Oracle® Enterprise Manager Ops Center
Create Oracle Solaris 11 Zones
12c Release 3 (12.3.2.0.0)
E60026-02
July 2016
This guide provides an end-to-end example for how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center to create Oracle Solaris 11 zones.
Introduction
With Oracle Solaris Zones, you can create one or more virtualized operating systems on a single Oracle Solaris 11 operating system (OS). Each zone is an isolated OS environment that you can use to run applications. The applications and processes that run in one zone do not affect what runs in other zones.
When you create a zone in Oracle Solaris 11, it has the following characteristics:
-
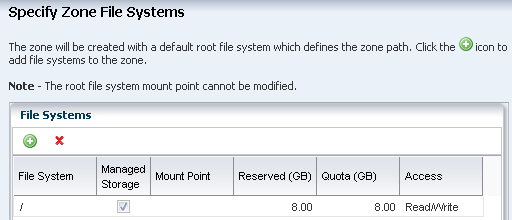
Uses a root file system that does not share components of the global zone's root file system (whole root zones.) The default root file system size is eight (8) GBytes.
-
Uses exclusive IP addresses.
-
Uses the ZFS file system.
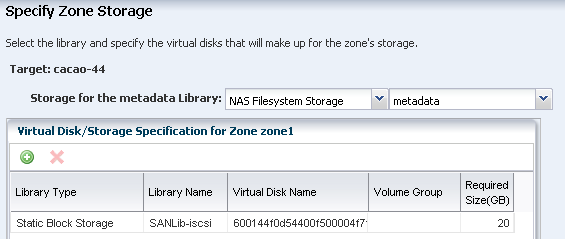
You must provide storage for the zone and zone metadata. When you create a zone, you assign it to one of the storage libraries associated with its virtual host.
-
Zone data: The zone's data that results from its operations. You can store zone data in a local library, iSCSI or SAN storage library. For zone migration, store the zone data in an iSCSI or SAN storage library.
-
Metadata: The zone's metadata is the configuration of the zone's operating system, CPU, memory, and network. You can store metadata in a local library or in a NAS library. For zone migration, store the metadata in a NAS storage library.
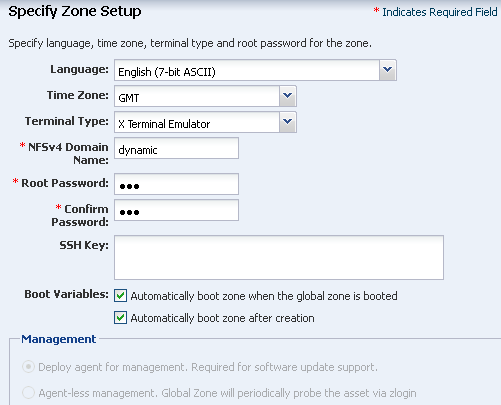
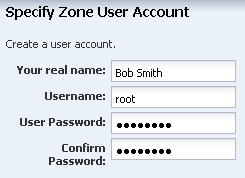
In Oracle Solaris 11, root is not a regular account, it is a role. With the default Oracle Solaris 11 setup, where root is just a role, you cannot log in as root. Instead, you must create an account to log in. With Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center, you have the option to create a special user account or log in as root.
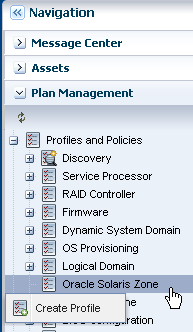
You can create Oracle Solaris 10 branded zones or Oracle Solaris 11 non-global zones on an Oracle Solaris 11 environment. You can create new zones from the Asset view or from the Plan Management view. This example describes how to create zones.
This example shows you how to create an Oracle Solaris 11 non-global zone from the Plan Management view. The zone is configured as follows:
-
SAN storage for the zone and NAS storage for the zone metadata.
-
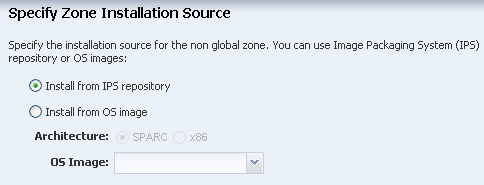
The zone is installed from the Oracle Solaris 11 Software Update library.
When you install from the repository, the default software group (
solaris-small-server) uses less space than when you install from an OS image.
With this configuration, you can add the zone to a server pool and use the zone migration feature. See Related Articles and Resources for links to related information about different zone configurations, including choosing the type of storage library, complex network configurations, and server pools that enable you to migrate zones within the pool.
Note:
You cannot create kernel zones in Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center 12c Release 3 (12.3.0.0.0).
What You Will Need
This example stores the zone data on a SAN storage device and the metadata in a NAS library.
You need the following before you can create an Oracle Solaris 11 zone:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center installed on an Oracle Solaris 11 operating system.
-
A discovered and agent-managed Oracle Solaris 11 operating system.
-
Oracle Solaris 11 Software Update Library that is configured to synchronize with the Oracle Solaris 11 Package Repository.
-
SAN storage for the zone data. You need at least 6 GB virtual disk for zone storage.
-
NAS storage device for the zone metadata.
-
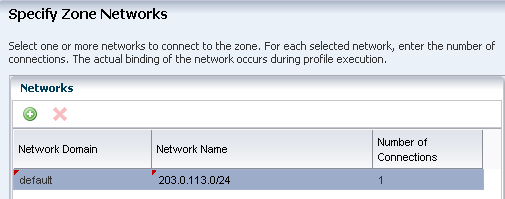
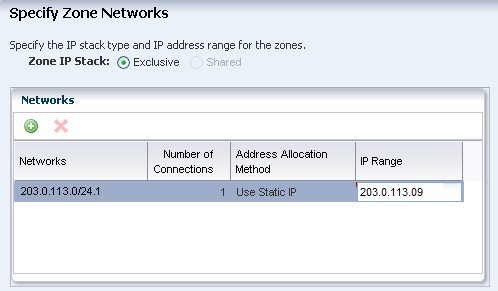
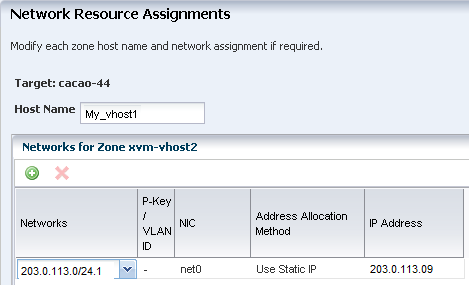
A network that is associated with the global zone and is available for the zone. This example uses the default network that is created when you manage the operating system.
-
IP address for the zone.
-
A user name and password to log in to the zone. This is the user account that you will use to log in to the zone.
-
The roles and permissions to complete the tasks. You need the following Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center roles:
-
Plan/Profile Admin to create and manage zone profiles and plans.
-
Virtualization Admin to create and manage the zones.
-
See Related Articles and Resources for links to related information and articles about how to set up and synchronize an Oracle Solaris 11 Software Update library, how to discover and manage an operating system, how to prepare your storage and network infrastructures, and how to modify user roles and permissions.
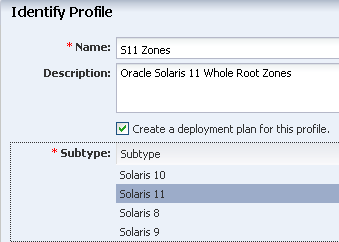
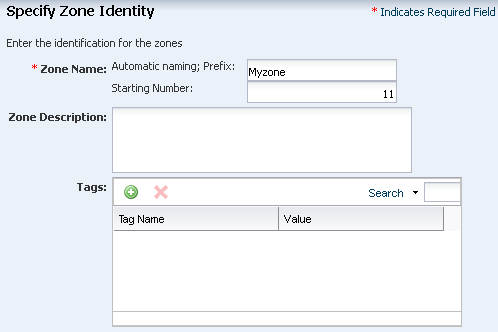
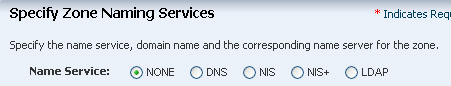
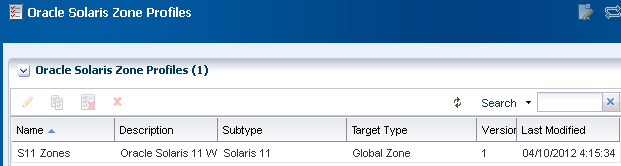
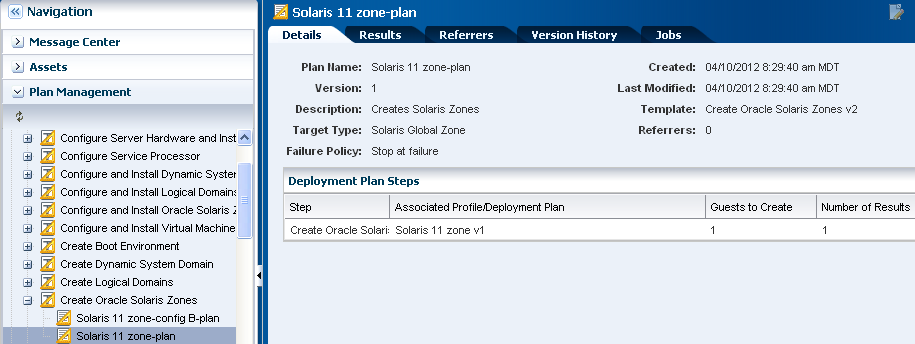
Create an Oracle Solaris 11 Zone Profile and Plan
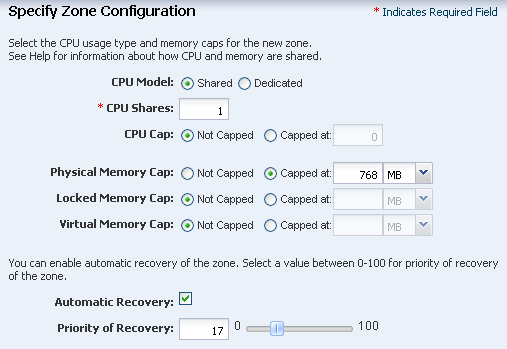
Creating a zone profile defines the zone configuration details and creates a deployment plan.
The zone profile and the corresponding deployment plan appear in the list of Oracle Solaris Zone Profiles and Oracle Solaris Zone Plans.
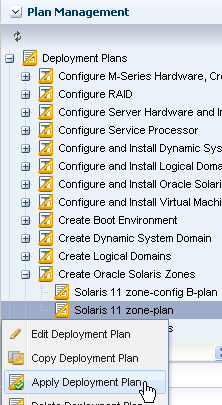
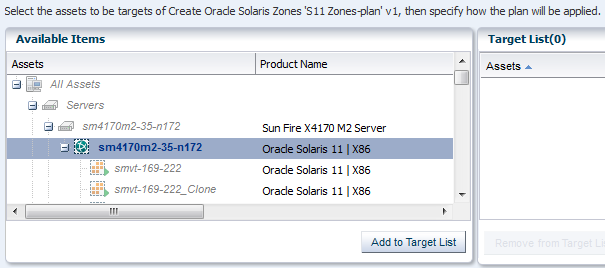
Deploy the Plan to Create a New Zone
Use the plan that you created in Create an Oracle Solaris 11 Zone Profile and Plan to create a zone, and then view the new zone in the UI. You have the opportunity to make changes in the plan before you submit the job to apply the plan. For example, you could edit the plan to create multiple zones.
What's Next?
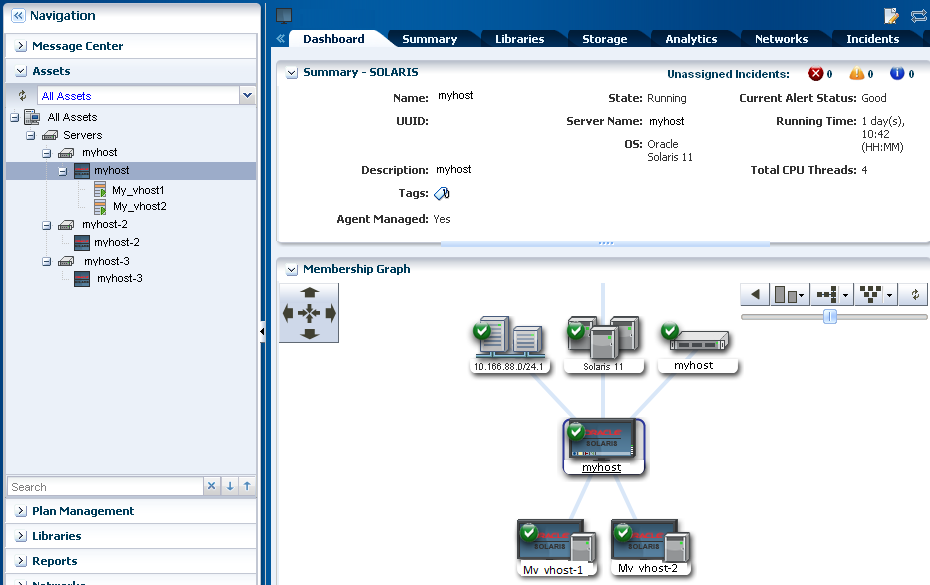
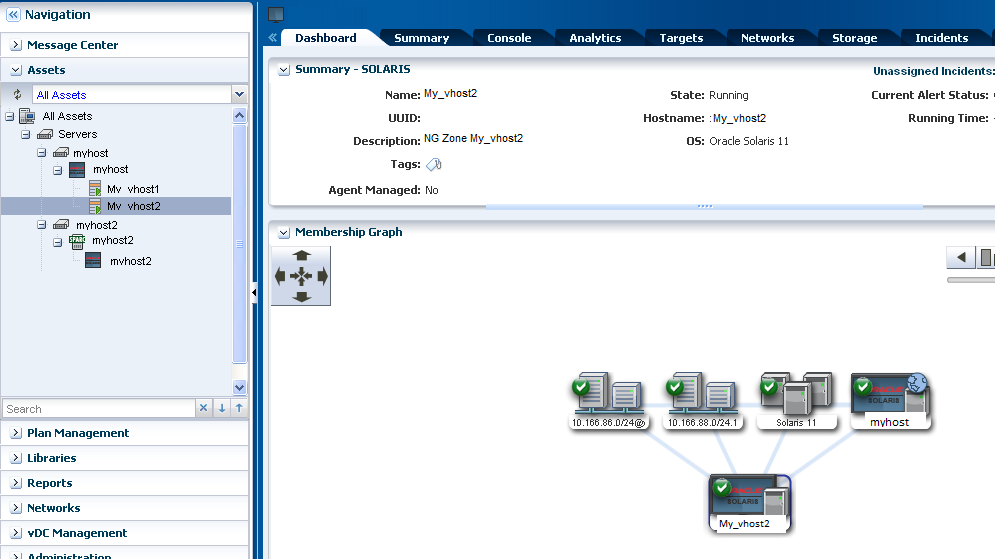
The zone is available for you to use as a separate operating system. Use the actions in the user interface to manage the zone and perform operations, such as rebooting and halting the operating system. Manage your zone's performance, including viewing the CPU utilization at the zone level, with the OS Analytics feature. You can reuse your Oracle Solaris Zones deployment plan to quickly add zones when and where you need them.
To improve high availability, you can use the zone created here in a zone server pool. A zone server pool is a group of zones that use the same network and storage resources. You can share resources among the zone members, schedule load balancing, minimize power consumption, and move zones to different physical servers within the pool.
Related Articles and Resources
Refer to the following documentation resources for more information:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center 12c documentation at
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E59957_01/index.htm. -
Deploy How To Library at
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E59957_01/nav/deploy.htm. -
Operate How To Library at
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E59957_01/nav/operate.htm. -
Product blog at
https://blogs.oracle.com/opscenter.
Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library at http://docs.oracle.com/en/operating-systems/
Oracle® Enterprise Manager Ops Center Create Oracle Solaris 11 Zones, 12c Release 3 (12.3.2.0.0)
E60026-02
Copyright © 2007, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle.