Defining Forecast Elements
To define forecast names, use the Forecast Names (RSF_FCAST_ID) component. To define forecast types, use the Forecast Type (RSF_FCAST_TYPE) component. To define revenue types, use the Revenue Type (RSF_REV_TYPE) component.
This topic discusses how to:
Define forecast names.
Define forecast types.
Define revenue types.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
RSF_FCAST_ID |
Define forecast names. |
|
|
RSF_FCAST_TYPE |
Define forecast types, which are user-defined classifications. |
|
|
RSF_REV_TYPE |
Define revenue types. |
Use the Forecast Name page (RSF_FCAST_ID) to define forecast names.
Navigation
Image: Forecast Name page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Forecast Name page.
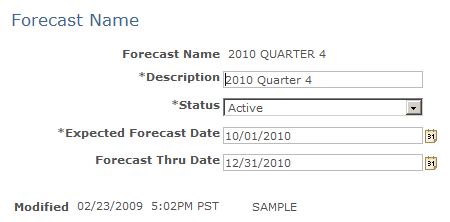
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Expected Forecast Date |
Enter the date on which sales users can use the forecast name to generate a forecast. For example, suppose that the current date is May 1, 2009, and you are setting up a forecast name called Freezers:June for a forecast that will occur in June 2009. You do not want to make this forecast name available until June 2009, so you would enter an expected forecast date of June 1, 2009. |
| Forecast Thru Date (forecast-through date) |
Enter the ending date for forecasting. For example, suppose you are going to stop selling a product at the end of 2009. You would establish a forecast name with a forecast-through date of December 31, 2009. Sales users cannot use the forecast name to generate a forecast for the product for any time frames that begin after December 31, 2009. |
The system generates a list of possible forecasts for a forecast name when there are time frame periods defined. For example, suppose you enter an expected forecast date of July 1, 2009, and a forecast-through date of September 30, 2009. The system builds a list of possible forecasts using that forecast name and the following time frames:
July, August, and September 2009 (if you use monthly time frames).
Third quarter 2009 (if you use quarterly time frames).
2009 (if you use yearly time frames).
The system displays the list of possible forecasts on the Search My Forecasts and Search Rollup Forecasts components.
Use the Forecast Type page (RSF_FCAST_TYPE) to define forecast types, which are user-defined classifications.
Navigation
Image: Forecast Type page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Forecast Type page.
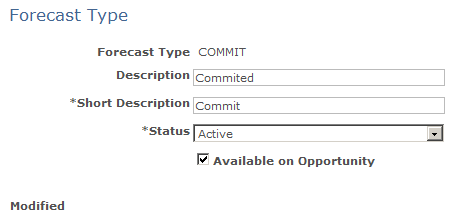
Use forecast types to categorize opportunity forecast revenue activity according to the business needs. For example, you might define forecast types of Adjusted, Confirmed, Committed, and Open. Forecast types are not predefined; typically, they vary considerably for different kinds of businesses.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Available on Opportunity |
Select to make the forecast type available on the opportunity pages where you define and update opportunities. When this check box is deselected, the forecast type is available only on forecast pages, where it is typically used to categorize types of adjustment activities. |
Use the Revenue Type page (RSF_REV_TYPE) to define revenue types.
Navigation
Image: Revenue Type page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Revenue Type page.
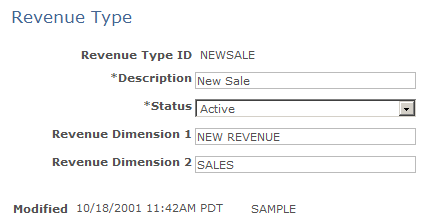
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Revenue Dimension 1 and Revenue Dimension 2 |
Revenue dimensions provide a mechanism for consolidating revenue types to forecast revenue analysis. When many revenue types exist, you can group them by using revenue dimensions. For example, one dimension might be the type of revenue (for example, New, Upsell, or Repeat) and the other dimension might be the type of product or service (for example, License, Warranty, or Maintenance).
When reviewing forecasts, you can generate subtotals for revenue types and revenue dimensions. |