Before You Begin
For a detailed description of all the architectural options and the design considerations, see Design the infrastructure to deploy Oracle Enterprise Performance Management in the cloud.
In this architecture, applications and databases are deployed in a single Google Cloud zone within the same Google Cloud region.
Application users access the EPM application through the EPM Oracle HTTP Server (OHS). The request is resolved by the Windows server application server to the Oracle Database.
Oracle Databases are protected by Oracle Autonomous Recovery services with zero data loss protection.
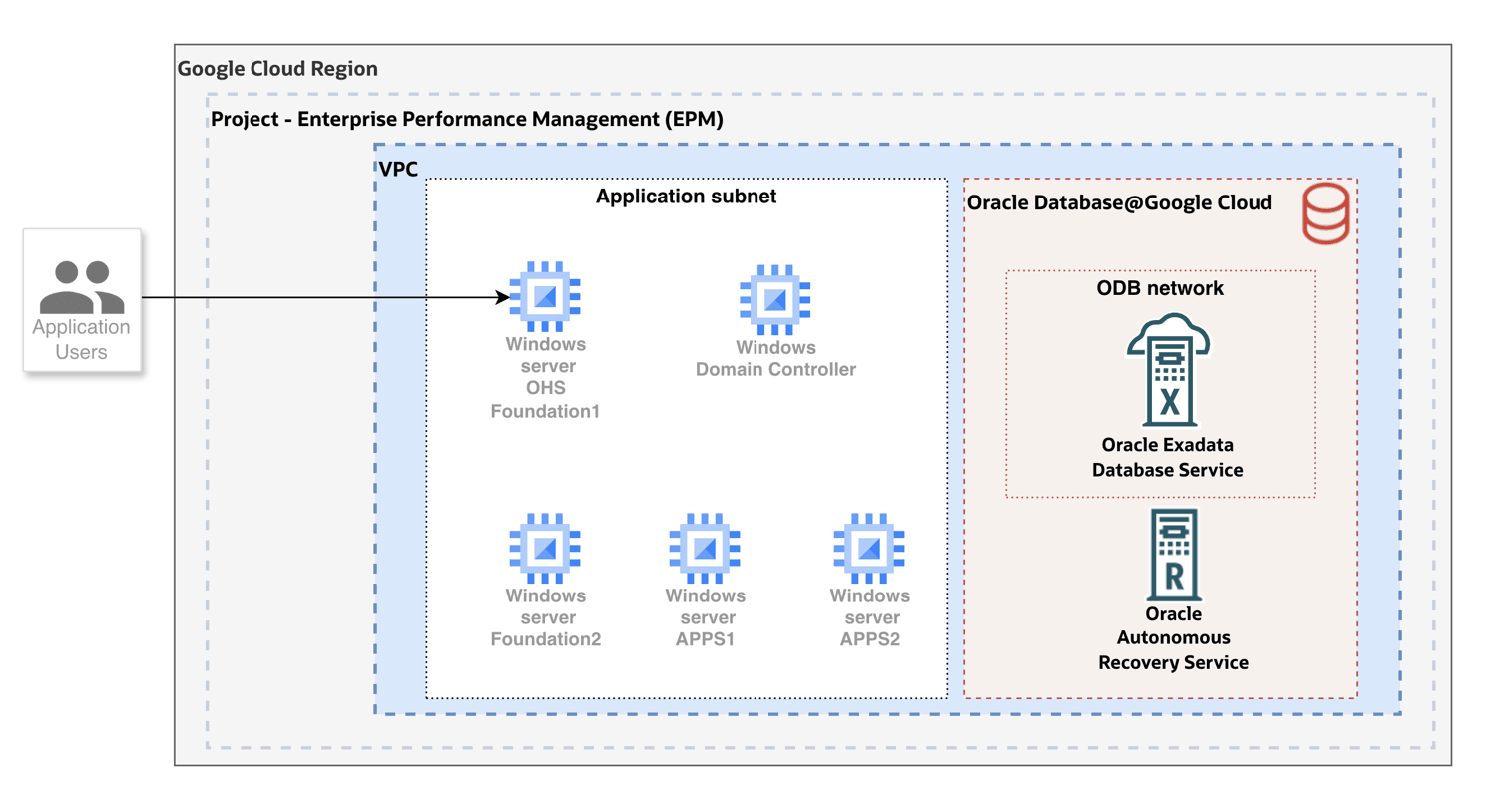
The architecture in the preceding diagram includes the following components
Table 4-1 Overview of Architecture and it's components
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
The Oracle EPM OHS tier consists of web servers that run independently on two Compute Engine VMs . |
|
|
Oracle EPM Application |
The Oracle EPM mid tier consists of Windows Server running independently on Compute Engine VMs. |
|
All of the Google Cloud resources in the architecture use a single VPC network. The web servers, mid-tier components, and databases are in separate subnets. |
|
| Oracle Database@Google Cloud |
Oracle Database@Google Cloud is a database service that lets you to access OCI managed Oracle Exadata infrastructure inside Google Cloud data centers. The Oracle EPM applications read data from and write to Oracle databases in Oracle Exadata Database Service. You provision Oracle Exadata Database Service by using Oracle Database@Google Cloud. You use Google Cloud interfaces like the Google Cloud console, the Google Cloud CLI, and APIs to create Exadata Infrastructure instances. Oracle sets up and manages the required compute, storage, and networking infrastructure in a data center within a Google Cloud region on hardware that's dedicated for your project. To optimize the latency between the application and the database, deploy the application in the same zone where you create the Exadata Infrastructure instances. |
| Exadata Infrastructure instance | The Exadata Infrastructure instance contains two or more physical database servers and three or more storage servers. These servers, which aren't shown in the diagram, are interconnected using a low-latency network fabric. When you create the Exadata Infrastructure instance, you specify the number of database servers and storage servers that must be provisioned. |
| Exadata VM Clusters |
Within the Exadata Infrastructure instance, you create one or more Exadata VM Clusters. For example, you can choose to create and use a separate Exadata VM Cluster to host the databases that are required for each of your business units. Each Exadata VM Cluster contains one or more Oracle Linux VMs that host Oracle Database instances. When you create an Exadata VM Cluster, you specify the following:
The VMs within Exadata VM Clusters are not Compute Engine VMs. |
| Oracle Database instances | You create and manage Oracle Database instances through the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) console and other OCI interfaces. Oracle Database software runs on the VMs within the Exadata VM Cluster. When you create the Exadata VM Cluster, you specify the Oracle Grid Infrastructure version and choose the license type. You can either bring your own licenses (BYOL) or opt for the license-included model. |
Table 4-2 Configuration and Architecture Details for Oracle EPM 11.2.23 Deployment on Google Cloud
| Google Cloud Setup Process | Details |
|---|---|
| EPM Architecture |
Assign Server Roles to the EPM Applications. Assign application components to the Virtual Machine (VM)s, for example:
|
| Set Up a Shared Storage Location |
Windows Network Share: How to create Network Share on Virtual Machine (VM) 1: Example 1:: Example 2:
|
| Virtual Machine (VM) Provisioning |
Determine the number of VMs needed:
|
| Virtual Machine (VM) Requirements Summary |
Virtual Machine (VM) Requirements
|
| Domain Requirements |
NOTE: All EPM Application VMs must join a Windows Domain.
|
| Domain Setup |
|
| Domain Credentials |
|
| Install and Configure |
Oracle EPM Standard Deployment Guide to install EPM components, adjusting for your topology. |
| Deployment Difference |
|