Provisioning (Role-Based Authorization)
Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System security determines user access to applications using the concept of roles. Roles are permissions that determine user access to application functions. Some EPM System components enforce object-level ACLs to further refine user access to their artifacts, such as reports and members.
Each EPM System component provides several default roles tailored to various business needs. Each application belonging to an EPM System component inherits these roles. Predefined roles from the applications registered with Oracle Hyperion Shared Services are available from Oracle Hyperion Shared Services Console. You may also create additional roles that aggregate the default roles to suit specific requirements. These roles are used for provisioning. The process of granting users and groups specific roles belonging to EPM System applications and their resources is called provisioning.
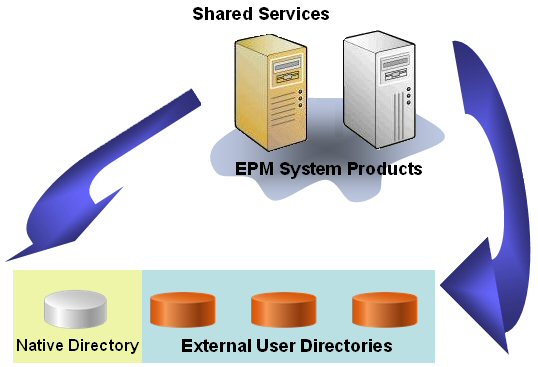
Native Directory and configured user directories are sources for user and group information for the provisioning process. You can browse and provision users and groups from all configured user directories from Shared Services Console. You can also use application-specific aggregated roles created in Native Directory in the provisioning process.
An illustrated overview of the authorization process:
-
After a user is authenticated, EPM System component queries user directories to determine the user's groups.
-
The EPM System component uses group and user information to retrieve the user's provisioning data from Shared Services. The component uses this data to determine which resources a user can access.
Product-specific provisioning tasks, such as setting product-specific access control, are completed for each product. This data is combined with provisioning data to determine the product access for users.
Role-based provisioning of EPM System products uses these concepts.
Roles
A role is a construct (similar to an access control list) that defines the access permissions granted to users and groups to perform functions on EPM System resources. A role is a combination of resource or resource types (what users can access, for example, a report) and actions that users can perform on the resource (for example, view and edit).
Access to EPM System application resources is restricted. Users can access them only after a role that provides access is assigned to the user or to the group to which the user belongs. Access restrictions based on roles enable administrators to control and manage application access.
Global Roles
Global roles, which are Shared Services roles that span multiple products, enable users to perform certain tasks across EPM System products. For example, the Shared Services Administrator can provision users for all EPM System applications.
Predefined Roles
Predefined roles are built-in roles in EPM System products. You cannot delete them. Each application instance belonging to an EPM System product inherits the predefined roles of the product. These roles, for each application, are registered with Shared Services when you create the application.
Aggregated Roles
Aggregated roles, also known as custom roles, aggregate multiple predefined roles belonging to an application. An aggregated role can contain other aggregated roles. For example, a Shared Services Administrator or Provisioning Manager can create an aggregated role that combines the Planner and View User roles of a Oracle Hyperion Planning application. Aggregating roles can simplify the administration of applications that has several granular roles. Global Shared Services roles can be included in aggregated roles. You cannot create an aggregated role that spans applications or products.
Users
User directories store information about the users who can access EPM System products. Both the authentication and the authorization processes use user information. You can create and manage Native Directory users only from Shared Services Console.
Users from all configured user directories are visible from Shared Services Console. These users can be individually provisioned to grant access rights on the EPM System applications registered with Shared Services. Oracle does not recommend provisioning individual users.
Default EPM System Administrator
An administrator account, with default name admin, is created in Native Directory during the deployment process. This is the most powerful EPM System account and should be used only to set up a System Administrator, who is the Information Technology expert tasked with managing EPM System security and environment.
The user name and password of EPM System Administrator is set during Oracle Hyperion Foundation Services deployment. Because this account cannot be subjected to corporate account password policies, Oracle recommends that it be deactivated after creating a System Administrator account.
Generally, the default EPM System Administrator account is used to perform these tasks:
-
Configure the corporate directory as an external user directory. See Configuring User Directories.
-
Create a System Administrator account by provisioning a corporate Information Technology expert with the Shared Services Administrator role. See "Provisioning Users and Groups" in the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System User Security Administration Guide.
System Administrator
The System Administrator is typically a corporate Information Technology expert who has read, write, and execute access rights to all servers involved in an EPM System deployment.
Generally, the System Administrator performs these tasks:
-
Disable the default EPM System Administrator account.
-
Create at least one Functional Administrator.
-
Set the security configuration for EPM System using the Shared Services Console.
-
Optionally configure user directories as an external user directory.
-
Monitor EPM System by periodically running the Log Analysis tool.
The tasks that Functional Administrators perform are described in this guide.
Procedures to create a Functional Administrator:
-
Configure the corporate directory as an external user directory. See Configuring User Directories.
-
Provision a user or group with the required roles to create a Functional Administrator. See "Provisioning Users and Groups" in the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System User Security Administration Guide.
The Functional Administrator must be provisioned with these roles:
-
LCM Administrator role of Shared Services
-
Administrator and Provisioning Manager role of each deployed EPM System component
-
Functional Administrators
The Functional Administrator is a corporate user who is an EPM System expert. Typically, this user is defined in the corporate directory that is configured in Shared Services as an external user directory.
Functional Administrator performs EPM System administration tasks such as creating other Functional Administrators, setting up delegated administration, creating and provisioning applications and artifacts, and setting up EPM System auditing. The tasks that Functional Administrators perform are described in the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System User Security Administration Guide.
Groups
Groups are containers for users or other groups. You can create and manage Native Directory groups from Shared Services Console. Groups from all configured user directories are displayed in Shared Services Console. You can provision these groups to grant permissions for EPM System products registered with Shared Services.