, the assignment engine matches values for customer, site, region, product group, product, service (or service activity) competency.
For Service Center for Higher Education cases, the assignment engine matches values according to either help desk or support case criteria, based on the caller for the case. If the caller is a worker, help desk criteria is used: if the caller is a company contact or consumer (constituent), support criteria is used.
|
Assignment Criteria |
Used in Support Case? |
Used in Help Desk Case? |
Used in Help Desk Change Request? |
Used in Service Order? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Competency - CTD |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
NA |
|
Competency - Problem Type |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
NA |
|
Competency - Service |
NA |
NA |
NA |
Yes |
|
Customer |
Yes |
NA |
NA |
Yes |
|
Location |
NA |
Yes |
Yes |
NA |
|
Product |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Product Group |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Region |
Yes |
NA |
NA |
Yes |
|
Site |
Yes |
NA |
NA |
Yes |
|
Person Type |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Department |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Security Role |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
As mentioned in the table, the assignment engine uses the region information to perform service order and support case assignment. A region search occurs when the Incident Address group box is available on a Case or Service Order page (according to the associated configuration template) with a specified incident location or when a region is associated with the site, contact, or customer on the transaction. The assignment engine runs the region search based on the zip code that you specify in the incident location.
Note: This is only if the incident location is being displayed. If not, the region is determined by the customer specified. In this case, the region match starts with this region (not the parent region like it does for zip code). The region is derived from a hierarchy based upon the site, contact and customer. When a service order or case is created, the region is determined by obtaining the region, if available, from the site, then the contact and customer. If a new region is specified for the site, customer or contact, there will be no region to match on with the assignment engine.
Before using zip codes as regions as assignment criteria, you must:
Use the Region component to add zip codes as individual regions.
Create a region, such as the Santa Clara county, and make it the parent region for all appropriate zip codes.
Note: You should define regions with the category of Geography.
When the assignment engine runs, the zip code of the incident location determines the region. The system looks for the zip code with a category of Geography in the region table and starts with the parent region for assignment matches.
The system continues to look at the region hierarchy and reports region matches for any provider groups and group members that match the parent or grandparent regions. For example, if the parent region of Santa Clara County is Northern California, then the system includes any provider groups or group members associated with Santa Clara County or Northern California. If the provider group or group member is associated with both Santa Clara and Northern California, the match will be on the lower region (in this case, Santa Clara County).
Case-Specific Assignment Criteria
For assignment searches that you perform for cases, you can match the problem type and CTD competencies of the case with competencies that are defined for group members and provider groups.
You can specify competencies for problem types, categories, specialty types and details to be used when the system performs an assignment search from a case in PeopleSoft Support or HelpDesk.
The assignment engine matches the competency values in these fields on the case with group members or provider groups that are associated with the same competency values. Any provider group or group member that does not meet the minimum competency proficiency defined for the CTD or problem type will not have a match for the competency.
Note: There is a hierarchical relationship among category, specialty type, and detail. A category includes specialty types, which contain details. When all three levels of information are available in a case that needs to be assigned, the value from the lowest available level is used in the assignment search. For example, if the case has a category, specialty type and detail, the assignment uses the competency information that is defined for detail when performing the assignment search. If it has category and specialty type, the system uses the competency information for type. If it has only the category, the system uses the competency information for category.
Service Order-Specific Assignment Criteria
For assignment searches that you perform for service orders, the assignment engine matches (besides general assignment criteria) the competency proficiency of provider groups and group members with the minimum competency proficiency requirements on the service (or service activity). Any provider group or group member that does not meet the minimum competency proficiency that is defined for the service or service activity will not have a match for the competency.
The service competency data that the assignment engine uses depends on:
Whether competency data is defined for a service or service activity.
Whether the assignment search is initiated from the service order activity actions section or the service order line.
If activities are defined for the service, the assignment engine uses only the competency requirements that are defined for the activities, even if competencies are also defined for the service.
If you perform the assignment search from the service order activity actions for a service with one or more activities, the system evaluates provider group or group member competency against the competency requirements that are defined for all activities that are associated with the service.
If you perform the assignment search from the service order line, the system considers only the competency requirements of the activity on the line.
If no activities are defined for the service, the assignment engine uses the competency information that is defined for the service. If no competencies are defined for the service, the assignment engine does not perform a competency match; it uses only assignment criteria matches to evaluate candidates for service order assignment.
Weighting Factors
You can define the relative importance of assignment criteria for provider group and group member searches. These weights may differ between the provider group and group member.
For example, if the CTD competency (applicable to support and help desk cases) has no importance when assigning provider groups in cases, but region is important, set the group weight for the CTD competency to 0 and the weight for region to 5.
If CTD competency and product are equally important and customer is somewhat important for group member searches, you can then set the weights to 5, 5, and 3, respectively.
Assignment Search Data Model
This diagram illustrates the information that the assignment engine uses to generate a list of provider groups or worker candidates to assign to tasks on a help desk case, support case, or service order and to display current availability status:
Image: Assignment Search Data Model
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Assignment Search Data Model.
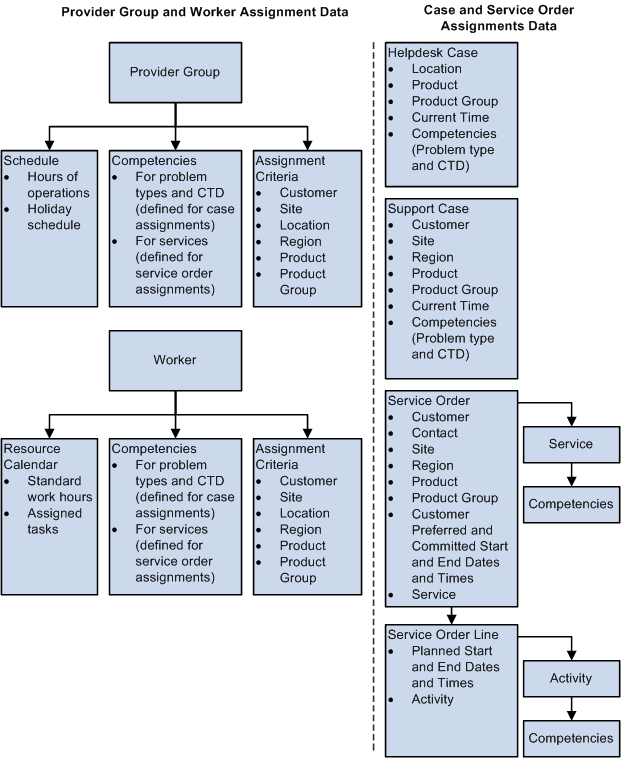
Note: The HelpDesk case, provider group assignment criteria, and worker assignment criteria should also contain the person type.
For both provider group and group member searches, the assignment engine builds a table in the database that represents each criteria match between provider groups or group members and the values on a service order or case.
After completing the search, the system returns a list of the provider groups or group members with criteria matches. The aggregate fit score of the provider groups or group members sequences the list.
Evaluating Workforce Assignment
For each assignment criteria match between a provider group or group member and the evaluated help desk case, support case, or service order, the system inserts a row into a temporary table called Criteria Fit (RF_ASSIGN_FIT).
Each row includes the name of the group member or provider group, the criteria that was matched, and the relative importance, or weight, of the match. The weight value for the match becomes the number of points that are assigned to the match.
For matches on problem type competency, CTD competency, or both, the number of points depends on the number of competencies and the provider group or group member's proficiency for those competencies.
For service competency matches, the number of points also depends on the number of competencies and the provider group or group member's proficiency for those competencies. For these reasons, the number of competency points may be less than the competency weight.
Determining Workforce Availability
The system determines the availability status of each provider group or group member. For provider groups, the system checks the hours of operation and the holiday schedule that you define for the provider group on the Schedule page in the Provider Group component.
If the customer preferred (or committed, if customer preferred doesn't exist) start and end dates and times on a service order, or the current date and time on a case, correspond to an open period for the provider group, and if the start and end dates are not on their holiday schedule, the provider group is considered available for assignment.
For group members, the system checks for tasks on the worker's resource calendar as well as the worker's schedule.
If the customer preferred start and end dates and times on a service order (if they don't exist, the system uses the committed dates), or the current date and time on a case, correspond to a period during the group member's standard work hours for which no other task has been assigned, the group member is considered available for assignment.
Establish standard workweek and workday hours during installation on the Calendar Options page (select ). You can modify an individual worker's standard hours on the Schedule page in the Worker component.
Displaying Case Load for Candidates
For group member assignment searches that you perform from a case, the system determines how many open cases are currently assigned to the group member. To facilitate workload balancing, this information appears for each agent who is returned for a group member search.
Calculating Candidate Fit Scores
For each provider group or group member with a criteria match that is recorded in the Criteria Fit table, the system sums the weight value that is associated with each criteria match row and calculates the fit score for the provider group or group member using this equation:
Image: Fit score
This text provides a sample candidate fit scores calculation:

where the number of possible match points is defined by the criteria weight factor.
For example, for a group member assignment search, suppose that Jon Smith matched three assignment criteria (region, customer, and site) on a service order for which no competency requirements were defined, and this is the weight for each of the matching assignment criteria that applies to service orders:
Customer = 5
Region = 4
Product = 3
Site = 0
Competency - Service = 4
The total number of possible match points is the total of the weight values: 5 + 4 + 3 + 0 + 4 = 16.
For the service order in this example, Jon Smith matched region, customer, and site. His total number of match points is calculated as follows:
4 + 5 + 0 = 9
Jon's fit score = 9 / 16 x 100 =56%
Accounting for Competency Proficiency on a Service Order
When calculating fit scores for service order assignments, the assignment engine accounts for the provider group or group member's competency proficiency and the relative importance of the competency that is defined for the service or service activity using this equation:
Image: Competency score
This text provides a sample competency score calculation:
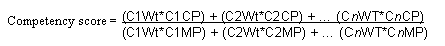
CnWt is the weight of the competency defined for the service or service activity.
CnCP is the candidate's proficiency rating for the competency.
CnMP is the maximum proficiency rating.
For example, suppose that the service order in the previous example was for an air-conditioner maintenance service with no activities. The air-conditioner maintenance service has two competency requirements: basic maintenance and compressor replacement.
The basic maintenance competency requires a minimum proficiency of 2 on a 1 to 6 rating scale, where 6 is the maximum proficiency rating. The compressor replacement competency requires a minimum proficiency of 3 on the same rating scale.
The service definition for air-conditioner maintenance weights the relative importance of the basic maintenance competency for performing the service as a 5 on a 0 to 5 scale, while the relative importance of the compressor replacement competency is weighted at 2 on the same scale.
This table summarizes the competency data for the air-conditioner maintenance service:
|
Competency |
Minimum Proficiency |
Relative Importance to the Service (CnWt) |
Maximum Proficiency on Rating Model (CnMP) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Basic Maintenance (C1) |
2 |
5 |
6 |
|
Compressor Replacement (C2) |
3 |
2 |
6 |
This table shows the competency proficiency rating for three technicians, Jon Smith, Bill Jones, and Jane Markowitz:
|
Worker |
Basic Maintenance Competency Proficiency (C1CP) |
Compressor Replacement Competency Proficiency (C2CP) |
|---|---|---|
|
Jon Smith |
4 |
3 |
|
Bill Jones |
2 |
0 |
|
Jane Markowitz |
5 |
4 |
The competency score for each technician is calculated as follows:
Jon Smith's competency score = (5 * 4) + (2 * 3) / (5 * 6) + (2 * 6) = 0.62
Bill Jones' competency score = (5 * 2) / (5 * 6) + (2 * 6) = 0.24
Notice that Bill Jones did not match the proficiency requirements for the compressor replacement competency; therefore, no points for the match are included in the calculation.
Jane Markowitz's competency score = (5 * 5) + (2 * 4) / (5 * 6) + (2 * 6) = 0.79
To calculate the fit score for each worker, the competency score is multiplied by the assignment weighting factor of the corresponding assignment criterion, which is defined for you in your installation.
Let's assume that the same criteria weight factors as in the previous fit score calculation example: Customer = 5, Region = 4, Product = 3, Site = 0, Competency - Service = 4.
Let's also assume that, except for the competency proficiency on competency - service, Jon, Bill, and Jane matched on identical criteria. Their fit scores are calculated as follows:
Jon Smith's fit score = 4+5+0+(4*0.62)/ 5+4+3+0+4 = 0.717
Bill Jones's fit score = 4+5+0+(4*0.24)/ 5+4+3+0+4 = 0.622
Jane Markowitz's fit score = 4+5+0+(4*0.79)/5+4+3+0+4 = 0.76
The assignment engine sorts these candidates:
Jane Markowitz, 76%
Jon Smith, 72%
Bill Jones, 62%
If you view the detail scores, the system displays the criteria matches that compose the fit scores. For example, under Jon Smith's name, you would see this breakdown:
|
Criteria |
Competency |
Score |
|---|---|---|
|
Region |
NA |
4/16 = 25% |
|
Customer |
NA |
5/16 = 31.3% |
|
Site |
NA |
0/16 = 0% |
|
Competency - Service |
Basic Maintenance |
(4 x (5 x 4) / 42) / 16) = 11.90% |
|
Competency - Service |
Compressor Replacement |
(4 x (2 x 3) / 42) / 16) = 3.6% |
Accounting for Competency Proficiency on a Case
Similar to calculating service and service activity competencies, when the assignment engine calculates fit scores for case assignments, it accounts for the provider group or group member's competency proficiency and the relative importance of the competency values that are specified for problem type or CTD on the case using this equation:
Image: Competency score
This text provides a sample competency score equation:
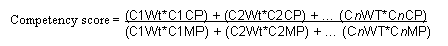
CnWt is the weight of the competency that is defined for the problem type or CTD.
CnCP is the candidate's proficiency rating for the competency.
CnMP is the maximum proficiency rating.
For example, suppose that the case involves a problem with a personal computer (PC) and the required problem type competency and category competency are IBM PC Hardware and PC Configuration, respectively. If Jon Smith has a proficiency of 4 on a 1 to 6 rating scale for both competencies, then Jon's competency score for problem type is:
4 /6 = 0.666
His competency score for the category is also 0.666.
Let's assume that the following criteria weight factors are set:
Customer = 5, Region = 4, Product = 3, Site = 0, Competency - Problem Type = 4, Competency - CTD = 4.
If Jon Smith matches the customer and both competencies on the case, then his fit score is calculated as follows:
Jon Smith's fit score = 5+(4*0.666)+(4*0.666) / 5+4+3+0+4+4 = 0.516 or 52%
Accounting for Product Proficiency on a Service Order or Case
When calculating fit scores for service order and case assignments, the assignment engine accounts for the provider group or group member's product proficiency using this equation:
Product score = PCP/PMP
PCP is the candidate's proficiency rating for the product.
PMP is the maximum proficiency rating.
For example, suppose that the case or service order involves a problem with an air conditioner.
If Bill Jones has a proficiency of 2 for this product on a 1 to 6 rating scale, then Bill's product score is:
2 / 6 = 0.333
Let's assume that the criteria weight factors are the same as in the previous examples:
Customer = 5, Region = 4, Product = 3, Site = 0, Competency - Problem Type = 4, Competency - CTD = 4.
If Bill Jones matches the customer and product on the case or service order, this is how his fit score is calculated:
Bill Jones' fit score = 5 + (3*0.333) / 5+4+3+0+4+4 = 0.299 or 30%